
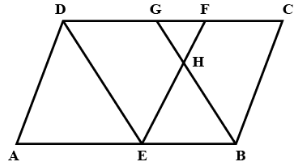
In the figure above ABCD is a parallelogram DE,EF and BG are the bisectors of \[\angle ADC,\angle DEB\;{\text{and}}\;\angle ABC\;\] respectively. BG and EF intersect at H. If \[\angle DAB = 70^\circ \] then find \[\angle BHE\]
A) \[50^\circ \]
B) \[{\left( {62\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^\circ }\]
C) \[75^\circ \]
D) \[{\left( {87\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^\circ }\]

Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: Here first we will find angle ADC using the property of adjacent angles of a parallelogram and then using exterior angle property of triangles and the value of angle ADC we will find the desired angle BHE.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here it is given that \[\angle DAB = 70^\circ \]
Now according to the property of parallelogram the sum of adjacent angles of a parallelogram is \[{180^ \circ }\]
Therefore,
\[\angle DAB + \angle ABC = {180^ \circ }\]
Now putting the known values we get:-
\[
{70^ \circ } + \angle ABC = {180^ \circ } \\
\angle ABC = {180^ \circ } - {70^ \circ } \\
\angle ABC = {110^ \circ } \\
\]
Now since the opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal therefore,
\[\angle ABC = {110^ \circ } = \angle ADC\]………………………….(1)
Now since it is given that DE is the bisector of \[\angle ADC\] therefore,
\[
\angle ADE = \angle CDE = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle ADC \\
\angle ADE = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{{110}^ \circ }} \right) \\
\angle ADE = {55^ \circ } \\
\]
Now in \[\Delta ADE\],
Since \[\angle DEB\] is the exterior angle therefore applying exterior angle property of triangles we get:-
\[\angle DEB = \angle ADE + \angle DAB\]
Putting in the respective known values we get:-
\[
\angle DEB = {55^ \circ } + {70^ \circ } \\
\angle DEB = {125^ \circ } \\
\]
Now since it is given that EF bisects \[\angle DEB\]
Therefore,
\[
\angle DEF = \angle BEF = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle DEB \\
\angle DEF = \angle BEF = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{{125}^ \circ }} \right) \\
\angle DEF = \angle BEF = {\left( {62\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^ \circ } \\
\]
Also, since it is given hat BG bisects \[\angle ABC\]
Therefore,
\[\angle HBE = \angle HBC = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle ABC\]
Putting value from equation 1 we get:-
\[
\angle HBE = \angle HBC = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{{110}^ \circ }} \right) \\
\angle HBE = \angle HBC = {55^ \circ } \\
\]
Now in \[\Delta HEB\],
\[\angle HBE = {55^ \circ }\]
\[\angle BEF = {\left( {62\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^ \circ }\]
Therefore applying angle sum property of triangles we get:-
\[
\angle HBE + \angle BEF + \angle BHE = {180^ \circ } \\
{55^ \circ } + {\left( {62\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^ \circ } + \angle BHE = {180^ \circ } \\
\angle BHE = {180^ \circ } - \left[ {{{55}^ \circ } + {{\left( {62\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)}^ \circ }} \right] \\
\angle BHE = {180^ \circ } - \left[ {{{\left( {117\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)}^ \circ }} \right] \\
\angle BHE = {\left( {62\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^ \circ } \\
\]
Hence option B is the correct option.
Note: If a bisector bisects an angle then that angle is divided into half.
The angle sum property states that sum of all angles of a triangle is
The exterior angle property of a triangle states that the exterior angle is equal to the sum of opposite angles.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Here it is given that \[\angle DAB = 70^\circ \]
Now according to the property of parallelogram the sum of adjacent angles of a parallelogram is \[{180^ \circ }\]
Therefore,
\[\angle DAB + \angle ABC = {180^ \circ }\]
Now putting the known values we get:-
\[
{70^ \circ } + \angle ABC = {180^ \circ } \\
\angle ABC = {180^ \circ } - {70^ \circ } \\
\angle ABC = {110^ \circ } \\
\]
Now since the opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal therefore,
\[\angle ABC = {110^ \circ } = \angle ADC\]………………………….(1)
Now since it is given that DE is the bisector of \[\angle ADC\] therefore,
\[
\angle ADE = \angle CDE = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle ADC \\
\angle ADE = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{{110}^ \circ }} \right) \\
\angle ADE = {55^ \circ } \\
\]
Now in \[\Delta ADE\],
Since \[\angle DEB\] is the exterior angle therefore applying exterior angle property of triangles we get:-
\[\angle DEB = \angle ADE + \angle DAB\]
Putting in the respective known values we get:-
\[
\angle DEB = {55^ \circ } + {70^ \circ } \\
\angle DEB = {125^ \circ } \\
\]
Now since it is given that EF bisects \[\angle DEB\]
Therefore,
\[
\angle DEF = \angle BEF = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle DEB \\
\angle DEF = \angle BEF = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{{125}^ \circ }} \right) \\
\angle DEF = \angle BEF = {\left( {62\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^ \circ } \\
\]
Also, since it is given hat BG bisects \[\angle ABC\]
Therefore,
\[\angle HBE = \angle HBC = \dfrac{1}{2}\angle ABC\]
Putting value from equation 1 we get:-
\[
\angle HBE = \angle HBC = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{{110}^ \circ }} \right) \\
\angle HBE = \angle HBC = {55^ \circ } \\
\]
Now in \[\Delta HEB\],
\[\angle HBE = {55^ \circ }\]
\[\angle BEF = {\left( {62\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^ \circ }\]
Therefore applying angle sum property of triangles we get:-
\[
\angle HBE + \angle BEF + \angle BHE = {180^ \circ } \\
{55^ \circ } + {\left( {62\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^ \circ } + \angle BHE = {180^ \circ } \\
\angle BHE = {180^ \circ } - \left[ {{{55}^ \circ } + {{\left( {62\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)}^ \circ }} \right] \\
\angle BHE = {180^ \circ } - \left[ {{{\left( {117\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)}^ \circ }} \right] \\
\angle BHE = {\left( {62\dfrac{1}{2}} \right)^ \circ } \\
\]
Hence option B is the correct option.
Note: If a bisector bisects an angle then that angle is divided into half.
The angle sum property states that sum of all angles of a triangle is
The exterior angle property of a triangle states that the exterior angle is equal to the sum of opposite angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




