
Find the depth of a cylindrical tank of radius 28m,if its capacity is equal to that of a rectangular tank of size \[28m\times 16m\times 11m\]
Answer
621.6k+ views
Hint: Find the volume of the rectangular tank using the given values in the question. Now, equate that volume to the volume of the cylinder which is given as \[\pi {{r}^{2}}h\], where ‘r’ is the radius of the circular base and ‘h’ is the height of the cylinder.
A cylinder is a three dimensional figure in geometry. The top face and the bottom face of a cylinder have the shape of the circle. The top and bottom faces are flat and also equal in size, these two faces are connected by a curved face that generally looks like a tube. The shape of a candle is a good example for the cylinder.
Now, let us determine the volume of a cylindrical tank, we shall take a cylindrical tank of radius ‘r’ and height ’h’ as mentioned below in the diagram.
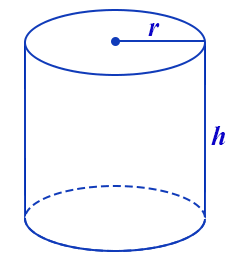
The area of the top or bottom surfaces is given as \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\], as they are in the shape of the circle.
Now, the volume is given as:
Volume=Area x height.
Volume =\[\pi {{r}^{2}}\times h\]
Therefore, volume=\[\pi {{r}^{2}}\times h\].
So, the volume of a cylindrical tank whose radius is ’r’ and height ’h’ is given as \[\pi {{r}^{2}}h\].
Now, let us compute the volume of the rectangular tank mentioned in the question whose size is \[28m\times 16m\times 11m\].
Volume of rectangle= length x breadth x height.
So, the volume =28x16x11
Volume=\[4928{{m}^{3}}\].
As the cylindrical tank also has the same volume, we have:
\[\pi {{r}^{2}}h=4928{{m}^{3}}\]
Where it is given that, \[r=28m\]and we know \[\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}\], substituting this in above equation, we get
\[\left( \dfrac{22}{7} \right){{\left( 28 \right)}^{2}}h=4928\]
\[h=\dfrac{4928\times 7}{22\times 28\times 28}\]
\[h=2m\].
Therefore, the height or depth of the required cylindrical tank is \[h=2m\]
Note: You can also use the formula of \[\dfrac{\pi {{d}^{2}}h}{4}\] for computing the volume of the cylinder, when the value of diameter is known. While substituting the values in the volume formula, we have to make sure that all the lengths are taken with respect to the same units.
A cylinder is a three dimensional figure in geometry. The top face and the bottom face of a cylinder have the shape of the circle. The top and bottom faces are flat and also equal in size, these two faces are connected by a curved face that generally looks like a tube. The shape of a candle is a good example for the cylinder.
Now, let us determine the volume of a cylindrical tank, we shall take a cylindrical tank of radius ‘r’ and height ’h’ as mentioned below in the diagram.

The area of the top or bottom surfaces is given as \[\pi {{r}^{2}}\], as they are in the shape of the circle.
Now, the volume is given as:
Volume=Area x height.
Volume =\[\pi {{r}^{2}}\times h\]
Therefore, volume=\[\pi {{r}^{2}}\times h\].
So, the volume of a cylindrical tank whose radius is ’r’ and height ’h’ is given as \[\pi {{r}^{2}}h\].
Now, let us compute the volume of the rectangular tank mentioned in the question whose size is \[28m\times 16m\times 11m\].
Volume of rectangle= length x breadth x height.
So, the volume =28x16x11
Volume=\[4928{{m}^{3}}\].
As the cylindrical tank also has the same volume, we have:
\[\pi {{r}^{2}}h=4928{{m}^{3}}\]
Where it is given that, \[r=28m\]and we know \[\pi =\dfrac{22}{7}\], substituting this in above equation, we get
\[\left( \dfrac{22}{7} \right){{\left( 28 \right)}^{2}}h=4928\]
\[h=\dfrac{4928\times 7}{22\times 28\times 28}\]
\[h=2m\].
Therefore, the height or depth of the required cylindrical tank is \[h=2m\]
Note: You can also use the formula of \[\dfrac{\pi {{d}^{2}}h}{4}\] for computing the volume of the cylinder, when the value of diameter is known. While substituting the values in the volume formula, we have to make sure that all the lengths are taken with respect to the same units.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




