
In a triangle\[ABC\], $D$ is a point on $BC$, such that $\angle CAD = \angle B$ then, $\angle ADC = \angle BAC$. State true or false.
(A)True
(B)False
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: In this type of question assumption for the diagram should be made first and one should know about the properties of the triangles for example angle sum property, exterior angle property, or congruency or similarity. When applying the exterior angle property you should take the other two angles to which you are applying this property.
Complete answer:
Assume
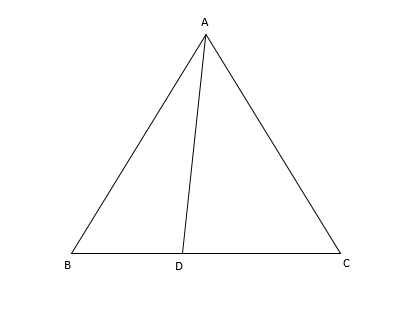
Given, triangle\[ABC\],$\angle CAD = \angle ABC$
If we see in triangle \[\;ABD\]
Apply the exterior angle property. The sum of two angles inside the triangle is equal to the angle adjacent to the third angle of triangle on the same lines.
For example in this case
$\angle ABC + \angle BAD = \angle ADC$ -- for triangle \[\;ABD\] – 1
We have given that angle
$\angle ABC = \angle CAD$--2
Put this value in 1
$\angle CAD + \angle BAD = \angle ADC$
$ \Rightarrow \angle BAC = ADC$
So the statement is true.
Note:
One can do mistake in exterior angle property so we should do it carefully. Add the angles carefully and assign names to them carefully. One should take care while doing calculations. Also one should remember all the properties of triangles and angles. An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the opposite interior angles. For more on this see Triangle external angle theorem. If the equivalent angle is taken at each vertex, the exterior angles always add to $360^o$ In fact, this is true for any convex polygon, not just triangles
Complete answer:
Assume

Given, triangle\[ABC\],$\angle CAD = \angle ABC$
If we see in triangle \[\;ABD\]
Apply the exterior angle property. The sum of two angles inside the triangle is equal to the angle adjacent to the third angle of triangle on the same lines.
For example in this case
$\angle ABC + \angle BAD = \angle ADC$ -- for triangle \[\;ABD\] – 1
We have given that angle
$\angle ABC = \angle CAD$--2
Put this value in 1
$\angle CAD + \angle BAD = \angle ADC$
$ \Rightarrow \angle BAC = ADC$
So the statement is true.
Note:
One can do mistake in exterior angle property so we should do it carefully. Add the angles carefully and assign names to them carefully. One should take care while doing calculations. Also one should remember all the properties of triangles and angles. An exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the opposite interior angles. For more on this see Triangle external angle theorem. If the equivalent angle is taken at each vertex, the exterior angles always add to $360^o$ In fact, this is true for any convex polygon, not just triangles
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE





