




Human Reproduction
The given document carries the Class 12 chapter named Human Reproduction as per the requirement of students preparing for the medical entrance exam. It will be beneficial for the last-minute revision of the chapter as it contains the most important topics of the chapter from which the questions are asked frequently and also the practice questions to test your knowledge.
By reading this document carefully one can find out all the answers to the important questions related to the chapter such as what is reproduction, describing the anatomy of the male and female reproductive system, what is the menstrual cycle, and what is gametogenesis, etc.
Important Topics of Human Reproduction
The Male Reproductive System
The Female Reproductive System
Gametogenesis
Menstrual Cycle
Fertilisation and Implantation
Parturition and Lactation
Important Concepts
Reproduction
It is defined as the process by which the living organism gives rise to new offsprings. It is a very important event as it ensures the continuity of the species. In human beings, reproduction involves the fusion of gametes i.e. sperms and eggs.
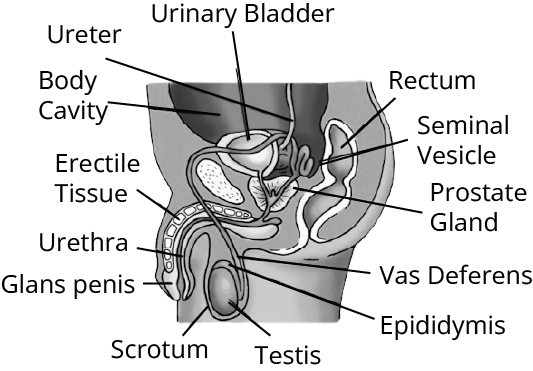
Male Reproductive System
The human male reproductive system consists of specialised organs that are responsible for the production of sperms and male-specific hormones such as testosterone.
The different organs that consist of the male reproductive system are as follows:
Testes
These are a pair of oval-shaped organs enclosed in a pouch-like structure named the scrotum.
These are responsible for the production of sperms and the male-specific hormone such as testosterone (the main hormone that regulates the male-specific characters as well as the production of male gametes such as sperms).
Scrotum
It is a pouch-like organ that hangs below the penis and behind it. The testis is located inside it.
It is present outside the body to maintain an ideal temperature that is required for the production and the survival of sperms.
Vas Deferens
The sperms produced in testes are stored in a tube named the epididymis. Here, the sperms get matured and pass to the urethra through the muscular tube-like structure called vas deferens.
Accessory Glands
These consist of seminal vesicles, the prostate gland, and the Cowper's gland. The secretions from these three glands mix together to form a fluid, called semen. It nourishes the sperms, increases the volume, and helps in lubrication as well.
Penis
It is a cylindrical tube-like organ that serves as a common passage for reproduction as well as excretion. It is the main organ that a human male uses for sexual intercourse with the female partner and then delivers sperms inside them.
Female Reproductive System
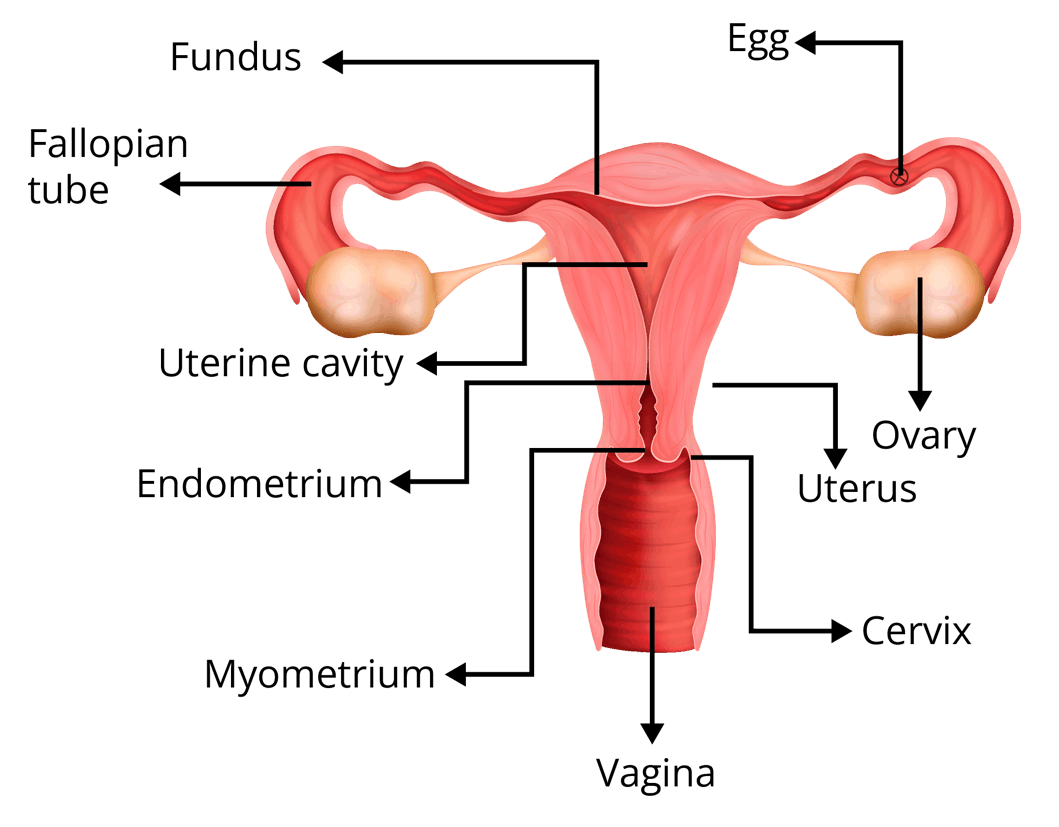
The human female reproductive system consists of specialised organs that are responsible for the production of ova and the female-specific hormone such as oestrogen and progesterone.
Ovary
These are the primary sex organs of the female that are responsible for the production of female gamete (ova) and female-specific hormones.
They are located one on each side of the lower abdomen.
Each ovary is about 2 to 4 cm in length and is connected to the pelvic wall and uterus via the ligaments.
Fallopian Tubes
These are the 10-12 cm long tubes that convey the ovum from the ovary to the uterus. The process of fertilisation (fusion of gametes) usually takes place in the upper portion of the fallopian tube that is in the ampullary region.
Uterus
It is also known as the womb. It is an inverted pear-shaped organ which opens into the vagina through the cervix.
The wall of the uterus has three layers of tissue, perimetrium, myometrium, and endometrium. The layer that undergoes cyclic changes during the menstrual cycle is the endometrium, while the myometrium exhibits strong contraction during the delivery of the baby.
Cervix
It is the distal-most portion of the uterus which connects the main body of the uterus to the vagina.
The cavity of the cervix is termed as the cervical canal. The birth canal consists of the cervical canal and the vagina.
Vagina
It is a muscular and elastic tube that connects the cervix to the external body.
During sexual intercourse, it functions as the receptacle for the penis and delivers sperm to the fallopian tubes and uterus.
Gametogenesis
It is defined as the process which involves the formation of gametes.
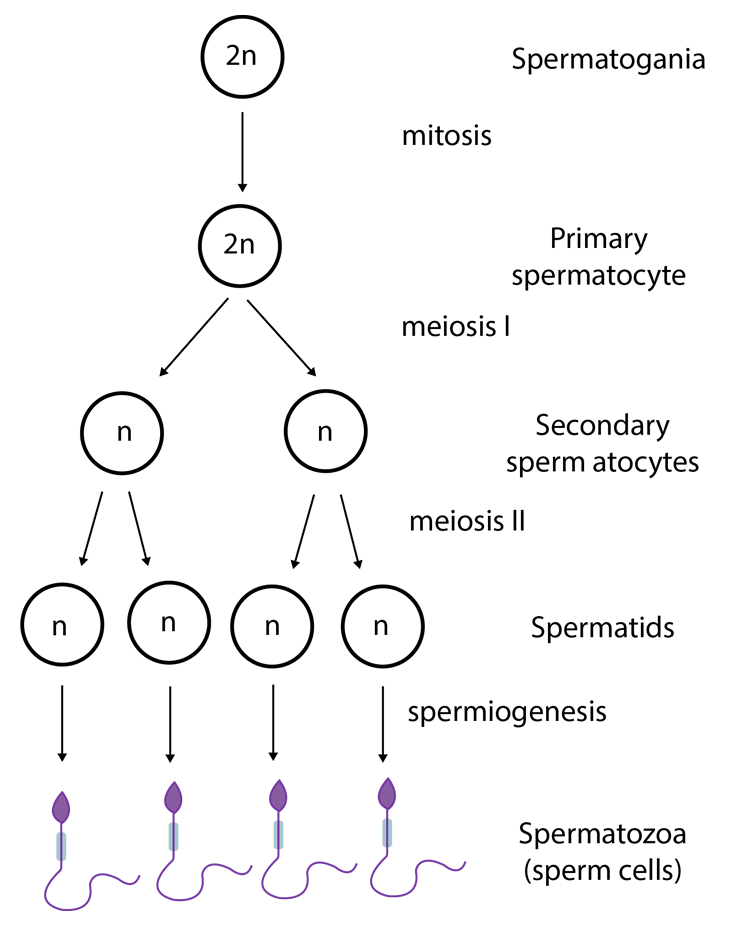
Spermatogenesis is defined as the formation of sperms/male gametes.
Oogenesis is defined as the formation of egg/female gametes.
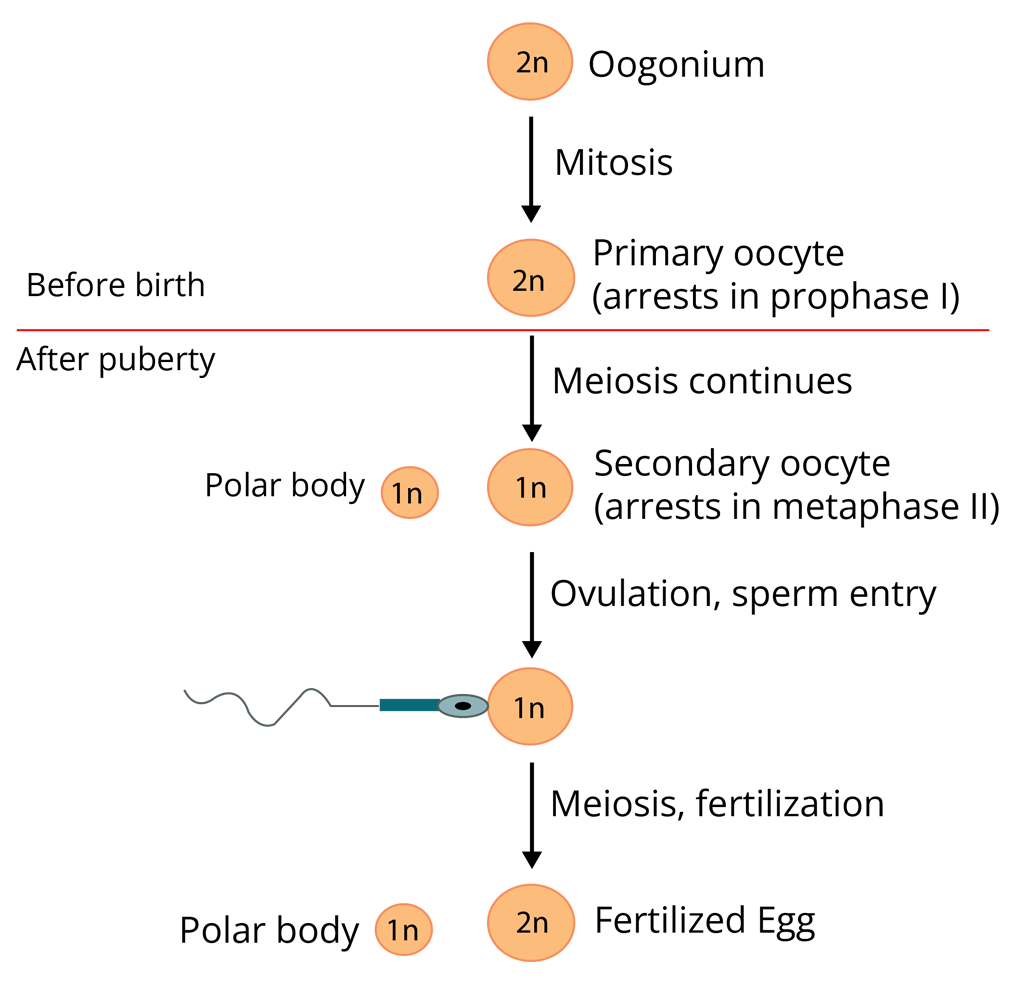
The table below shows the differences between spermatogenesis and oogenesis.
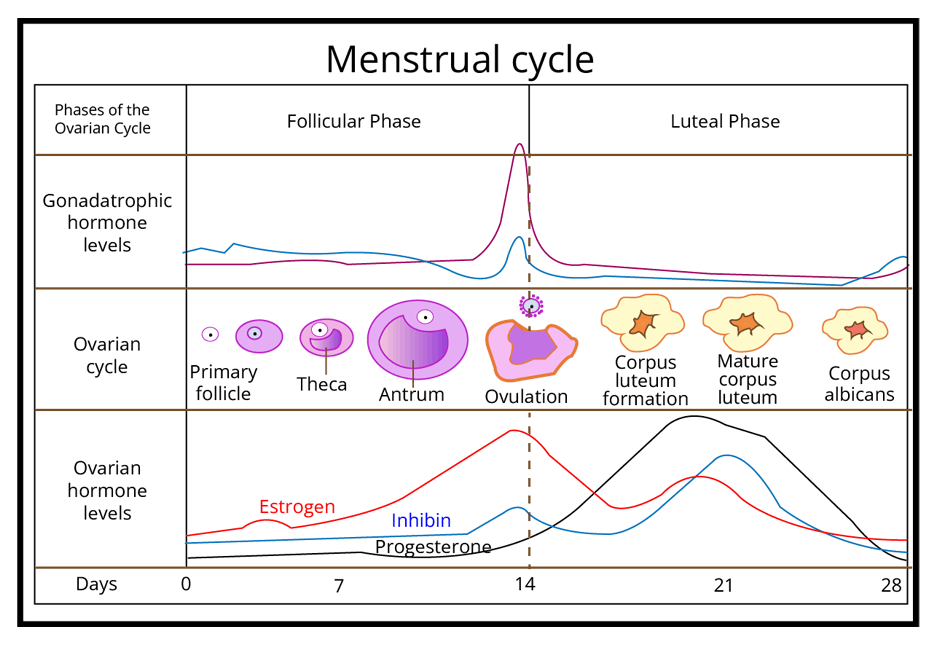
Menstrual Cycle
It is defined as the reproductive cycle that occurs in female primates (monkeys, apes, and human beings). A variety of changes occur in the female body during this cycle. This cycle repeats on an average interval of about 28/29 days. The first menstruation begins at puberty and is called menarche.
Phases of the Menstrual Cycle
There are basically four phases in the menstrual cycle. These include the following:
1. Menstrual Phase: During this phase, the uterus lining which is prepared for implantation starts to shed. This phase lasts for 3 to 5 days.
2. Follicular Phase: During this phase, the primary follicle starts developing into a mature Graffian follicle. The endometrium (lining of the uterus) also starts proliferating. The uterus prepares itself for another pregnancy.
3. Ovulatory Phase: During this phase, ovulation takes place, i.e., days 13-17. The end of the follicular phase along with the ovulation period is termed the fertilisation period.
4. Luteal Phase: It is the postovulatory phase where the fate of the corpus luteum is decided. If fertilisation happens, pregnancy starts. If fertilisation doesn’t occur, it marks the onset of another cycle.
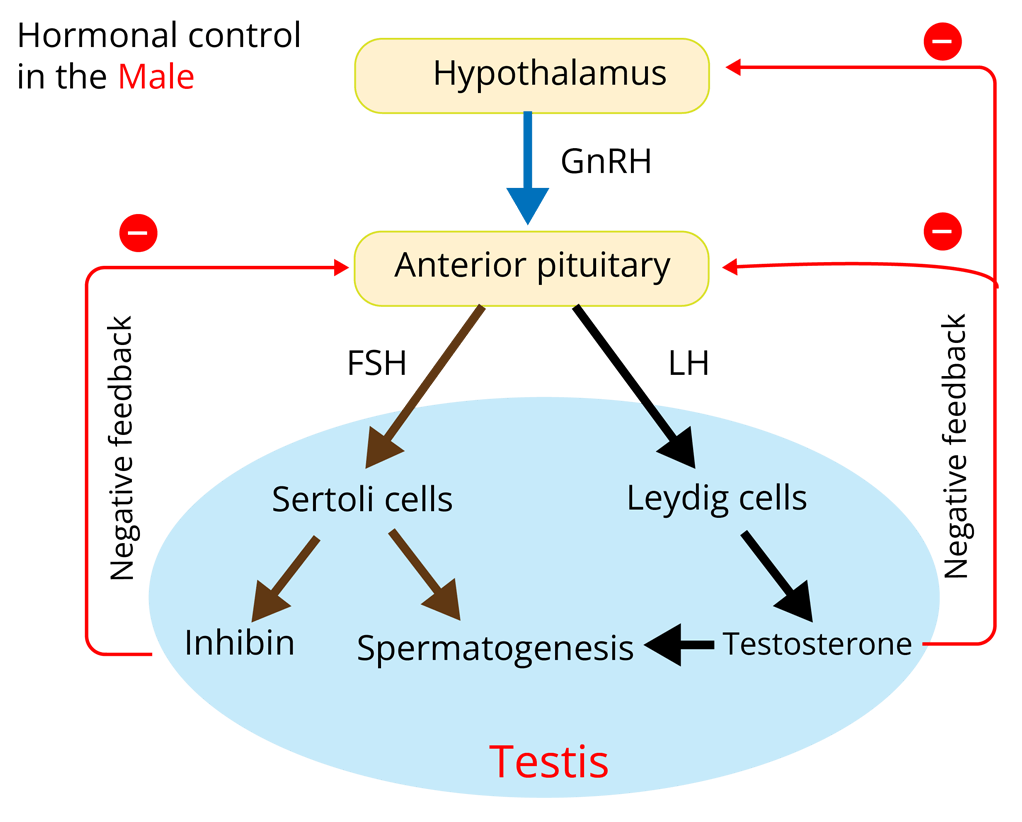
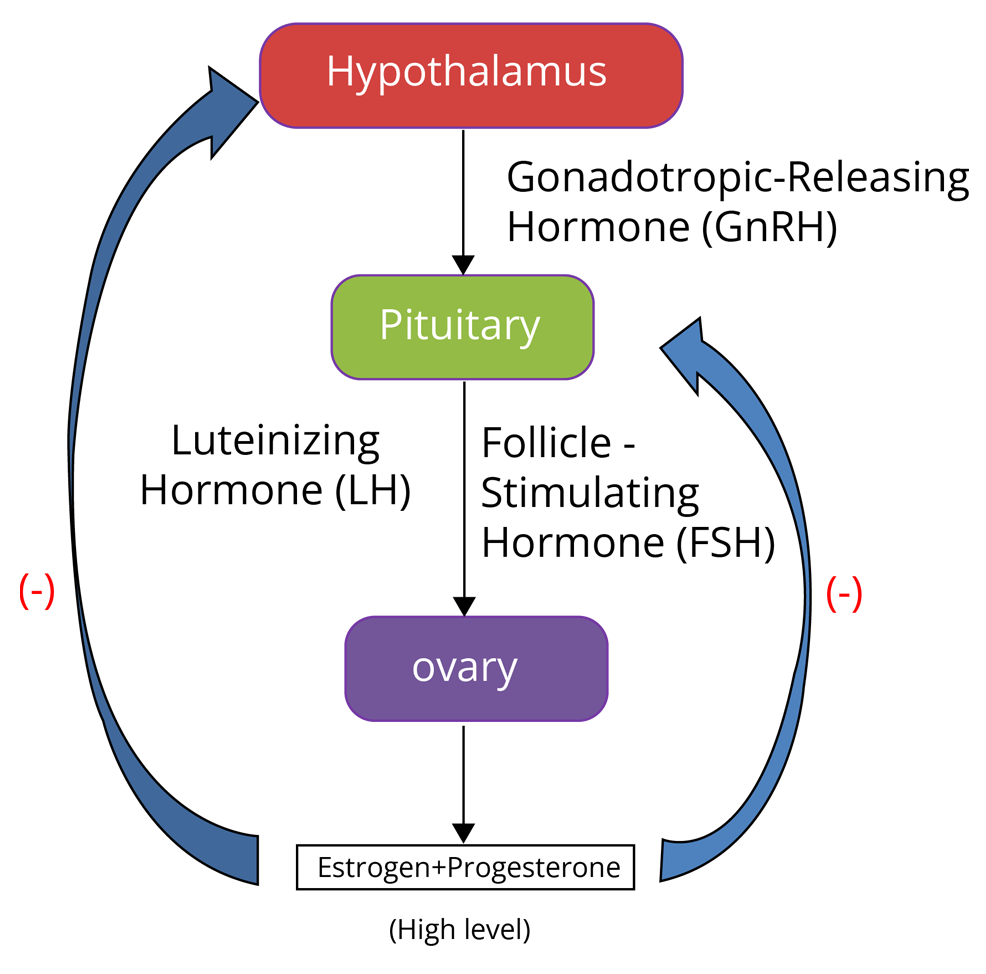
Role of Hormones in Menstrual Cycle
Hormones is the chemical messengers released by various endocrine glands present inside the body. They are responsible for bringing varieties of changes inside the human body.
Every phase of the menstrual cycle is influenced by varieties of female-specific hormones such as oestrogen, progesterone, FSH, and LH. The variation in the level of each of these hormones decides the phase that a woman undergoes.
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) are secreted by the anterior pituitary. FSH stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles that secrete the oestrogen. The Corpus luteum which is also known as the yellow body secretes progesterone.
The secretion of FSH and LH gradually increases during the follicular phase. Both these hormones stimulate the development of follicles and the release of oestrogen from them. The proliferation of the endometrium is stimulated by the oestrogen.
The level of LH and FSH peaks in the middle of the cycle. LH induces ovulation (the process in which the ovules release from mature Graafian follicles). Just before ovulation, there is a sudden surge in the level of luteinizing hormone.
After ovulation, the ruptured follicle develops into the corpus luteum which is also known as the yellow body that secretes progesterone; hence, the level of progesterone increases in the luteal phase.
Progesterone is required for the maintenance of the endometrium for implantation (attachment of an embryo to the uterus wall). In the absence of fertilisation, corpus luteum regresses and progesterone level goes down which leads to the disintegration of the endometrium and results in menstrual flow.
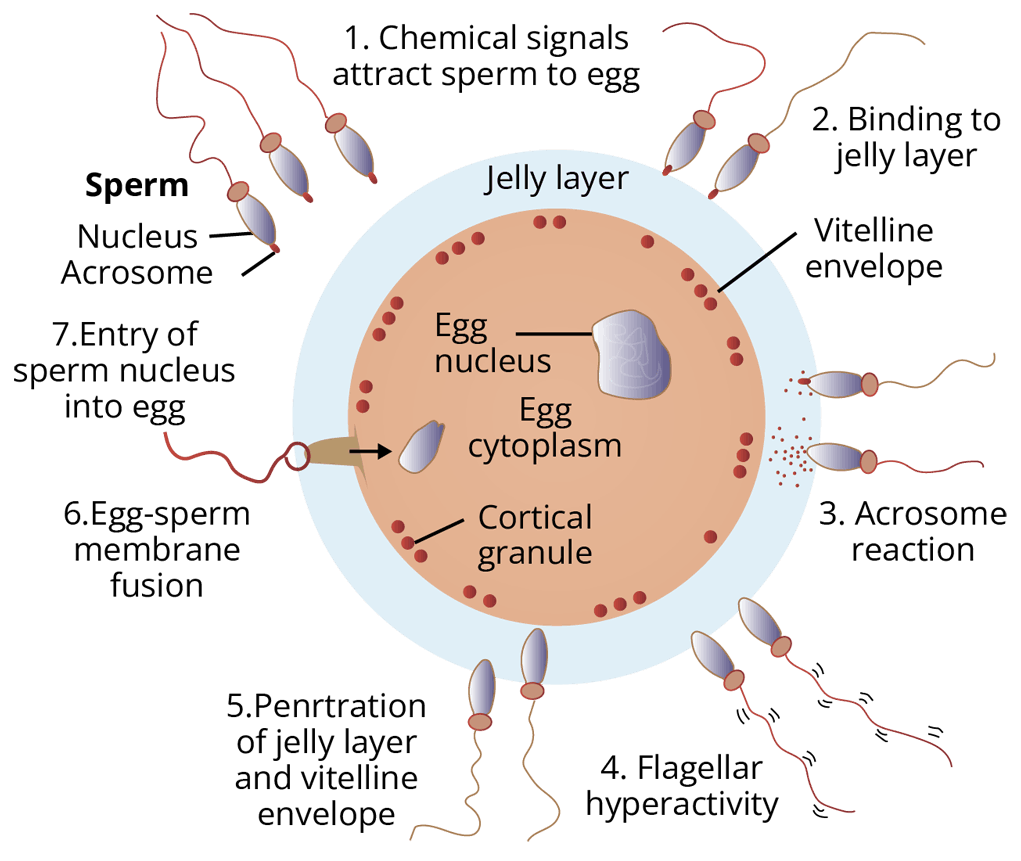
Fertilisation and Implantation
Fertilisation is the process which involves the fusion of gametes (male and female). The zygote is the product of fertilisation which after passing through various stages of development results in the production of the offspring or newborn.
Embryo Development/Cleavage
It is defined as a series of rapid mitotic divisions that results in the production of multicellular structures named blastula from the single-cell zygote.
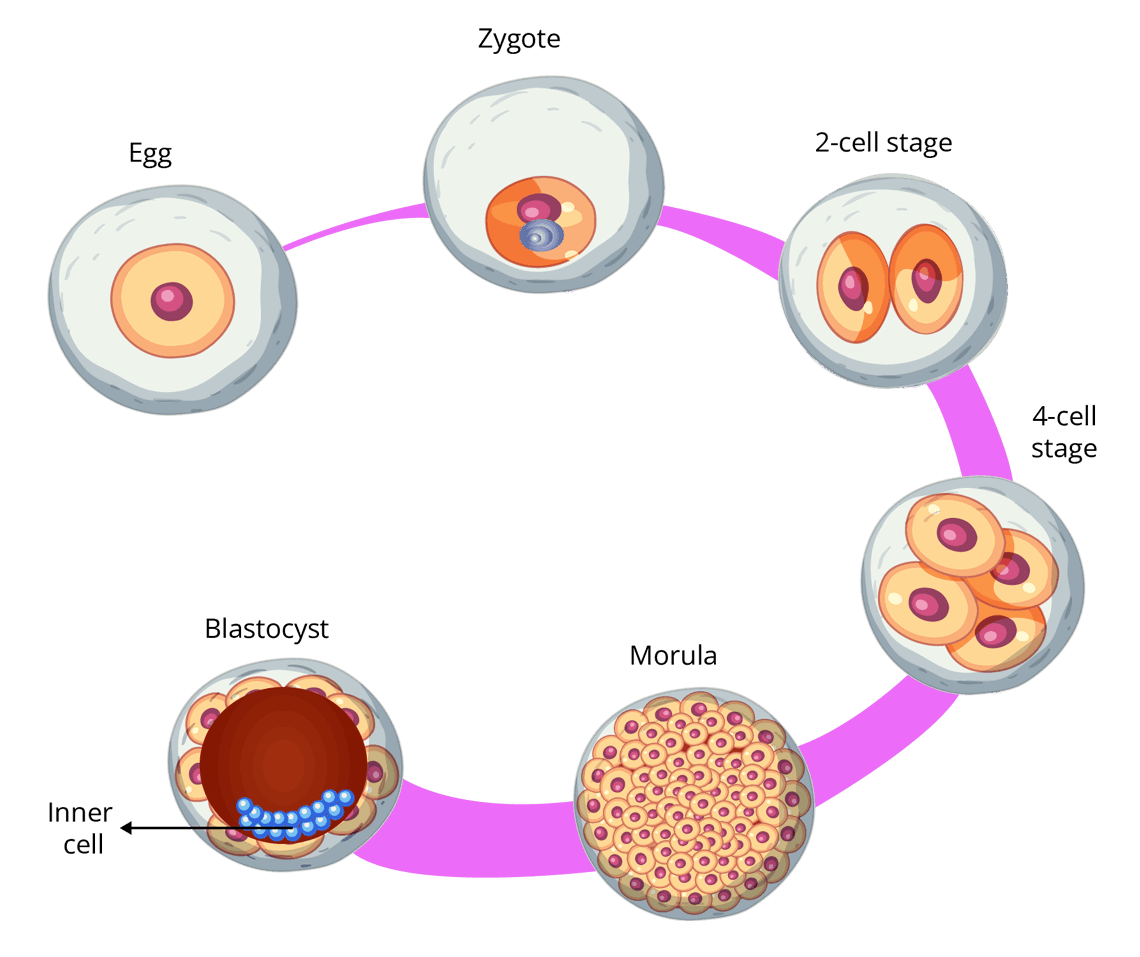
Implantation is defined as the adherence of a fertilised egg to the surface of the uterus wall. It is important for providing a suitable environment for further development inside the female body. It occurs after the 7 days of fertilisation.
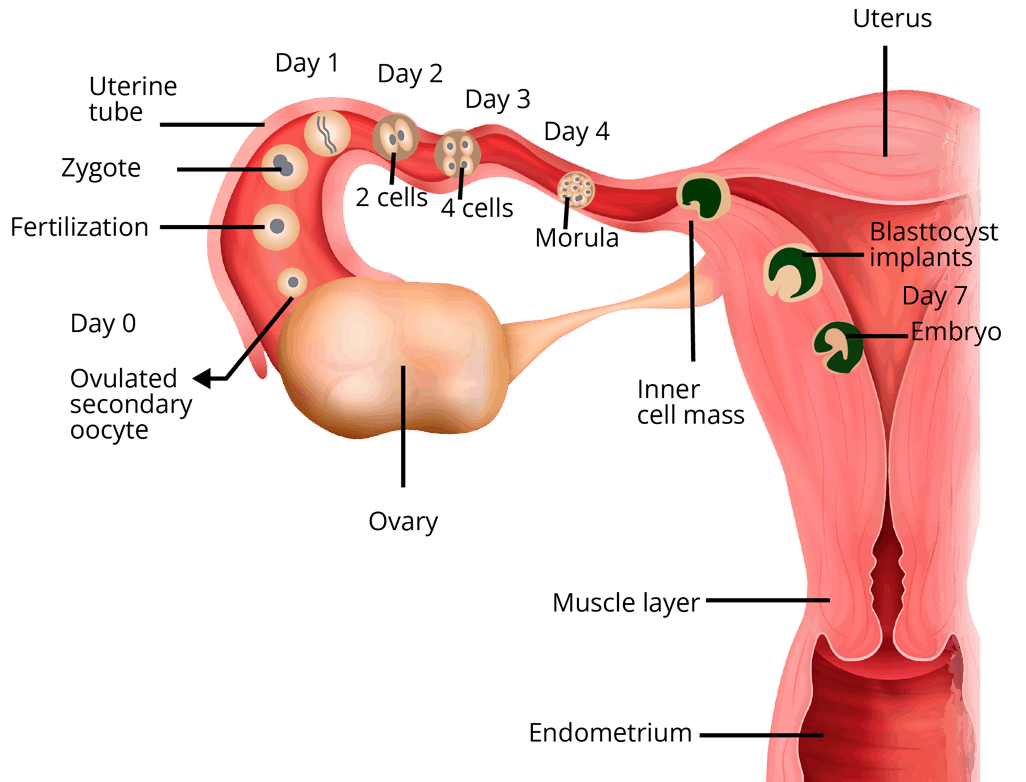
Parturition and Lactation
On average, the duration of pregnancy in human females is about 9 months, which is termed as gestation period. At the end of the pregnancy, vigorous contraction of the uterus causes expulsion or delivery of the foetus, which is termed as parturition. It is a complex neuroendocrine mechanism.
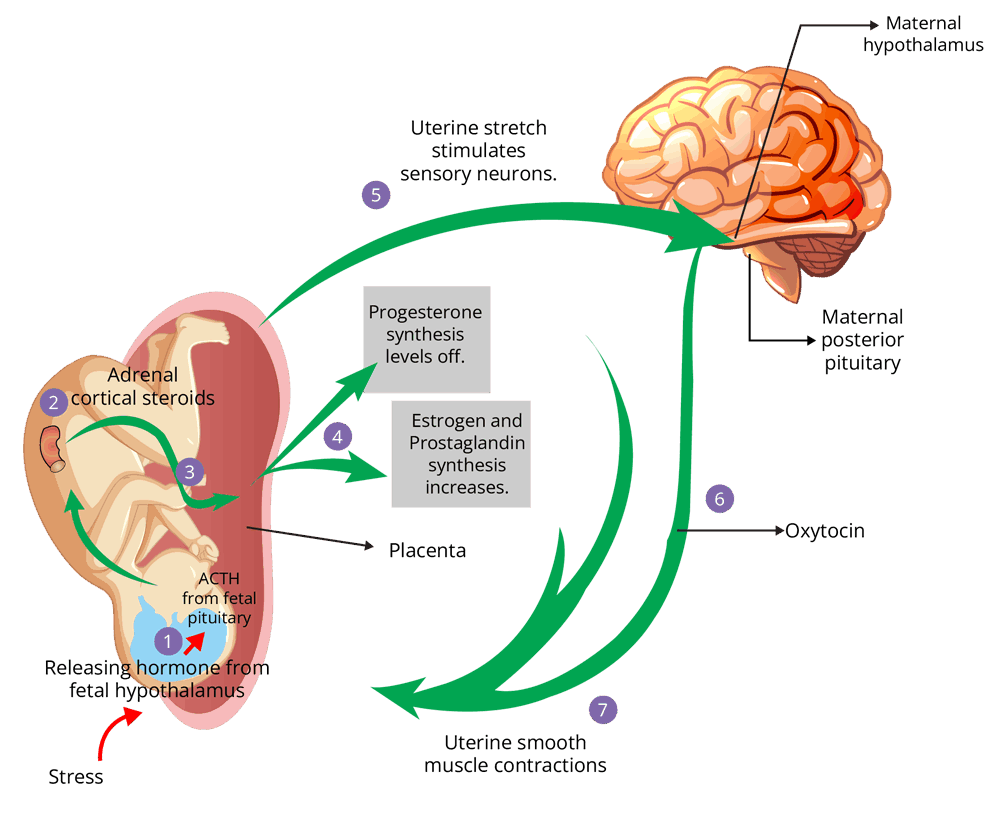
Lactation is the process that involves the production and secretion of milk by the mammary glands. It helps the mother to feed their newborn.
The milk which is produced by the mother during the initial days of lactation is called colostrum. It contains several antibodies that prove to be very essential to providing resistance against various kind of infections and for bringing up a healthy baby.
Solved Examples From the Chapter
1. Changes in GnRH pulse frequency in females are controlled by the circulating level of
A. Oestrogen & Progesterone
B. Oestrogen & Inhibin
C. Progesterone only
D. Progesterone & Inhibin
Ans: The correct answer is “A”.
GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) is a hormone that is secreted by the hypothalamus and stimulates the anterior lobe of pituitary to release LH (luteinizing hormone) & FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone). The main function that is performed by the FSH is the development of follicles.
The formation of estrogens is also stimulated by it. LH stimulates the corpus luteum (yellow body) to release progesterone. When the level of progesterone and oestrogen is high, then it inhibits the secretion of GnRH in a negative feedback manner which in turn inhibits the secretion of FSH and LH.
The Key Point to Remember is - Oestrogen and progesterone hormones regulate the level of GnRH and work in a negative feedback manner.
2. How many sperms are produced from secondary spermatocytes?
Ans: Spermatogenesis is the process of formation of sperms which represents the male gametes. Fusion with the female gamete (egg), it results in the production of a zygote that develops into an embryo after passing through the various developmental stages. The sequence of spermatogenesis is given in the illustration below. The secondary spermatocytes are divided by meiosis II and give rise to two spermatids.
Key Point to Remember - One secondary spermatocyte gives rise to two spermatozoa by the process of meiosis II.
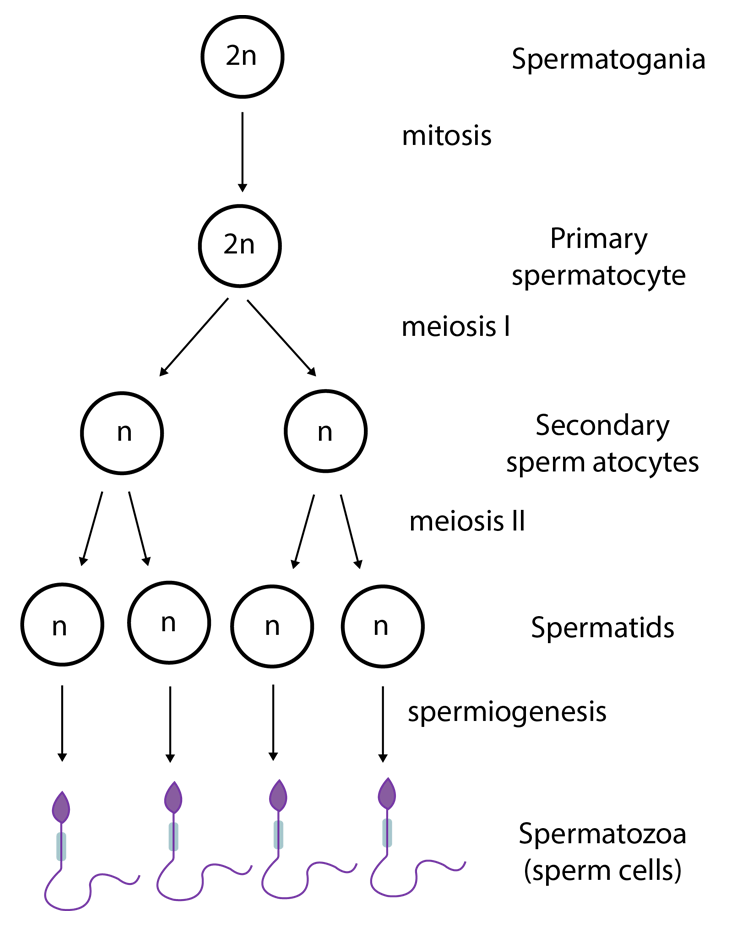
3. Which organ in human females is homologous to the male penis?
Ans: Clitoris is a tiny finger-like structure that lies at the upper junction of the two labia minora, above the urethral opening. It is part of the female external genitalia. This organ is capable of showing erection and plays a key role in sexual stimulation and pleasure. It is homologous (same anatomical structure but performs different functions) to the male penis.
Key Point to Remember - Homologous organs are those that have the same anatomical structure but perform different functions.
Solved Problems of Previous Year Questions
1. Read the following events and place them in the correct order.
Fertilisation D. Implantation
Gestation E. Insemination
Parturition F. Gametogenesis
A, B, C, D, E, F
D, G, E, A, B, C
F, E, A, D, B, C
E, F, D, A, C, B
Ans: The correct answer is “c”.
The correct sequence of the following events are as follows.
Trick to solve easily - FIG + IPG (replace L with I in LPG)
2. Several hormones like hCG, hPL, oestrogen, progesterone, etc. are produced by
Ovary
Placenta
Fallopian tube
Pituitary gland
Ans: The correct answer is “B”.
During pregnancy, the placenta acts as the temporary endocrine gland and produces a variety of hormones such as hCG, hPL, oestrogen, and progesterone to support the pregnancy. Among these hormones, hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) and hPL (human placental lactogen) are produced during the pregnancy only.
Trick to Solve Easily - HCG and HPL are produced during the pregnancy, which is true for the placenta as well.
3. Which part of the ovary in mammals acts as an endocrine gland after ovulation?
A. Germinal epithelium
B. Stroma
C. Graafian follicle
D. None of the above
Ans: The correct answer is “C”.
Ovulation is defined as the release of secondary oocytes from the Graafian follicle.The remnants of the Graafian follicle after ovulation are called corpus luteum/yellow body which is a glandular body that releases progesterone.
Trick to Solve Easily - Corpus luteum = Remnants of the Graafian follicle
Practice Questions
1. The process in which spermatids mature into spermatozoa is called
A. Spermiation
B. Spermatogenesis
C. Spermiogenesis
D. None of the above
Ans: The correct answer is “C”.
The major changes that occur during spermiogenesis or spermateleosis are the formation of the sperm head with condensation of chromosomes and the formation of the acrosomal cap, which contains proteolytic enzymes that are required by the sperm for the penetration of the ovum and the formation of the sperm tail.
Spermatogenesis is defined as the process of the formation of sperms or male gametes. It occurs in the seminiferous tubule of the testis. This process includes the formation of spermatids and the formation of spermatozoa. The process of releasing sperms from the seminiferous tubules is called spermiation.
2. Differentiate between gametogenesis and embryogenesis.
Ans: The following describes the differences between gametogenesis and embryogenesis.
3. Define the terms menarche and menopause.
Ans: Menarche is defined as the time of the beginning of menstruation or the first menstruation. It occurs at the age of 12-15 years. It is repeated on an average interval of 28/29 days.
Menopause is the time when the female ovary stops producing eggs and there is no menstruation. It is attained at the age of approximately 50 years.
Conclusion
This article contains all the important information as per the requirement of students who are preparing for the NEET 2026 and can be really helpful for quick and effective revision. It includes all the important concepts and topics covered in the Biology NCERT books, questions from the previous year's NEET 2026 exams, and NEET 2026 mock tests as well.
NEET 2026 Important Chapter - Human Reproduction

 Share
ShareFAQs on NEET 2026 Important Chapter - Human Reproduction
1. What is the weightage of the chapter Human Reproduction in the NEET 2026 exam?
Human reproduction in combination with reproduction health carries 18% of weightage in the NEET 2026 exam.
2. Are the NCERT books enough for preparing for the NEET 2026 exam?
Yes, it is enough because it covers all the important topics and the concepts which can be important for the exam.
3. What are the important topics of the chapter Human Reproduction?
Human Reproduction is one of the most important chapters in terms of the NEET 2026 exam. Some of the important topics from this chapter are gametogenesis, hormonal regulation in males and females, menstrual cycle, the function of different hormones, etc.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video


