




Solved Examples on Division: Quotient and Remainder Explained
Division can be defined as splitting large numbers into smaller groups having equal numbers each. The number of smaller groups obtained is called the quotient of a number. The quotient is the result obtained at the end of division like how sum, difference and product are for addition, subtraction and multiplication, respectively.
Dividing Cake using Division
Division is one of the most important mathematical operations used during calculations to obtain equal parts of the given whole of something. So when you are required to cut a whole cake into 12 slices of equal sizes, as you have 12 friends to share it with, you’re applying division.
What Should I Know to do Division?
If you have an idea of the other 3 mathematical operations listed below and a basic knowledge of divisibility you can master division too!
Multiplication tables till 9
Subtraction
Divisibility rules till 9 (This is optional to know if the number would produce a remainder or not)
What is Division?
Division is a process by which a large number is split into smaller groups each containing an equal number of parts in each group. It involves the multiplication and subtraction of some form to obtain the result known as the quotient. Another important aspect of division is the remainder which is the number that is left out after the process of division. Shown below is the symbol of division which is a line with dots placed above and below.

Division Symbol
How to Find the Quotient of a Given Perfectly Divisible Number?
For perfectly divisible numbers, we carry out the division till we obtain a remainder of 0 as illustrated below. We are to divide 625 by 5 as follows:

Division of 625 by 5
Here, the quotient obtained is 125 and the remainder obtained is 0. The simple division is carried out till a remainder of 0 is obtained in the case of a perfectly divisible number.
How to Find the Quotient and Remainder of a Given Number?
The above case illustrated is when the given number is perfectly divisible by the divisor. If the number given is not divisible by the divisor, a remainder is often obtained. To understand this case, we are going to divide 100 by 8 as follows:
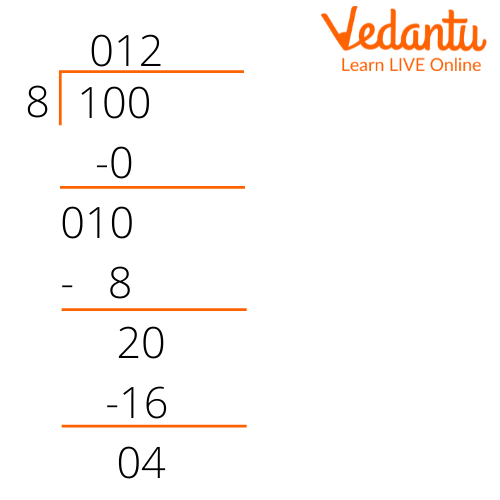
Division of 100 by 8
Here, the quotient obtained is 12 and the remainder obtained is 4. Simple division is carried out till a remainder obtained is lesser than the divisor in case of a number that is not divisible by the divisor.
Solved Examples
1. Find the quotient and remainder obtained when 420 is divided by 7.
Ans: We carry out the division as follows:

Division of 420 by 7
The quotient is found to be 60 and the remainder is found to be 0.
2. Divide 67 by 7.
Ans:
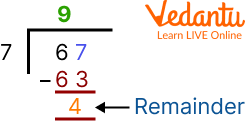
Division of 67 by 7
The quotient is 9 and the remainder will be 4.
3. Divide 888 by 7.
Ans:
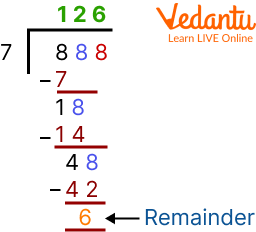
Division of 888 by 7
The quotient is 126 and the remainder is 6.
Practice Problems
1. Divide 506 by 7 and give the quotient and remainder.
Ans: Quotient - 72, remainder - 2.
2. Divide 782 by 5 and give the quotient and remainder.
Ans: Quotient - 156, remainder - 2.
3. Divide 932 by 4 and give the quotient and remainder.
Ans: Quotient - 233, remainder - 0.
4. Divide 327 by 2 and give the quotient and remainder.
Ans: Quotient - 163, remainder - 1.
5. Divide 144 by 3 and give the quotient and remainder.
Ans: Quotient - 48, remainder - 0.
Summary
Division is a basic mathematical operation where a larger number is split into smaller numbers containing equal groups. The result obtained at the end of the division is known as the quotient. The number that is left out at the end of the process of division which cannot be divided any further is called the remainder.
If the larger number divided by the smaller number is perfectly divisible by it, then we only obtain a quotient and the remainder is usually 0. If the larger number divided by the smaller number is not divisible by it, then we obtain a quotient and the remainder is the number that is left out at the end.
FAQs on Learn How to Find the Quotient and Remainder of Any Number
1. What are the four main components in a division problem?
Every division problem consists of four main components:
- Dividend: The number that is being divided.
- Divisor: The number by which the dividend is divided.
- Quotient: The result or the whole number answer obtained after the division.
- Remainder: The amount left over after the division is complete. The remainder is always less than the divisor.
2. How do you find the quotient and remainder of a number using long division?
To find the quotient and remainder, you can follow the steps of long division:
- Step 1: Arrange the dividend and the divisor in the long division format.
- Step 2: Divide the first digit (or first few digits) of the dividend by the divisor. Write the result (quotient) on top.
- Step 3: Multiply the quotient by the divisor and write the product below the part of the dividend you used.
- Step 4: Subtract this product from that part of the dividend to get a remainder.
- Step 5: Bring down the next digit of the dividend and repeat the process until no more digits are left to bring down. The final number on top is the quotient and the last leftover number is the remainder.
3. What is the formula to check a division answer using the quotient and remainder?
You can verify your division answer using the Division Algorithm formula. This formula establishes the relationship between the four components of division. The formula is: Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder. If your calculation is correct, the right side of the equation will equal the dividend.
4. What is the quotient and remainder when 45 is divided by 7?
When you divide 45 by 7:
- We look for the largest multiple of 7 that is less than or equal to 45, which is 42 (7 × 6).
- So, the quotient is 6.
- To find the remainder, we subtract 42 from 45: 45 - 42 = 3.
- Therefore, the remainder is 3.
5. In a division sum, can the remainder be larger than the divisor?
No, the remainder can never be larger than or equal to the divisor. The core principle of division is to see how many times the divisor can 'fit' completely into the dividend. If the remainder were larger than the divisor, it would mean that the divisor could have fit in at least one more time, and the division process would not be complete. Therefore, a correct division always results in a remainder that is smaller than the divisor.
6. What does it mean if the remainder is 0 after dividing?
If the remainder is 0, it means the dividend is perfectly divisible by the divisor. In other words, the divisor fits into the dividend a whole number of times with nothing left over. For example, when you divide 10 by 2, the quotient is 5 and the remainder is 0, which shows that 10 can be split into exactly 5 groups of 2.
7. How is finding a quotient and remainder used in everyday situations?
Finding the quotient and remainder is a practical skill used in many real-world scenarios. For example:
- Sharing items: If you have 25 sweets (dividend) to share among 4 friends (divisor), each friend gets 6 sweets (quotient), and you will have 1 sweet left over (remainder).
- Planning events: If you need to arrange 50 chairs in rows of 8, you will have 6 full rows (quotient) and 2 extra chairs (remainder) to place in a final, smaller row.
- Packaging goods: A factory might need to pack 100 eggs into cartons that hold 12 eggs each. They can fill 8 cartons completely (quotient) and will have 4 eggs left over (remainder).

















