




Know What is Total Leukocyte Count and Its Importance?
TLC stands for Total Leukocyte Count, a blood test that measures the number of white blood cells (WBCs) in the body. White blood cells play a crucial role in the immune system by fighting infections and diseases. The TLC test helps diagnose infections, immune system disorders, and other medical conditions.
Detailed Breakdown of White Blood Cells
There are five main types of white blood cells, each with distinct functions:
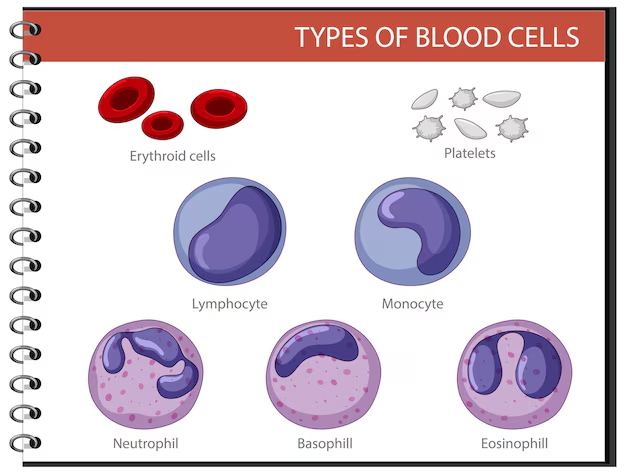
Neutrophils – These are the most abundant WBCs and are the first responders to bacterial infections and injuries. They help in inflammation control and pathogen destruction.
Lymphocytes – These include B-cells and T-cells that produce antibodies and help in the immune system’s adaptive response.
Monocytes – Large white blood cells that act as scavengers by engulfing and digesting dead cells and pathogens.
Eosinophils – Involved in allergic reactions, they combat parasitic infections and regulate inflammation.
Basophils – The least common type of WBC, they release histamine and play a role in allergic reactions and immune responses.
Alternative Names for the TLC Test
The TLC test is also known as:
WBC Count Test
Leukocyte Count Test
White Blood Cell Count Test
Complete Blood Count (CBC) with WBC Count
How to Prepare for the TLC Test?
No special preparation is required.
Avoid strenuous exercise before the test, as physical activity may temporarily increase WBC levels.
Inform the doctor about any medications being taken, as certain drugs (such as steroids or antibiotics) can affect the TLC count.
Normal TLC Count Range
The normal range of total leukocyte count in the blood varies based on age and individual health conditions:
Adults: 4,000 – 11,000 WBCs per microliter of blood (cells/μL)
Children: 5,000 – 10,000 cells/μL
Newborns: 9,000 – 30,000 cells/μL
Causes and Symptoms of Low TLC Count (Leukopenia)
A lower-than-normal TLC count, known as leukopenia, may indicate an impaired immune system. Causes include:
Viral infections (HIV, hepatitis, influenza, dengue)
Autoimmune diseases (lupus, rheumatoid arthritis)
Bone marrow disorders (leukaemia, aplastic anemia)
Nutritional deficiencies (vitamin B12, folate)
Side effects of chemotherapy or radiation therapy
Symptoms of Low TLC Count:
Increased susceptibility to infections
Chronic fatigue and weakness
Unexplained fever and chills
Swollen lymph nodes
Causes and Symptoms of High TLC Count (Leukocytosis)
A high TLC count, known as leukocytosis, can signal an infection or inflammation. Common causes include:
Bacterial infections (pneumonia, tuberculosis, urinary tract infections)
Inflammatory conditions (arthritis, allergies, inflammatory bowel disease)
Blood cancers (leukaemia, lymphoma)
Physical or emotional stress
Smoking and exposure to pollutants
Use of certain medications (steroids, epinephrine)
Symptoms of High TLC Count:
Persistent fever
Body aches and joint pain
Difficulty breathing
Fatigue and dizziness
Night sweats
Why is the TLC Test Important?
Doctors may recommend a TLC test in the following situations:
Persistent fever or unexplained infections
Symptoms of immune system dysfunction
Monitoring recovery after chemotherapy or radiation
Pre-surgical evaluations
Diagnosing blood disorders or inflammation
Possible Risks of the TLC Test
Since it is a standard blood test, risks are very low.
Some people may experience slight pain or bruising at the needle insertion site.
Rarely, individuals may feel lightheaded after the test.
Conclusion
TLC (Total Leukocyte Count) is an essential diagnostic test used to assess immune system health and detect infections, inflammations, or underlying diseases. Maintaining a normal TLC count is crucial for overall health, and any abnormalities should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
FAQs on TLC Full Form: Total Leukocyte Count
1. What does TLC mean in medical terms?
TLC stands for Total Leukocyte Count, a blood test that measures the number of white blood cells present in the blood.
2. Why is the TLC test performed?
The TLC test is done to detect infections, inflammatory diseases, immune system disorders, and blood-related conditions.
3. What is the normal range for TLC?
The normal TLC range for adults is 4,000 – 11,000 WBCs per microliter of blood.
4. What are the five types of white blood cells and their functions?
Neutrophils – Fight bacterial infections.
Lymphocytes – Produce antibodies and regulate immunity.
Monocytes – Help remove dead cells and pathogens.
Eosinophils – Combat allergies and parasites.
Basophils – Mediate allergic reactions and inflammation.
5. What does a high or low TLC indicate?
High TLC (Leukocytosis) may indicate infections, inflammation, stress, or leukaemia.
Low TLC (Leukopenia) may indicate viral infections, autoimmune diseases, or bone marrow disorders.
6. How is the TLC test performed?
A healthcare professional draws a small blood sample from a vein in your arm, which is then analysed in a laboratory to measure the number of white blood cells.
7. Do I need to fast before a TLC test?
No, fasting is not required for a TLC test. However, inform your doctor about any medications you are taking, as some may affect the results.
8. What can cause temporary fluctuations in TLC levels?
Factors such as stress, strenuous exercise, pregnancy, smoking, or recent infections can cause temporary increases or decreases in white blood cell count.
9. Can a high TLC count be dangerous?
A high TLC count may indicate a severe infection, chronic inflammation, or blood disorders like leukaemia. Further tests may be required to determine the exact cause.
10. How can I maintain a healthy TLC count?
A balanced diet, regular exercise, proper hydration, good hygiene, and managing stress can help maintain a normal TLC count and overall immune health.























