ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 11 Selina Concise Solutions - Free PDF Download
FAQs on Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 11 - Sense Organs
1. What are the key features of Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 11 - Sense Organs?
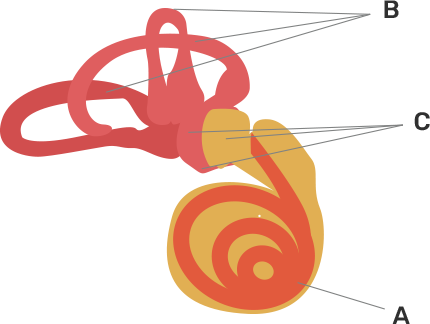
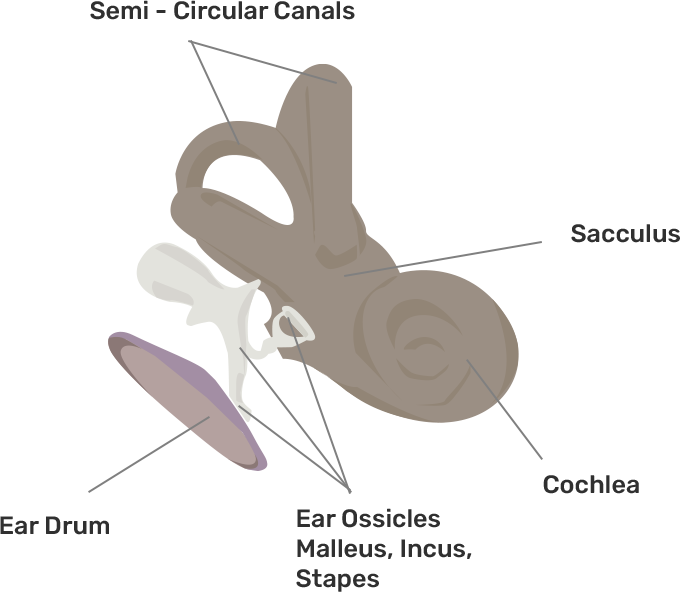
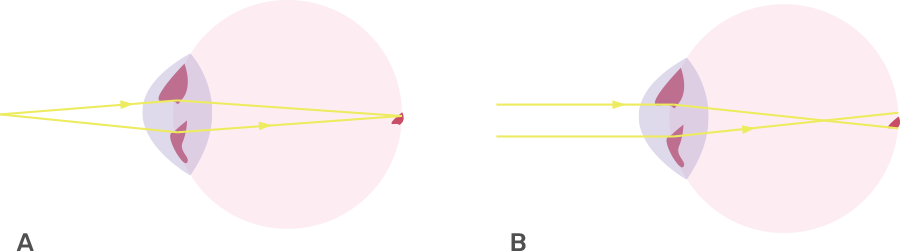
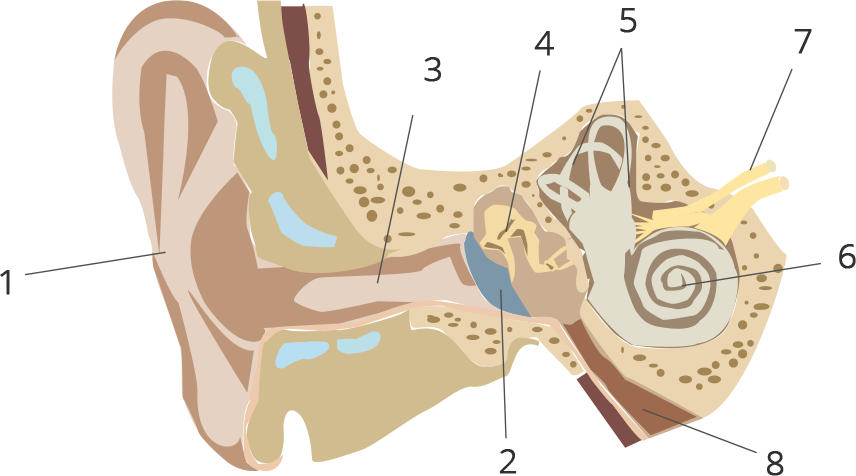
The Selina solutions have been curated by some of our teachers who hold expertise in this particular subject. The solutions have a detailed explanation in simple and easy language that can be understood by every student. The chapter deals with the features of sense organs, their types, and their importance. It also deals with the defect that can arise in each sense organ. The solution book is so well crafted that the students can easily follow the book and get a good score in the examination. The pointers used in the books to explain the points are a great way to promote learning.
2. Why should we refer to Selina Solutions Concise Biology Class 10 book for Sense Organ Chapter?
The Selina solution book has all the questions with their solution and detailed explanation, which makes it easy for the students to follow. The detailed explanation helps the students in clearing their doubts and improving their understanding skills while they are preparing for their board exams. The line-by-line explanation helps the student understand the concept better and also helps in building a strong foundation. The solutions are so well crafted that the students would not require any extra help to understand the chapter.
3. Why should we follow Vedantu for Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 11 - Sense Organs?
Vedantu is an online platform providing the students with materials for their preparation in PDF format for free. On Vedantu we can find the solutions for the concise biology book in such a manner that it can easily be grasped by the students. The solutions help the students in their self-study and are a perfect guide to the students. The Vedantu website is easy to use and the offline PDF can also be used later on by the students when they do not have access to the internet.
4. Where can we get Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 11 - Sense Organs?
The Selina solutions are easily available online for the students to download and understand the chapter. They are available in two forms, that is they can either be viewed online or can be downloaded. The solutions are also available on the Vedantu website which provides accurate solutions keeping the best interest of the student in mind. These solutions help the students in understanding the question and help them solve the question in an easy and faster method keeping the understanding of the student in mind.
5. Can we download Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 11 - Sense Organs online?
The Selina publication Biology book cannot be downloaded online. Though these books can be bought online from different online stores, it isn't possible to download them online. These books can also be brought from the nearest book store easily. Though the book cannot be downloaded for free from online websites, the solution to these books can easily be downloaded without any difficulties from the Vedantu website. The students can download the solutions for free from the website in PDF format.