




Why Understanding Division Matters for Students
An Introduction to Division Methods
When you divide, you begin to create equal portions of a group of items. Counting objects into equal groups is one method that is commonly applied when learning to divide. For instance, if you had three dolls and needed to place 12 bracelets on each of them, you may distribute the bracelets evenly among the dolls until there are none remaining. Here, each doll would receive 4 bracelets since $\dfrac{12}{3}$ equals 4. The dividend in this instance is 12, the divisor is 3, and the quotient is 4. We must first know the components of a division problem in order to understand how to divide. The significant figure you are dividing is the dividend. The divisor is the quantity into which you are dividing the dividend. When you divide, the result is the quotient. Let's discuss how to divide in the further section.
What is Division?
In mathematics, the division is the process of dividing a number into equal parts and estimating the maximum number of equal parts that may be formed. For example, in this case, dividing 15 by 3 resulted in the division of 15 into 3 groups of 5 each.
The character "$\div$" or often "/" stands for division.
Components of Division
A long division equation is made up of many unique components. Let's understand these components in detail which makes sure your kids recognise what they represent and how to identify them.
1. The number under the line on the right side of the calculation is the dividend. It stands in for the dividing amount.
2. The number on the left, which is doing the dividing, is the divisor.
3. The number at the top is the quotient. When the equation is finished, it indicates the solution or the number of units in each place value.
4. The figure at the bottom is the remaining amount. It stands for the units that remain after being divided into the quotient unevenly.
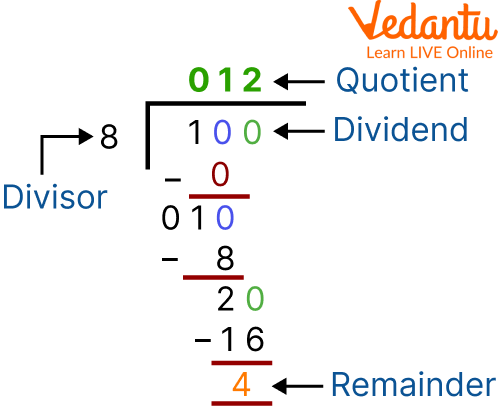
Components of Division
The following statement shows the relation between these four components:
Dividend = Divisor x Quotient + Remainder
To determine whether or not the solution is right, use this formula, often known as the division formula.
Short Division
A large number can be divided by a one-digit number using the short division, while a two-digit or more number can be divided by a large number using the long division.
Here is an illustration to help us better comprehend this concept.
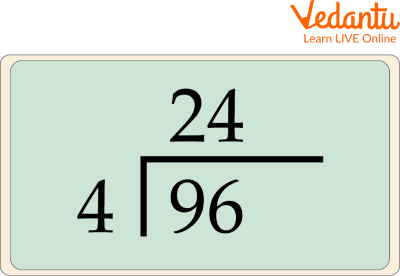
Short Division
In this image, four is multiplied by nine twice, leaving a remainder of one. The remainder is then added to the following number (six), making a total of 16. Four enters 16 four times, resulting in a total answer of 24.
Long Division
Long division is a mathematical technique used to divide big numbers into smaller groups or parts. Dividing a problem into small, straightforward steps can be helpful. There are dividends, divisors, quotients, and remainders in long divisions. Decimal numbers can also be divided into equal groups using long division. It follows the same processes as long division, which are to divide, multiply, subtract, bring down, and repeat or get the remainder.
Let’s see an example of Long division by 10. Here, 621300 is divided by 10.

Long division by 10
And this is how teachers will know how to do division for kids. Let’s see some solved example:
Solved Examples
Example 1: Divide 726 by 4
Solution: Firstly, Put the divisor, or the number you're dividing by another number, outside the long division bar to properly format the problem. The number you will be dividing by the divisor, the dividend should be put inside the long division bar. Your result, or the quotient, will come above the division bar.
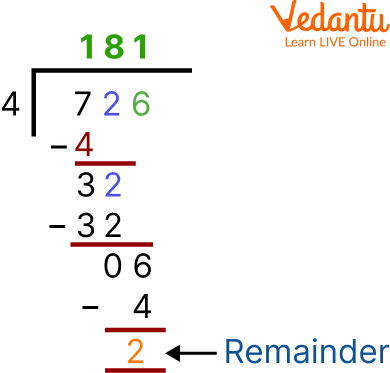
Division
As a result, the problem's quotient is 181, and the remainder is 2.
Example 2: Laila's mother gathered every family photo and planned to put them all in an album. How many pages will she need if there are 285 photos if each page of an album can hold 9 pictures?
Solution: Given 285 photos if 9 photos are there on one page the 285 photos require 285 $\div$ 9
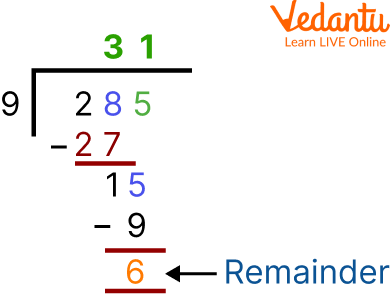
Division
Here the quotient is 31, and the remaining number is 6. She, therefore, requires 32 pages, or 31 + 1 (for the left six photos).
Practice Problems
Q1. If the remainder is 4, the quotient is 71, and the divisor is 8, find the dividend.
Ans: 572
Q2. Five garlands are to be constructed from the 75 flowers. What number of flowers will be in each garland?
Ans: 15
Summary
We have already discussed that we can split up huge numbers into numerous smaller groups or portions with the long division method. The number of groups that can be formed when a dividend is divided by a divisor is given by the quotient, and the number of elements or integers that will remain ungrouped is given by the remainder. Larger numbers can be divided by one-digit numbers using the short division, while larger numbers can be divided by two-digit or more numbers using the long division. Some solved examples and practice questions are also provided in this article. Grab your pen and pencil and start solving these questions.
FAQs on Division for Kids: Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
1. What is division in simple terms for kids?
Division is a way of sharing things equally or splitting a large number into smaller, equal groups. For instance, if you have 12 chocolates and want to share them fairly among 3 friends, division helps you find out that each friend will get 4 chocolates. It is the opposite of multiplication.
2. How can I solve a division problem step-by-step?
To solve a simple division problem like 15 ÷ 5, you can think of it as, "How many groups of 5 can I make from 15?" Here are the steps:
- Step 1: Start with the total number, which is 15 (the dividend).
- Step 2: Use the number you are dividing by, which is 5 (the divisor).
- Step 3: Count in 5s until you reach 15: 5, 10, 15. You counted three times.
- Step 4: The answer, known as the quotient, is 3. So, 15 ÷ 5 = 3.
3. Why is it important to learn division?
Learning division is a very important skill because it helps in many real-world situations. It teaches you how to share fairly, which is useful when splitting toys with siblings or pizza with friends. Understanding division also builds a strong foundation for learning more complex maths concepts later, such as fractions, decimals, and ratios, making you a better problem-solver.
4. What are some real-life examples where division is used?
We use division every day, often without realising it. Here are some common examples:
- Sharing Food: Splitting a packet of biscuits or a cake equally among family members.
- Organising Items: Arranging 20 books equally onto 4 shelves.
- Saving Money: Figuring out how much you need to save each week to buy a toy in a month.
- Team Sports: Creating equal teams for a game from a group of players.
5. What is the difference between short division and long division?
Short and long division are two methods for dividing numbers. The main difference is their use and how steps are written.
- Short division is a quicker method used when dividing by a single-digit number (e.g., 84 ÷ 4). Most calculations are done mentally.
- Long division is used for dividing larger numbers, especially by two or more digits (e.g., 575 ÷ 25). Each step (Divide, Multiply, Subtract, Bring down) is written out to avoid errors.
6. How are division and multiplication connected?
Division and multiplication are inverse operations, which means they are opposites that undo each other. They belong to the same 'fact family.' For example, if you know that 6 x 4 = 24, you automatically know two related division facts:
- 24 ÷ 4 = 6
- 24 ÷ 6 = 4
This relationship is very helpful. If you are stuck on a division problem, you can use multiplication to find the answer.
7. What does a 'remainder' mean in division?
A remainder is the number that is 'left over' after dividing when a number cannot be split into perfectly equal groups. For example, if you have 14 pencils to share among 3 friends, each friend gets 4 pencils (3 x 4 = 12). You will have 2 pencils left over because they cannot be shared equally among the 3 friends. In this case, the remainder is 2.
8. What are the names of the different parts of a division problem?
Understanding the vocabulary of division is key. In any division equation, there are three main parts:
- Dividend: The number being divided (the total amount). In 20 ÷ 5 = 4, the dividend is 20.
- Divisor: The number you are dividing by. In 20 ÷ 5 = 4, the divisor is 5.
- Quotient: The answer to the division problem. In 20 ÷ 5 = 4, the quotient is 4.

















