




Learn How DNA and Genes Control Heredity
The Molecular Basis of Inheritance explains how genetic information is stored, replicated, and passed from one generation to another. DNA, the genetic material, contains instructions for protein synthesis, controlling traits in all living organisms. Key concepts like replication, transcription, and translation help decode how genes function. This knowledge is vital for understanding heredity, genetic disorders, and advancements in biotechnology.
This page aims to simplify these processes and highlight their significance in genetics, medicine, and research.
Important Topics of Molecular Basis of Inheritance
The search for genetic material
Structure of polynucleotide chain
Double-Helix model of DNA
Packaging of DNA
Central dogma of biology
DNA replication
Transcription
Genetic code
Translation
Regulation of gene expression:Lac operon
Human genome project
DNA fingerprinting
Important Concepts
Search for Genetic Material
There were varieties of experiments that had been performed by the different scientists to answer the question of what molecule was actually the genetic material. The list and the overall conclusion of the experiments are given in the table below.
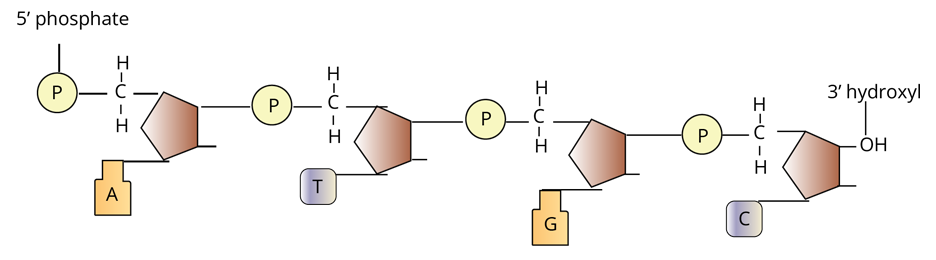
Structure of Polynucleotide Chain
Each nucleotide consists of three components that are listed below.
1. Nitrogenous Bases: They are of two categories such as:
Purines: It includes Adenine(A) and Guanine (G). Both the purines are present in the case of DNA as well as in RNA.
Pyrimidines: It includes Cytosine(C) and Thymine(T) in the case of DNA and Cytosine(C) and Uracil(U) in RNA.
2. Sugar: In the case of nucleotides, pentose sugar is present i.e. Ribose sugar in case of RNA and deoxyribose sugar in case of DNA.
3. Phosphate-group: It plays an important role in the formation of sugar-phosphate back-bone that acts as the structural framework of the nucleic acids.
Nucleoside: It consists of a nitrogenous base and the sugar.
Nucleotide: It consists of a nitrogenous base, sugar, and the phosphate group.
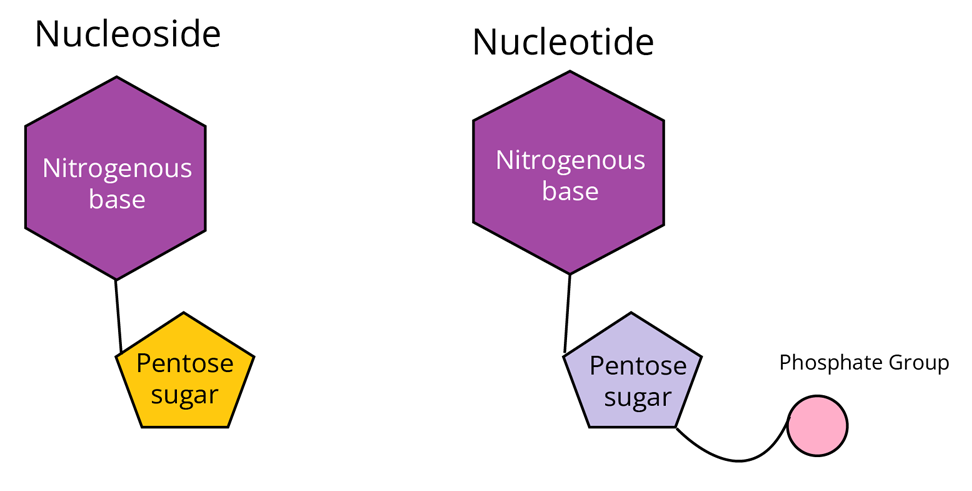
Trick: In the nucleoside, the phosphate group is kept aside.
Double-Helix Model of DNA
This model describes the structure of DNA. It was given by Watson & Crick in 1953. According to this model, two polynucleotide chains make DNA, where the backbone consists of sugar-phosphate and nitrogenous bases are present towards the inside. Both the chains run opposite to each other in terms of polarity i.e. one with 5’→3’ end and the other one with 3’→5’ end. Purine always pairs with pyrimidine with the help of hydrogen bonds (A to T or U with 2 hydrogen bonds, C to G with three hydrogen bonds).
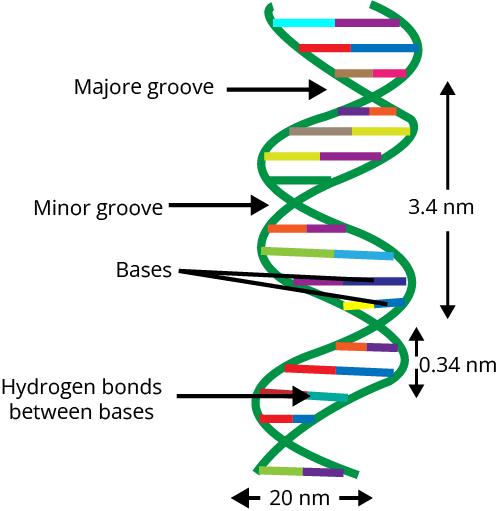

Chargaff’s Rule
It states that in the DNA, there is always equality in quantity between the bases A and T and between the bases G and C.
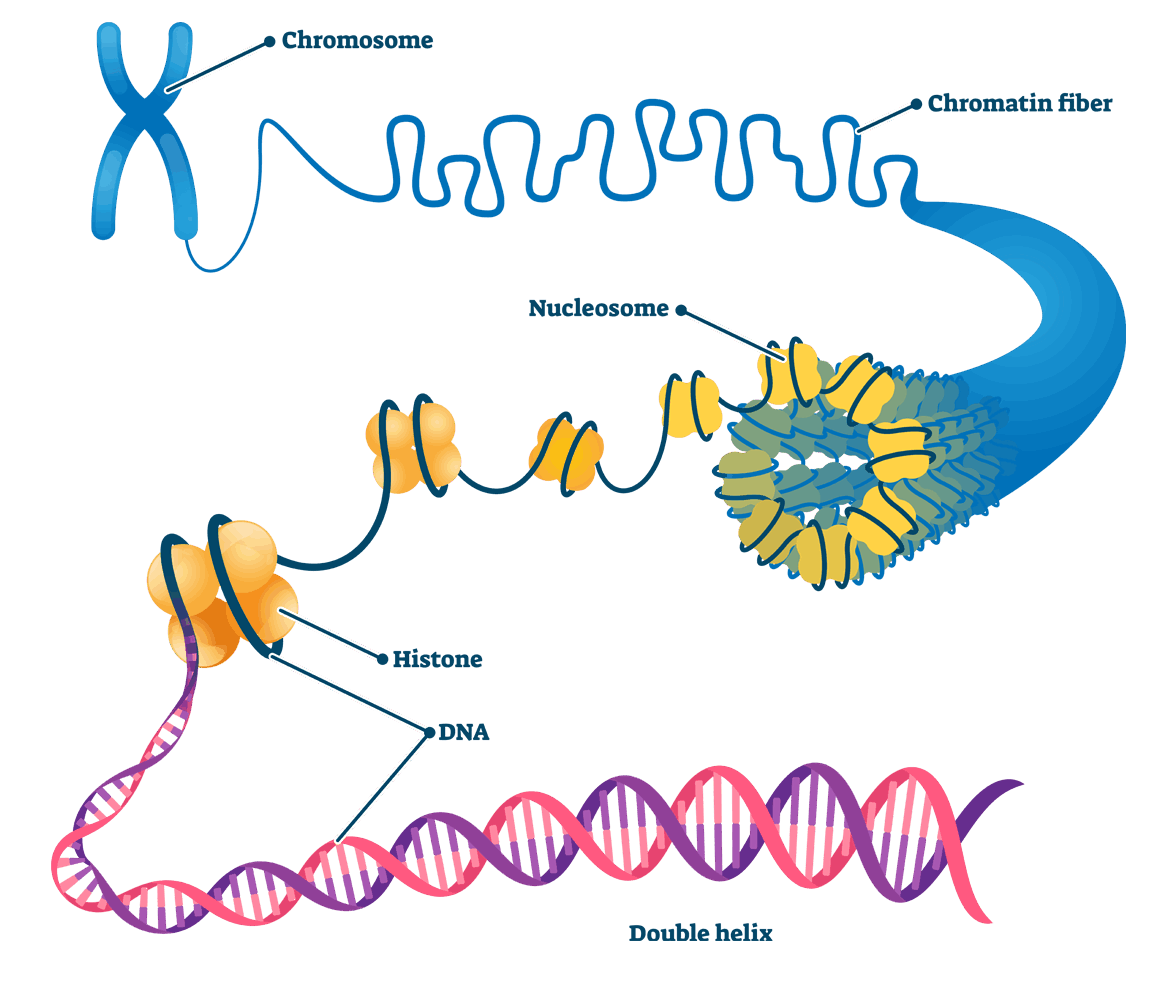
Packaging of DNA
In eukaryotes, there is a complex organization of DNA in the chromosome. The negatively charged DNA is wound around the core of histone (positively charged proteins) octamer to form a nucleosome which is the monomeric unit of chromatin.
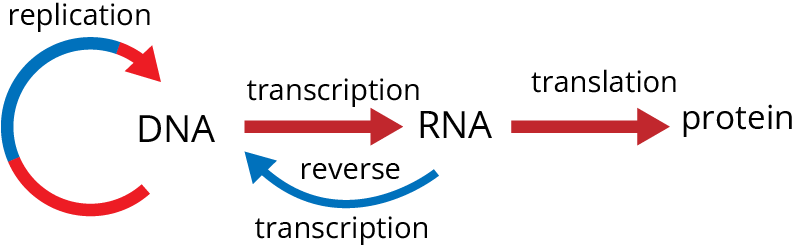
Central Dogma of Biology
It states that genetic information flows from DNA → RNA → Protein. It was proposed by Francis Crick.
DNA-replication
In 1958, Meselson and Stahl experimentally proved that the DNA replicates itself in the semi-conservative manner.
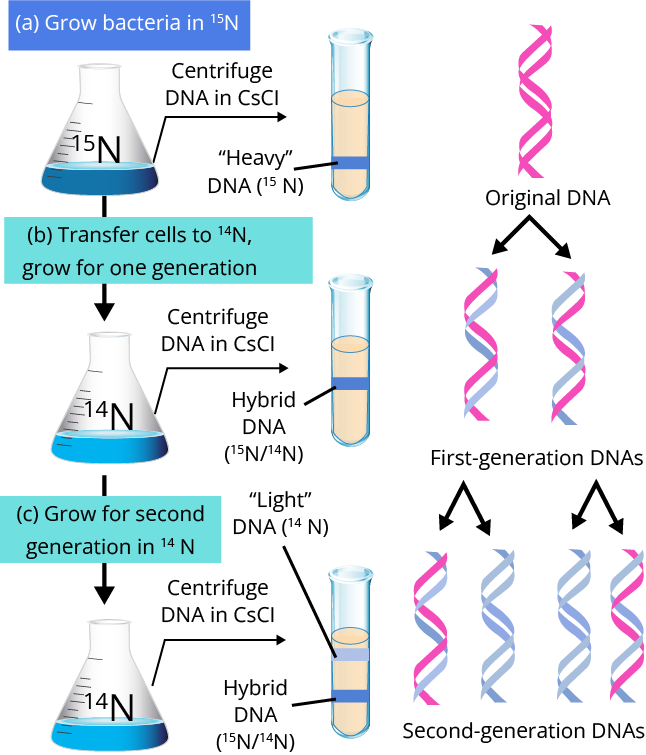
The process which involves the duplication of DNA is called DNA replication.
It mainly occurs in the S-phase of the cell cycle.
The process of DNA replication initiates at Ori(origin of replication).
The process of DNA replication is catalyzed by an enzyme named DNA polymerase and the energy for catalyzing it comes from the enzyme Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate which can also act as the substrate. DNA polymerase always polymerises in the 5'→3’ direction.
In the process of replication, two kinds of strands are formed i.e. lagging strand and leading strand.
The lagging strand is formed in a discontinuous manner and each fragment is known as Okazaki fragments which are joined together by the enzyme DNA ligase.
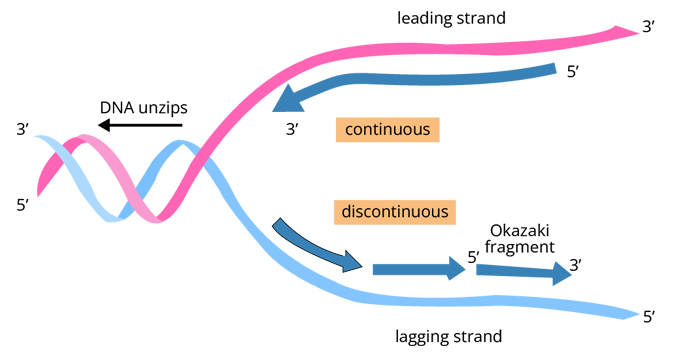
Transcription
The process involves the copying of genetic information from one strand of the DNA into RNA. During this process, only one strand of the DNA gets copied to RNA.
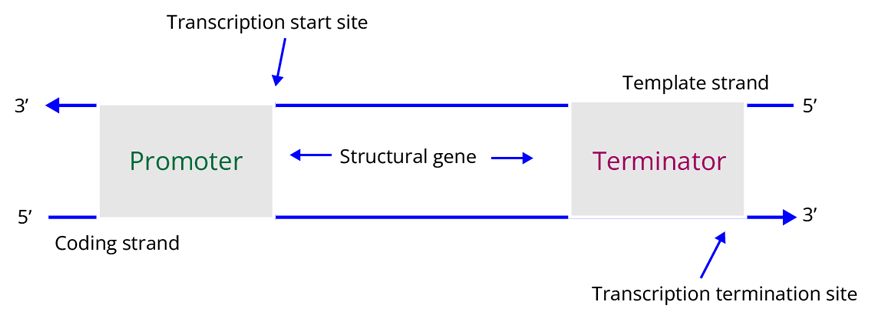
Transcription Unit
It can be defined by the three regions as mentioned below:
Promoter: It is the region where RNA polymerase binds and the process of transcription initiates.
The Structural Gene: It is the region between the promoter and the terminator.
Terminator: It is the region which marks the end of the transcription process.
Transcription in Prokaryotes vs Eukaryotes
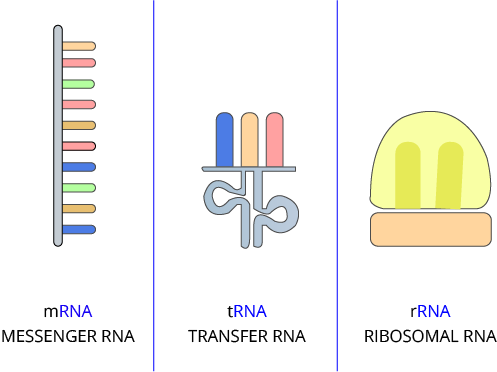
Types of RNAs
Genetic Codon
These are the sequence of bases in the mRNA that codes for a particular amino acid in the protein synthesis. It is made up of three nucleotides and is termed as triplets. There are a total of 64 codons, out of which 61 codes for amino acids. The remaining three codons are named as stop codons such as UAA, UAG, and UGA.

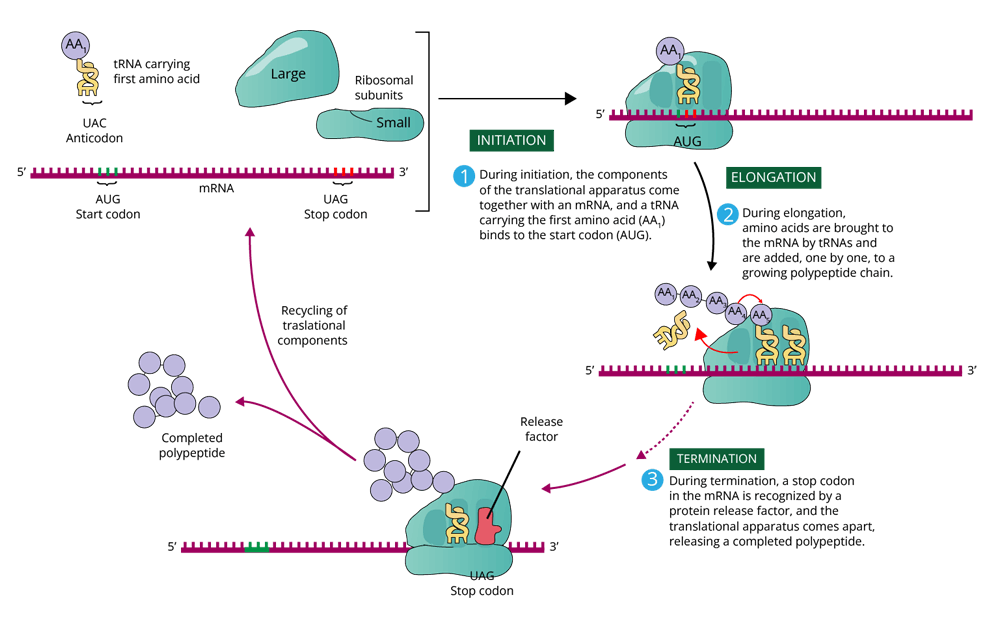
Translation
The process involves the polymerization of amino acids. During this process, the messenger RNA works together with the transfer RNA i.e. tRNA and ribosome for the synthesis of proteins. The process of translation completes in three steps:
Initiation
Elonation
Termination
Regulation of Gene Expression
Gene regulation is defined as the process of turning on/off the genes. It ensures that particular genes are expressed at a particular time. It is important for the proper development of the embryo as well as also allows the cells to react quickly to the changes in their environments. In eukaryotes, it can be performed on various levels such as transcriptional level, processing level, transport of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, and translational level while in prokaryotes control of gene expression is mainly at the initiation of transcription.
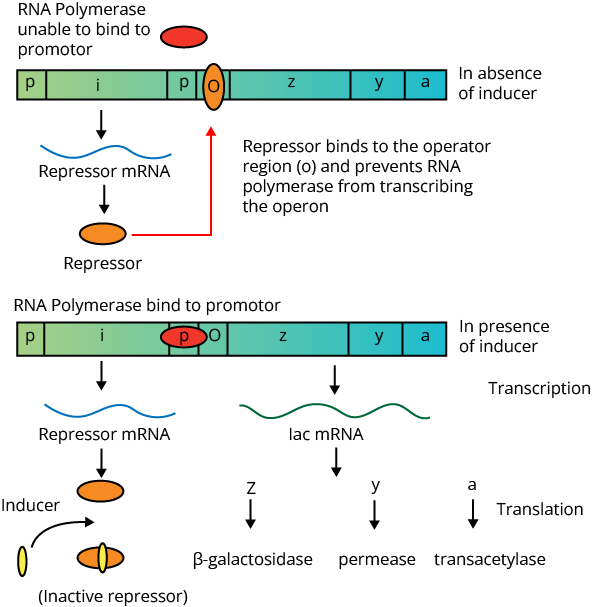
LAC Operon
Operon is defined as the genetic regulatory system found in bacteria and viruses. It was Jacob and Monad who first showed the transcriptionally regulated system in the lac operon.
Human Genome Project
Human genome project was called a mega-project. It was launched in the year of 1990. The main objectives of this project were:
Identification of the complete human genome.
Development of genome sequence databases to store the data.
Transfer related technologies to other sectors, such as industries.
Improvement in tools for data analysis.
The human genome project was completed in 2003.
DNA Fingerprinting
DNA fingerprinting is the method of finding out the genetic makeup of any organism. It is also known as DNA profiling, genetic fingerprinting, etc. The procedure involves:
DNA sample collection
Cleavage of DNA into DNA fragments by restriction endonuclease
Separation of DNA fragmentation by electrophoresis
Southern blotting
Autoradiography to obtain the bands
Visualization of DNA fingerprints
The Applications of this Technique are as Follows:
In forensic science, it is used to identify the criminal.
By using this technology, one can map the evolutionary history of an organism and its overall linkage with the other groups.
It is used to identify the biological parents of the respective individual/offspring.
DNA fingerprinting can also be utilized in the field of agriculture. The information about the disease-causing agent can be identified.
Solved Examples From the Chapter
1. Give a reason for the discontinuous synthesis of DNA on one of the parental strands?
Ans: The biological process of DNA synthesis naturally occurs in 5′ to 3′ directions in the double-stranded DNA. During the synthesis of DNA, both the strands act as templates, only one out of two (3′ to 5′ direction) can synthesize the parallel strand in 5’→3′ direction. The other strand (5′ to 3′ direction) is synthesized in the opposite direction producing small stretches of DNA which are known as Okazaki fragments which are joined together by the DNA ligase. Hence, it is because of this reason that there is the discontinuous synthesis of DNA on one of the parental strands.
2. Sometimes, the young ones born have an extremely different set of eyes or limbs. Give a relevant explanation for the abnormality.
Ans: This abnormality may be caused due to variety of factors such as alcohol abuse by the mother during her pregnancy, side effects of medicine, environmental factors, such as maternal exposure to the chemicals, radiations, viruses, and it can also occur due to the non-coordination in the regulation of expression in the set of genes that are associated with the development of the organs.
3. Complete the blanks a, b, c, and d on the basis of the Frederick Griffith Experiment.
S Strain →→ inject into mice →→ (a)
R strain →→ inject into mice →→ (b)
S strain (heat killed) →→ inject into mice →→ (c)
S strain (heat killed) + R strain (live) →→ inject into mice →→ (d)
Ans:
(a) It will result in the death of the mice.
(b) The mice will live.
(c) The mice will live.
(d) It will result in the death of the mice.
The principle of transformation was given by Griffth. In this experiment, he concluded that in the infected mice, some “transforming principle” gets transferred from heat-killed S-strain of Streptococcus pneumoniae to R-strain and this enables them to make the smooth polysaccharide coat which enables them to become virulent. This may be due to the transfer of the genetic material. However, the biochemical nature of genetic material was unknown.
Solved Problems of Previous Year Question From the Chapter
1. The final proof for DNA as the genetic material comes from the experiments of ______.
A. Macleod and Avery
B. Griffith
C. Harvey Mcbride
D. Hershey and Chase
Ans: The correct answer will be option ”D”.
Hershey and Chase found that the bacteria which were infected with viruses that had radioactive DNA were radioactive, indicating that DNA was the material that passed from the virus to the bacteria while the bacteria that were infected with viruses that had radioactive proteins were not radioactive, which indicates that proteins did not enter the bacteria from the viruses. Hence, it is the DNA which acts as the genetic material.
2. All of the following are part of an operon except______.
A. structural genes
B. a promoter
C. an enhancer
D. an operator
Ans: The correct answer is option “C”.
Operon is defined as the genetic regulatory system found in bacteria and viruses.
Enhancers are the regulatory sequence of the DNA. Specific proteins through which they are bound are called transcription factors. They enhance the rate of transcription of target genes. They are not the part of operon.
3. Complete the flowchart on central dogma.
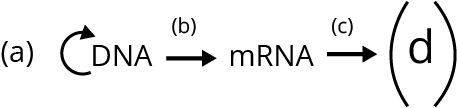
A. (a) - Replication; (b) -Transcription; (c) - Transduction; (d) - Protein
B. (a) -Translation; (b) - Replication; (c) -Transcription; (d) -Transduction
C. (a) - Replication; (b) - Transcription; (c) - Translation; (d) - Protein
D. (a) - Transduction; (b) - Translation; (c) - Replication; (d) - Protein
Ans: The correct answer is option “C”.
Central dogma states that genetic information flows from DNA → RNA → Protein. It was proposed by Francis Crick.
Practice Questions
1. Three codons on mRNA are not recognised by tRNA what are they? What is the general term used for them and what is their significance in protein synthesis?
Ans: Genetic codes are the sequence of bases in the mRNA that codes for a particular amino acid in the protein synthesis. It is made up of three nucleotides and is termed as triplets. There are a total of 64 codons, out of which 61 codes for amino acids. The remaining three codons are named as stop codons such as UAA, UAG, and UGA. As we know that these three codons are not recognised by any tRNA, hence, they are helpful in the termination of the protein chain during translation.
2. Why is DNA not RNA the genetic material in the majority of organisms?
Ans: The hydroxyl (-OH) group in the nucleotides of RNA is much more reactive and makes RNA labile and easily degradable. Thus, it is the DNA that acts as genetic material in the majority of organisms.
3. Why is it that transcription and translation could be coupled in a prokaryotic cell but not in a eukaryotic cell?
Ans: In prokaryotes, the mRNA synthesized does not require any kind of processing to become active, so the process of transcription and translation occurs simultaneously in the cytosol while in eukaryotes, primary transcript/pre-mRNA contains both exon and intron and is subjected to a process named as splicing where introns are removed or exons are joined in a definite order to form mature mRNA.
4. In the DNA of an animal, the percentage of adenine is 30, then what will be the percentage of guanine?
a) 40
b) 30
c) 20
d) 70
Ans: The correct answer is option “c”.
Chargaff rule states that in DNA there is always equality in quantity between the bases A and T and between the bases G and C (where A is adenine, T is thymine, G is guanine, and C is cytosine). It is based upon the complementary base pairing between nitrogenous bases of two antiparallel strands of a double-stranded DNA molecule.
Given,
Adenine=30%
Thymine=30%(A=T)
G+C=40
x+x=40
2x=40
x=40/2
x=20
Hence, guanine will be 20%.
Conclusion
This article contains all the important information as per the requirement of students who are preparing for the NEET and can be really helpful for a quick and effective revision. It includes all the important concepts and topics, questions from the previous year's NEET exam, NEET mock test as well as the Biology NCERT. Make sure to try the Practice question on your own to test your knowledge and to get desired outputs.
Essential Study Materials for NEET UG Success
Understanding the Molecular Basis of Inheritance

 Share
ShareFAQs on Understanding the Molecular Basis of Inheritance
1. Is the molecular basis of inheritance important for NEET?
Yes, it is important for the NEET exam because it covers most of the important topics and the concepts that are useful for the exam.
2. What are the important topics of the chapter Molecular Basis of Inheritance?
Although it is one of the most important chapters in terms of the NEET exam, some of the important topics from where the questions are asked are the search for genetic material, double-helical structure of DNA, packaging of DNA, the central dogma of biology, replication, transcription, translation, gene regulation:Lac operon, etc.
3. Is NCERT enough for preparing for the NEET exam?
Yes, it is enough. One can score very well by going through it again and again because every time a person receives new information which is very important in terms of exams.
4. What is the molecular basis of inheritance?
The molecular basis of inheritance refers to how genetic information is stored in DNA, replicated, and passed from one generation to another.
5. What is the role of DNA in inheritance?
DNA carries genetic instructions that determine traits, controls cell functions, and is passed from parents to offspring through replication.
6. What are the key processes in the molecular basis of inheritance?
The major processes include replication (copying DNA), transcription (DNA to RNA), and translation (RNA to protein synthesis).
7. What is the structure of DNA?
DNA is a double-helical structure made of nucleotides, consisting of a sugar-phosphate backbone and nitrogenous bases (A, T, G, C).
8. How does DNA replication occur?
DNA replication is semi-conservative, meaning each new DNA molecule consists of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
9. What is the role of RNA in inheritance?
RNA helps in gene expression by converting genetic information from DNA into proteins through transcription and translation.
10. What are genes, and how do they affect inheritance?
Genes are specific DNA sequences that code for proteins, determining inherited traits and influencing biological functions.
11. What is the difference between transcription and translation?
Transcription converts DNA into mRNA, while translation uses mRNA to produce proteins with the help of ribosomes.
12. How do mutations affect inheritance?
Mutations are changes in DNA sequences that can lead to genetic disorders, variations, or even evolutionary adaptations.
13. Why is understanding the molecular basis of inheritance important?
It helps in genetic research, disease treatment, biotechnology, forensic science, and improving agricultural and medical advancements.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video


