ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 5 Selina Concise Solutions - Free PDF Download
Updated ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 5 - Transpiration Selina Solutions are provided by Vedantu in a step by step method. Selina is the most famous publisher of ICSE textbooks. Studying these solutions by Selina Concise Biology Class 10 Solutions which are explained and solved by our subject matter experts will help you in preparing for ICSE exams. Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions can be easily downloaded in the given PDF format. These solutions for Class 10 ICSE will help you to score good marks in ICSE Exams 2024-25.
The updated solutions for Selina textbooks are created in accordance with the latest syllabus. These are provided by Vedantu in a chapter-wise manner to help the students get a thorough knowledge of all the fundamentals.
Access ICSE Selina Solutions for Class 10 Biology Chapter 5 - Transpiration
Progress Check
1. Transpiration is best defined as (tick-mark the correct option)
(a) loss of water from the plant.
(b) loss of water as vapour from the plants.
(c) evaporation of water from the surface of leaves.
Ans: The correct answer is option (c) evaporation of water from the surface of leaves.
The evaporation of water from plants, particularly leaves, is known as transpiration. It spreads via the plant's leaves and other elements. It occurs when the stomata of the leaves remain open.
2. In one of the experiments to demonstrate transpiration, we used cobalt chloride paper. What are the characteristics of this paper that suit the experiment?
Ans: The blue colour of cobalt chloride paper changes to pink when it comes into contact with water vapour. Cobalt chloride paper is used in tests to prove the process of transpiration. When there is transpiration, the blue colour changes to pink as we know that transpiration involves the loss of water vapour.
3. Look at the experiment shown in Fig. 5.4. Suppose you took a single flower with a long stalk dipping in water, instead of a leafy twig. Will it serve the purpose? Yes/No. Give Reason.
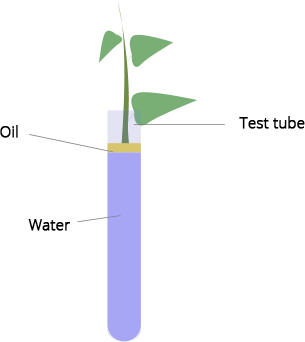
Ans: If we take a single flower with a long stalk dipped in water, instead of a leafy twig, then there will be no transpiration. This is because transpiration is the process of the loss of water vapour from the leaves. In leaves, there is the presence of stomata that results in loss of water when it is open.
4. Mention any two limitations in the use of potometers.
Ans: The limitations in the use of potometers are:
In the potometer, the introduction of the air bubble is very difficult.
It takes time to show the results, as a result, the twig cannot remain alive for a long time.
Progress Check
1. From the following list, pick out the parts through which the water vapour of transpiration leaves the leaf and rearrange them in proper sequence.
Xylem vessels, mesophyll cells, stoma, intercellular space and substomatal space.
Ans: Transpiration occurs through the stoma. The proper sequence is Xylem vessels, Mesophyll cells, intercellular spaces, sub stomatal space and stoma.
2. Does diffusion play a role in the passage of water vapour from the leaf during transpiration? If so, how?
Ans: Yes, diffusion plays a role in the passage of water vapour from the leaf during transpiration. Stomata allow water vapours to diffuse from intercellular spaces to the atmosphere during transpiration.
3. In any experiment to demonstrate transpiration, the leaf must remain attached to its parent plant. Why is this so?
Ans: A leaf must remain attached to its parent plant because if it is detached from the plant it will no longer be supplied to the water and minerals. As a result, it undergoes senescence.
4. Out of the three kinds of transpiration, which one is maximum and which one is minimum?
i) Maximum
ii) Minimum
Ans: There are three kinds of transpiration-
Stomatal Transpiration- This transpiration occurs through stomata.
Lenticular Transpiration- This transpiration occurs through lenticels that are minute openings on the surface of old woody stems.
Cuticular Transpiration- This transpiration occurs from the surface of the leaves and stems.
The maximum transpiration occurs through stomata. So, stomatal transpiration is maximum.The minimum transpiration occurs through the cuticle. So, Cuticular transpiration is minimum.
Progress Check
1. How will the following conditions affect transpiration?
i) Still air
Ans: When there is no air or the air is still, humidity can develop around the plant, reducing the amount of water released.
ii) Midday High Temperature
Ans: When the temperature rises, the stoma opens and a large volume of water is discharged into the environment.
iii) Dry Air
Ans: As the air becomes dry, the rate of transmission drops in proportion.
iv) Dim Sunlight
Ans: It causes a decrease in transpiration, allowing the plant to conserve water.
v) Insufficient Absorption of Water by the Roots
Ans: In this case, the water is less absorbed by the plants, thereby the transpiration will also decrease.
2. List any three adaptations in plants to reduce transpiration.
Ans: The three adaptations in plants to reduce transpiration are-
The narrow structure of the leaf.
A thick layer of cuticle covers the leaf.
Less number of stomata in the upper epidermis of the leaf.
Progress Check
1. List any four advantages of transpiration to the plant.
Ans: The four advantages of transpiration to the plant are-
As the evaporation of water lowers the temperature of the leaf surface, transpiration has a cooling impact on the plant body.
Transpiration aids sap ascent by creating a suction force that acts from the plant's top.
Water and mineral salts are distributed throughout the plant body through transpiration.
Excess water is removed by transpiration.
2. How would you justify the statement that transpiration contributes to bringing rain?
Ans: Excess water in plants is evaporated through stomata in a process known as transpiration. Water vapour is released into the sky during this process, where it condenses and aids in the creation of clouds, which bring rain. As a result, we may conclude that transpiration aids in the precipitation process.
3. Differentiate between guttation and transpiration.
Ans: The difference between guttation and transpiration is-
Sl. No. | TRANSPIRATION | GUTTATION |
01 | Loss of water takes place in vapour form. | Loss of water takes place in liquid form. |
02 | Water does not contain any dissolved solids or solutes since it evaporates in vapour form. | Water includes numerous dissolved particles and solutes since it is lost in liquid form. |
03 | As a result of the water loss caused by the sun, transpiration occurs exclusively during the day. | This happens in the early morning or late at night when there is no sunshine. |
4. Plants have no blood, yet we sometimes say that a plant is bleeding. How do you justify this?
Ans: The process through which a plant loses its components from a cut is known as bleeding. Latex and other exudates are collected from the plant body's wound.
Review Questions
A. Multiple Choice type
1. Transpiration pull will be maximum under which set of the following conditions?
(a) Open stomata, dry atmosphere and moist soil
(b) Open stomata, high humid atmosphere and well-irrigated soil
(c) Open stomata, high humid atmosphere and dry soil
(d) Closed stomata, dry atmosphere and dry soil
Ans: (a) Open stomata, dry atmosphere and moist soil
Transpiration pull will be maximum under Open stomata, dry atmosphere and moist soil.
2. With the decrease in atmospheric pressure, the rate of transpiration will
a) Increase
b) Decrease rapidly
c) Decrease slowly
d) Remain the same
Ans: (a.)increase
With the decrease in atmospheric pressure, the rate of transpiration will increase. As the atmospheric pressure drops, air will readily move out of the plant. As a result, the rate of transpiration rises, making it easier for plants to lose water.
3. One of the internal factors which affect the rate of transpiration is
a) Big size of the leaf
b) Colour of the leaf
c) Sunken stomata
d) Sunny day
Ans: (c.) sunken stomata
One of the internal factors which affect the rate of transpiration is Sunken Stomata. Stomata that are not directly exposed to the surface are referred to as "sunken." It's in a shallow hole that hides the escaping vapour from air currents, reducing leaf water loss.
4. Guttation takes place through
a) Stomata
b) Lenticels
c) Lower epidermis of leaves
d) Hydathodes
Ans:(d.) hydathodes
Guttation is the process through which plants release liquefied water. It happens through Hydathodes.
5. Transpiration will be fastest when the day is
a) Cool, humid and windy
b) Hot, humid and still
c) Hot, humid and windy
d) Hot, dry and windy
Ans: (c.) Hot, humid and windy
Transpiration will be fastest when the day is hot, dry and windy. On this day, the loss of water vapour is highest thus, transpiration is highest.
6. Most of the transpiration in tall trees occurs through
a) Stomata
b) Lenticels
c) Cuticle
d) Bark
Ans: (a.) stomata
Most of the transpiration in tall trees occurs through Stomata
7. Transpiration is best defined as
a) Loss of water by the plant
b) Evaporation of water from the surfaces of the plant
c) Loss of water, as water vapour, by a plant
d) Release of water by a plant into the atmosphere.
Ans: (c.) Loss of water, as water vapour, by a plant
Transpiration is best defined as Loss of water, as water vapour, by a plant.
B. Very Short Answer Type
1. Name the following:
a) Openings on the stem through which transpiration occurs.
Ans: Lenticels are the openings on the stem through which transpiration occurs.
b) The process by which intact plants lose water in the form of droplets.
Ans: Guttation is the process by which an intact plant loses water in the form of droplets. This takes place in hydathodes.
c) An instrument used to find the rate of transpiration.
Ans: The instrument used to find the rate of transpiration is a potometer.
d) A plant in which stomata are sunken.
Ans: Nerium is the plant in which stomata are sunken.
e) The apparatus to record the rate of transpiration in a cut shoot.
Ans: Ganong's photometer is used to record the rate of transpiration in a cut shoot.
f) Any two parts of the leaf which allow transpiration.
Ans: Stomata and cuticle are the two parts of the leaf that allow transpiration.
g) The structure in a leaf that allows guttation.
Ans: Guttation is the process by which an intact plant loses water in the form of droplets. This takes place in hydathodes of leaves.
h) Loss of water droplets from the margins of certain leaves.
Ans: Guttation is the process that involves the loss of water droplets from the margins of certain leaves.
2. Fill in the blanks:
(a) Transpiration is the loss of water as water….. from the…..parts of the plant.
Ans: Transpiration is the loss of water as water vapour from the aerial parts of the plant. Plants receive water through their roots and then release water vapour through pores in their leaves, which is known as transpiration.
(b) Closing of ............ and shedding of leaves reduce .............
Ans: Closing of stomata and shedding of leaves reduce transpiration. Thereby, reducing the loss of water from the plants.
(c) Transpiration helps in creating ............. force and in eliminating excess ......
Ans: Transpiration helps in creating suction force and in eliminating excess
C: Short Answer Type
Given below is an example of a certain structure and its special functional activity:
chloroplasts and photosynthesis
In a similar way, write the functional activity against each of the following:
(a) Hydathodes and ....................................
Ans: Hydathodes and Guttation
(b) Leaf spines and ....................................
Ans: Leaf spines and reduced transpiration
Spines are modified leaves. Spines result in reduced transpiration.
(c) Lenticels and ........................................
Ans: Lenticels and transpiration
Lenticels are the openings on the stem through which transpiration occurs.
(d) Xylem and ...................................
Ans: Xylem and conduction of water
Water and mineral salts are transported from the roots to various regions of the plant via xylem.
2. (a) State whether the following statement is True (T)or False(F)?
(b) Rewrite the false statements in (a) above, in the correct form.
(i) Most transpiration occurs at midnight (T/F)
Ans: The above statement is False. Most transpiration occurs at mid-day.
(ii) Transpiration creates a pull for upward movement of the sap. (T/F)
Ans: The above statement is True. Transpiration creates a pull for the upward movement of the sap. The reason for this is that when the water level increases, it produces a vacuum, which causes the draw.
(iii) Wind velocity has an effect on transpiration. (T/F)
Ans: The above statement is True. Wind velocity has an effect on transpiration. A higher transpiration rate is caused by increased airflow around a plant.
(iv) Atmospheric humidity promotes transpiration from a green plant. (T/F)
Ans: The above statement is False. Atmospheric humidity reduces transpiration from a green plant
(v) Transpiration helps to cool the body of the plant. (T/F)
Ans: The above statement is True. Transpiration promotes cooling by removing heat from surrounding cells and surfaces and evaporating it as it passes through tubes in plants.
3. Give a suitable explanation for the following:
(a) A higher rate of transpiration is recorded on a windy day rather than on a calm day.
Ans: The rate of transpiration rises as the wind speed rises. The water vapour produced during transpiration is eliminated faster when the wind blows faster, and the space surrounding the transpiring leaf is not saturated with water vapour.
(b) Excessive transpiration results in the wilting of the leaves.
Ans: The cells lose their turgidity when the rate of transpiration greatly surpasses the rate of water absorption by roots. As a result, high transpiration causes the leaves to wilt.
(c) Some plants show wilting of their leaves at noon even when the soil is well-watered.
Ans: Plants continually collect water through their roots, which is subsequently carried upwards to all of the plant's aerial components, including the leaves. Only a little portion of this water is needed for photosynthesis and other processes, around 0.02 per cent. The remaining water is exhaled as water vapour. As a result, the water absorbed equals the water transpired.
(d) More transpiration occurs from the lower surface of a dorsiventral leaf.
Ans: The lower surface of a dorsiventral leaf has more stomatal holes. The rate of transpiration increases as the number of stomata increases. As a result, the lower surface transpires more.
(e) The stomata in most plants are more numerous on the lower surface of a leaf as compared to the upper surface.
Ans: As the lower surface of a leaf does not get direct sunlight, most plants have more stomata on the lower surface than on the top surface. This layout aids in the reduction of transpiration.
(f) Forests tend to bring more rains.
Ans: Huge amounts of water are released into the atmosphere by enormous areas of land, particularly forests, due to transpiration. As a result, transpiration increases the amount of moisture in the atmosphere, causing more rain to fall.
(g) On a bright sunny day, the leaves of certain plants roll-up.
Ans: The rate of transpiration is substantially higher on a bright sunny day than on any other day. On a bright sunny day, the leaves of certain plants roll up to lower the exposed surface area and consequently the rate of transpiration.
D. Descriptive Type:
1. Define the following terms:
(a) Transpiration
Ans: Transpiration is the loss of water from the plant's aerial portions (leaves and stem) in the form of water vapour.
(b) Exudation
Ans: Exudation is the process by which plants discharge water or other fluids, as well as dissolved compounds, in liquid form rather than as water vapour.
(c) Potometer
Ans: A potometer is a device that monitors a plant's rate of water intake, which is nearly equal to the amount of water lost through transpiration.
(d) Wilting
Ans: Wilting is the collapse of leaves caused by an excessive loss of water, such as transpiration, or by a disease.
(e) Hydathodes
Ans: Hydathodes are special pore-bearing structures found on the leaf's edges that facilitate guttation.
(f) Cuticle
Ans: The cuticle is a waxy covering formed by the epidermis on the two surfaces of the leaf that prevents water from evaporating.
2. Distinguish between
(a) Stomata and Lenticels
Ans: The differences between stomata and lenticels are:
Stomata | Lenticels |
1. They are minute openings in the epidermal layer of leaves. | 1. They are minute openings on the surface of old woody stems. |
2. Maximum transpiration occurs through stomata. | 2. Lesser transpiration occurs through lenticels. |
(b) Guttation and Bleeding
Ans: The differences between guttation and bleeding are:
Guttation | Bleeding |
1. It is the removal of excess water from the plants because of excess water build-up in the plant. | 1. It is the removal of water from the plant because of injury. |
2. Water escapes from specialized structures called hydathodes. | 2. Water escapes in the form of sap from the injured part of the plant. |
3. It occurs during early mornings or late nights. | 3. It occurs at the time of injury. |
(c) Transpiration and Evaporation
Ans: The differences between transpiration and evaporation are:
Transpiration | Evaporation |
1. It is the loss of water in the form of vapour from the aerial parts of the plant. | 1. It is the loss of water from the surface of water bodies in the form of vapour. |
2. It is a slow process. | 2. It is comparatively a faster process. |
3. Suppose you have a small rose plant growing in a pot. How would you demonstrate transpiration in it?
Ans: Place the little potted rose plant in a clear polythene bag and cover it. Tie the mouth of the creature to the stem's base. Allow the plant to sit in direct sunshine for an hour or two.
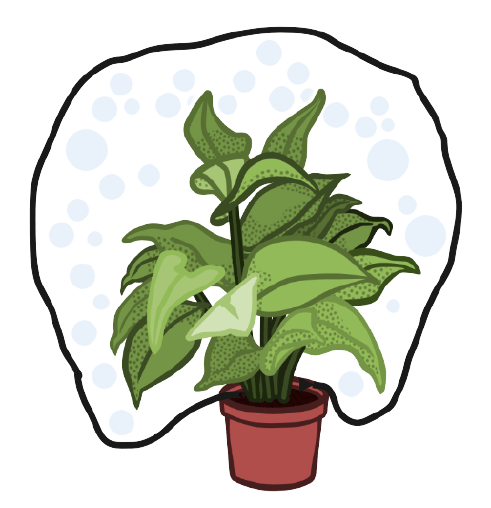
Due to the saturation of water vapour given out by the leaves, drops of water will quickly develop on the inside surface of the bag. In the same way, an empty polythene bag with its mouth sealed and stored in the sun would display no water drops. This is the way to demonstrate that plants transpire. The droplets will be verified as water only if tested with dry cobalt chloride paper.
4. What is lenticular transpiration? Mention one major difference between lenticular transpiration and stomatal transpiration.
Ans: Lenticels form on the barks of older stems. These allow gases to diffuse for both respiration and photosynthesis. Lenticels never come to an end. They stay open at all times.
The differences between stomatal transpiration and lenticular transpiration are:
Stomatal transpiration | Lenticular transpiration |
1. They are minute openings in the epidermal layer of leaves. | 1. They are minute openings on the surface of old woody stems. |
2. Maximum transpiration occurs through stomata. | 2. Lesser transpiration occurs through lenticels. |
5. Droplets of water may sometimes be seen along the margins of the leaves of a banana plant, growing in wet soil in the mornings. Are these dew drops? Comment upon your answer.
Ans: They aren’t dewed drops. This is the water that the plant body exudes through guttation. The banana plant's transpiration is impeded since it grows in a humid climate. The roots, on the other hand, continue to absorb water from the earth. This creates a tremendous amount of hydrostatic pressure within the plant, forcing excess water out of the hydathodes, which are holes found at the ends of veins in the leaf. This is most noticeable in the mornings.
6. Briefly explain how the rate of transpiration is affected by:
(a) Intensity of light
Ans: Intensity of light- During the day, the stomata are open to let carbon dioxide diffuse inside for photosynthesis. They are closed at night. As a result, there is increased transpiration during the day. The stomata are partly closed and transpiration is decreased during cloudy days.
(b) Humidity of the atmosphere
Ans: When the air is humid, it can only contain a little amount of water vapour. As a result, increased air humidity slows the outward diffusion of internal water vapour through stomata, lowering the rate of transpiration.
(c) Temperature
Ans: The rate of transpiration increases as the temperature rises, especially during the growing season when the air is warmer due to more sunshine and warmer air.
E. Structured/ Application/ Skill Type
The given figure represents an experiment:
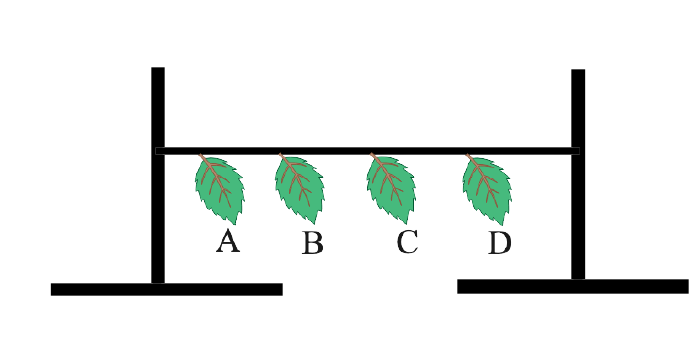
(a) Leaf A was coated with grease on both surfaces.
(b) Leaf B was coated with grease on the lower surface.
(c) Leaf C was coated with grease on the upper surface.
(d) Leaf D was left without any application of grease.
All the four leaves A, B, C and D were left in a room for about 24 hours.
(i) Which leaf dries first? Give reason.
Ans: Leaf D i.e. the leaf with no grease on either surface would dry earliest because it would lose water from both surfaces at the same time, i.e. it would lose its most water due to transpiration.
(ii) Which leaf dries last? Give reason
Ans: Leaf A which was greased on both surfaces will dry last. Greasing reduces evaporation of water because transpiration occurs through stomata, which are more abundant on the bottom surface of the leaf.
2. Given below is the diagram of an apparatus used to study a particular phenomenon in plants:
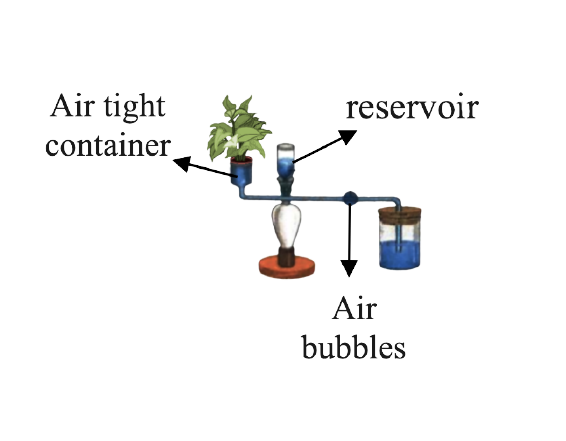
(a) Name the apparatus.
Ans: The name of the apparatus is Ganong’s potometer.
(b) What is it used for?
Ans: Ganong’s potometer is used to measure the rate of water intake by a plant.
(c) What is the role played by the air bubble in this experiment?
Ans: As the water from the twig is lost, a suction force is created, which draws the water from the beaker and causes the bubble in the capillary tube to travel forward. The volume of water lost in a particular period would be determined from the readings on the capillary tube.
(d) What is the use of the reservoir?
Ans: The use of the reservoir is to open the stop cock and let the water into the capillary tube.
(e) What happens to the movement of the air bubble if the apparatus is kept: Give a reason in each case.
(i) In the dark
Ans: There will be no transpiration if the device is maintained in the dark since the stomata will be closed. As a result, the air bubble would have no movement and would remain stationary.
(ii) In sunlight
Ans: The stomata are open throughout the day to allow CO2 to diffuse inside for photosynthesis. They are closed at night. As a result, there is increased transpiration during the day. The stomata are partly closed and transpiration is decreased when it is overcast throughout the day. As a result, the air bubble would travel faster since there would be more water lost through transpiration.
(iii) In front of a fan
Ans: The rate of transpiration will be higher if the equipment is placed in front of a fan. As a result, the air bubble would travel faster since there would be greater water loss due to transpiration as the wind/air velocity increased.
3. Given ahead is the diagram of an experimental set up to study the process of transpiration in plants. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
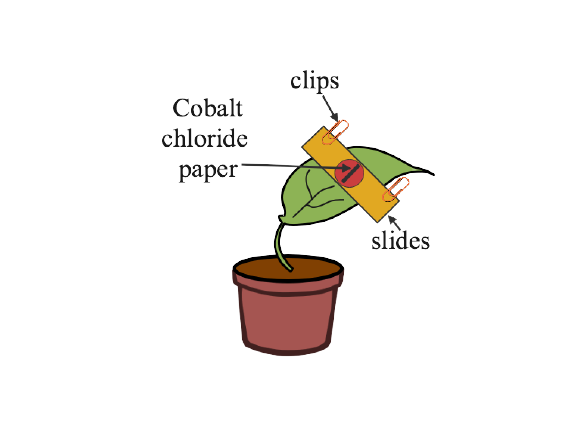
(a) Name the colour of dry cobalt chloride paper.
Ans: The colour of dry cobalt chloride paper is blue.
(b) Is the experimental leaf a monocot or a dicot? Give a reason to support your answer.
Ans: Stomata are tiny pores in the leaf's epidermal layer. Two bean-shaped guard cells surround each stomata. A dicot leaf's underside allows for more transpiration. The underside of a dicot leaf has more stomatal openings, resulting in higher transpiration.
(c) Why are glass slides placed over the dry cobalt chloride papers?
Ans: Glass slides are mounted on the top of the dried cobalt chloride sheets to keep the strips in place.
(d) After about half an hour what change, if any, would you expect to find in the cobalt chloride paper placed on the dorsal and ventral sides of the leaf? Give a reason to support your answer.
Ans: After about half an hour we observe that,
1. The water vapour condensed on its inner walls.
2. The second bell jar (B) would similarly demonstrate condensation, and the initially blue cobalt chloride paper in it would change pink at the same time.
4. An outline sketch of a tree is shown in a diagram below. Study the same and answer the questions that follow:
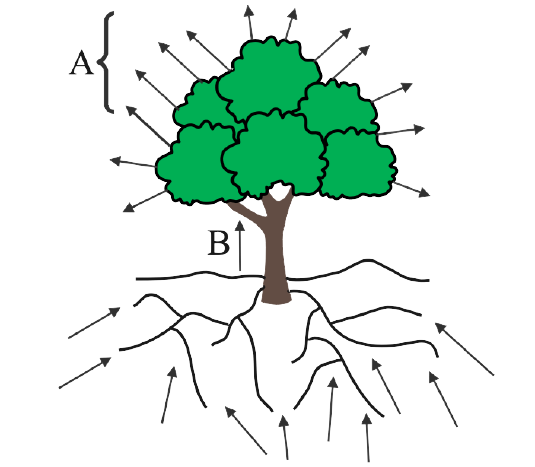
(a) Name and define the phenomenon labelled A in the diagram.
Ans: The phenomenon labelled A is Transpiration.
The evaporation of water from plants, particularly leaves, is known as transpiration. It spreads via the plant's leaves and other elements. It occurs when the stomata of the leaves remain open
(b) Write the significance of the process mentioned in A for the plants.
Ans: The significance of the transpiration is-
As the evaporation of water lowers the temperature of the leaf surface, transpiration has a cooling impact on the plant body.
Transpiration aids sap ascent by creating a suction force that acts from the plant's top.
Water and mineral salts are distributed throughout the plant body through transpiration.
Excess water is removed by transpiration.
(c) What do the direction of arrows in B and C indicate? Name the phenomenon.
Ans: Lenticular transpiration/ascent of sap is indicated by arrow B as water passes up the trunk. Water absorbed by roots from the soil is shown by arrow C, and the phenomenon is known as endosmosis.
Endosmosis is the process through which water molecules enter a cell. Water passing from root hair cells to cortical cells of the root is an example.
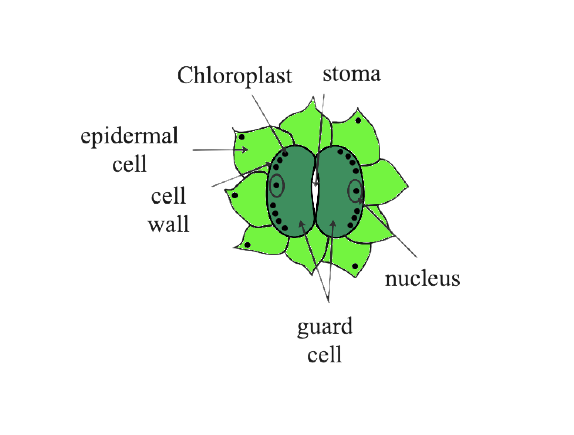
(d) Draw a neat and labelled diagram of an opened stomata.
Ans:
5. The figure given below represents an experimental setup with a weighing machine to demonstrate a particular process in plants. The experimental setup was placed in bright sunlight. Study the diagram and answer the following questions.
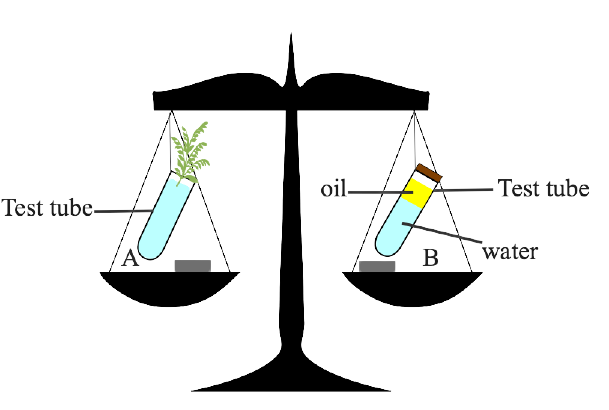

(a) Name the process intended for study.
Ans: Transpiration is the process intended for study.
(b) Define the above mentioned process
Ans: Transpiration is the loss of water in the form of water vapour from the leaves and other aerial parts of the plant.
(c) When the weight of the test tubes A and B is taken before and after the experiment, what change is observed? Justify.
Ans: When test tube A's weight was measured before the experiment, it was higher than when it was measured after the experiment. As a result of transpiration, the water in test tube A has evaporated.
As no water is lost in test tube B, the weight of the tube remains constant before and after the experiment. This is due to the fact that oil is accumulating on the test tube.
(d) What is the purpose of keeping the test tube B in the experimental setup?
Ans: The purpose of keeping the test tube B in the experimental setup is that this makes the observation of the change in test tube A easy.
6. An apparatus as shown below was set up to investigate a physiological process in plants. The setup was kept in sunlight for two hours. Droplets of water were then seen inside the bell jar. Answer the questions that follow:
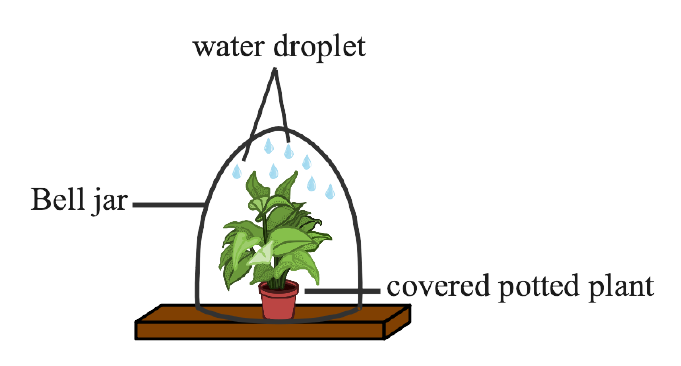
(a) Name the process being studied.
Ans: The process is shown in the figure above is transpiration.
(b) Explain the process named above in (a).
Ans: The evaporation of water from plants, particularly leaves, is known as transpiration. It spreads via the plant's leaves and other elements. It occurs when the stomata of the leaves remain open
(c) Why was the pot covered with a plastic sheet?
Ans: The pot is covered with a plastic sheet to prevent evaporation of water from the soil.
(d) Suggest a suitable control for this experiment.
Ans: A control for this experiment will be an empty polythene bag with its mouth tied.
(e) Mention two ways in which this process is beneficial to plants.
Ans: Transpiration is beneficial to plants in the following ways:
It creates a suction force in the stem that helps the roots to absorb water and minerals.
It helps in cooling the plant in hot weather.
(f) List three adaptations in plants to reduce the above mentioned process.
Ans: The three adaptations in plants to reduce the above mentioned process are-
The leaves may be converted into spines such as cactus whereas pine leaves can be changed into needles.
Stomata are reduced in quantity and may be submerged in pits.
Leaves may be rolled up or folded.
7. The apparatus shown in the following diagram is Garreau’s potometer designed to demonstrate unequal transpiration from the two surfaces of a dorsiventral leaf. Before keeping the leaf in between the cups, anhydrous calcium chloride (CaCl2) contained in two small vials were weighed and placed in both the cups. The ends of the cups were closed with corks through which two mercury manometers were connected. After few hours, CaCl2 vials were taken out and weighed again.
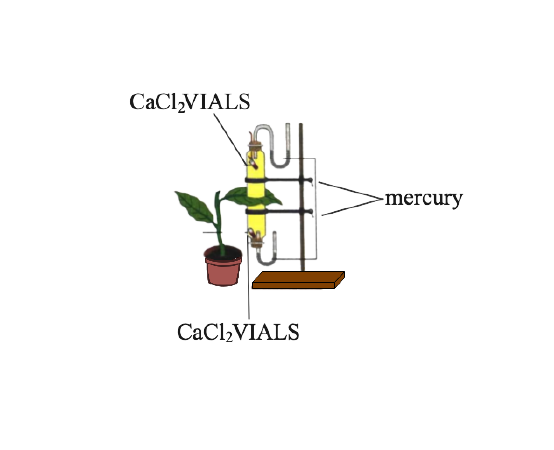
(a) What is the purpose of keeping CaCl2vials inside the cup?
Ans: The purpose of keeping CaCl2vials inside the cup is to absorb water.
(b) After few hours CaCl2vials were taken out and weighed again. Will you expect any difference in weight? If so, give reason.
Ans: Yes, there is a difference in weight. After a few hours the weight of the CaCl2 vials will increase because they will absorb water lost by the leaf of the plant due to transpiration.
(c) What is the purpose of using a manometer?
Ans: The purpose of using the manometer is that it measures the pressure exerted by the fluid.
(d) What do you mean by transpiration?
Ans: Transpiration is the loss of water in the form of water vapour from the leaves and other aerial parts of the plant.
ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter - 5 - Transpiration
The ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter - 5 talks about transpiration in plants. This process involves the evaporation of water through leaves, stems, or other aerial parts. Then, the chapter explains the different types of transpiration i.e. Stomatal, Cuticular, and Lenticular.
Stomatal transpiration occurs via the stomata of the plant where each stoma is guarded by two cells to regulate the opening and closing of the stomata. The process begins when the stoma is open and immediately stops when it closes. In Cuticular transpiration, the water evaporates through the cuticle. If the cubicle is thin, the rate of transpiration will be higher. Lastly, Lenticular transpiration occurs in woody plants or fruits through lenticels. These lenticels have small openings that remain open all the time due to the absence of guard cells.
Afterwards, you get to learn how to measure transpiration through different methods i.e. Weighing method, the Photometer method, and the Cobalt Chloride Paper method. All these methods use different devices to measure the rate of transpiration.
There are multiple factors that affect Transpiration such as humidity, temperature, light, the velocity of wind, atmospheric pressure, etc. All these factors affect the transpiration process in different ways. For example, the rate of transpiration will increase with an increase in temperature as there is more evaporation in hot weather. When the atmospheric pressure is less, the rate of transpiration will increase.
Since excessive transpiration is dangerous for plants, there are multiple ways to reduce the evaporation of water from these plants. Then, the chapter leads you to the importance of transpiration. In the end, you will be left with Guttation and bleeding. Guttation refers to the process of loss of water in the form of water droplets from the small pores of the leaf of a herbaceous plant.
Contents of Chapter - 5 - Transpiration
Let us have a quick look at the topics that the chapter entails:
Transpiration
Demonstration of Transpiration
Measurement of Transpiration
Kinds of Transpiration
Factors that affect Transpiration
Adaptations in plants to reduce excessive transpiration
Significance of Transpiration
Direct loss of water by plants – Guttation and Exudation
Exercise Questions
The weightage of this chapter from the examination point of view is discussed below:
Multiple Choice Type - 9 Questions
Very Short Type - 2 Questions
Short Type - 5 questions
Long Type - 9 questions
Structural or Skill type - 7 Questions.
FAQs on Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 5 - Transpiration
1. Where to find revision notes for Class 10 Biology?
2. What do Selina Concise Slutions for ICSE Class 10 Biology chapter 5 contain?
The Selina Concise Solutions for ICSE Class 10 Biology chapter 5 come with an explanation to every question from your textbook. It contains a detailed version of the answers to even those questions that are harder than others. This handy tool can help you with the toughest of questions that you are not able to solve yourself. Since each answer is explained in-depth, you can use the pdf to revise the chapter instead of going through the entire chapter again.
3. What is the importance of Transpiration?
Transpiration refers to the loss of water in the form of water vapour from the leaves, stems, flowers, and other aerial parts of the plant. It is a useful process for plants as it creates a suction force in the stem, which enables the roots to absorb water and mineral nutrients. It cools down the plant in hot weather, which is important for the plants as extreme temperatures can slow down their growth, energy levels, stop flowering, and can even cause them to die.
4. What are the tips to score high in Class 10 Biology?
You can follow a few simple tricks to score high in Class 10 Biology. First, create a schedule for studying and focus on the concepts you are weak in. The diagrams in Biology can be a little tricky. You have to practice drawing them every day to ensure you do not miss any part in your exam. Solve as many sample papers and previous year question papers to know about the variety of questions.
5. What is Wilting?
When the non-wooden parts of the plant lose rigidity, it is known as wilting. It can be caused due to excessive loss of water during transpiration or a disease. On hot days, or after some days with no watering, the transpiration causes the water to evaporate more than it is coming in. Due to this, the water balance within the plant gets thrown off. The dehydrated cells of the leaves and stems cannot remain erect for longer, which results in wilting of plants.










































