
In $\vartriangle ABC$, $DE||BC$. Find $AD$ if $DB = 7.2cm$, $AE = 1.8cm$ and $EC = 5.4cm$.
Answer
602.7k+ views
Hint: Firstly, we will create the figure with the help of given data. Then, use the theorem of Basic Proportionality which states that:
If a line is drawn parallel to one side of the triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio. We will put in all the values of the other 3 edges and get the required value.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us first create the figure of the given triangle with mention of side lengths $DB = 7.2cm$, $AE = 1.8cm$ and $EC = 5.4cm$ as follows:
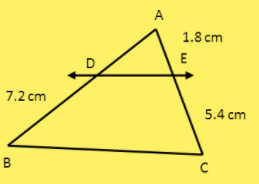
Now, we also have the Basic Proportionality theorem which states that If a line is drawn parallel to one side of the triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio. We will put in all the values of the other 3 edges and get the required value.
Now, in our triangle, we already have $DE||BC$ and $DE$ cuts $AB$ and $AC$ in distinct points.
So, we can apply the Basic Proportionality theorem here.
By using it, we will get:
$\dfrac{{AD}}{{DB}} = \dfrac{{AE}}{{EC}}$ ……(1)
(Because the sides are divided in same ratio)
Now, we already have the values: $DB = 7.2cm$, $AE = 1.8cm$ and $EC = 5.4cm$
Putting in all these values in (1):
$\dfrac{{AD}}{{7.2}} = \dfrac{{1.8}}{{5.4}}$
Taking 7.2 from denominator here to RHS, we will have:-
$AD = \dfrac{{1.8}}{{5.4}} \times 7.2$
Simplifying it, we get:
$AD = 2.4cm$
Hence, $AD = 2.4cm$.
Note: The student might make the mistake of applying this theorem anywhere, without checking the conditions, it requires. So, we must observe the conditions very carefully.
The student might make the mistake of not drawing the figure first, and directly writing the fraction, which may lead to the wrong answer due to the common mistake of imagining something else. So, we must always draw the figure first before trying to solve it.
We must remember the theorem “Basic Proportionality theorem” used in the solution of this question.
Fun Fact:- The “Basic Proportionality theorem” is also known as “Thales theorem” because a famous Greek Mathematician, Thales discovered the theorem.
If a line is drawn parallel to one side of the triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio. We will put in all the values of the other 3 edges and get the required value.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us first create the figure of the given triangle with mention of side lengths $DB = 7.2cm$, $AE = 1.8cm$ and $EC = 5.4cm$ as follows:

Now, we also have the Basic Proportionality theorem which states that If a line is drawn parallel to one side of the triangle to intersect the other two sides in distinct points, the other two sides are divided in the same ratio. We will put in all the values of the other 3 edges and get the required value.
Now, in our triangle, we already have $DE||BC$ and $DE$ cuts $AB$ and $AC$ in distinct points.
So, we can apply the Basic Proportionality theorem here.
By using it, we will get:
$\dfrac{{AD}}{{DB}} = \dfrac{{AE}}{{EC}}$ ……(1)
(Because the sides are divided in same ratio)
Now, we already have the values: $DB = 7.2cm$, $AE = 1.8cm$ and $EC = 5.4cm$
Putting in all these values in (1):
$\dfrac{{AD}}{{7.2}} = \dfrac{{1.8}}{{5.4}}$
Taking 7.2 from denominator here to RHS, we will have:-
$AD = \dfrac{{1.8}}{{5.4}} \times 7.2$
Simplifying it, we get:
$AD = 2.4cm$
Hence, $AD = 2.4cm$.
Note: The student might make the mistake of applying this theorem anywhere, without checking the conditions, it requires. So, we must observe the conditions very carefully.
The student might make the mistake of not drawing the figure first, and directly writing the fraction, which may lead to the wrong answer due to the common mistake of imagining something else. So, we must always draw the figure first before trying to solve it.
We must remember the theorem “Basic Proportionality theorem” used in the solution of this question.
Fun Fact:- The “Basic Proportionality theorem” is also known as “Thales theorem” because a famous Greek Mathematician, Thales discovered the theorem.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Find the greatest fivedigit number which is a perfect class 9 maths CBSE

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Find the sum of series 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + + 100 class 9 maths CBSE




