ICSE Class 10 Biology Chapter 10 Selina Concise Solutions - Free PDF Download
FAQs on Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 10 - The Nervous System
1. Are there multiple choice-based questions in the Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 10 - The Nervous System?
Yes, there are. The main purpose of adding the multiple-choice based questions in Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 10 - The Nervous System is to help students understand which ones among the given options are the ones that are right. This enhances the student’s ability to reason and comprehend the answers. Finding the right answer out of the options might seem easy for those who are already aware of the answers and their reasons. But for those who are not aware of how to find the answer and their reasons, Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 10 - The Nervous System is a good guide.
2. How does Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 10 - The Nervous System help understand the brain and its functions?
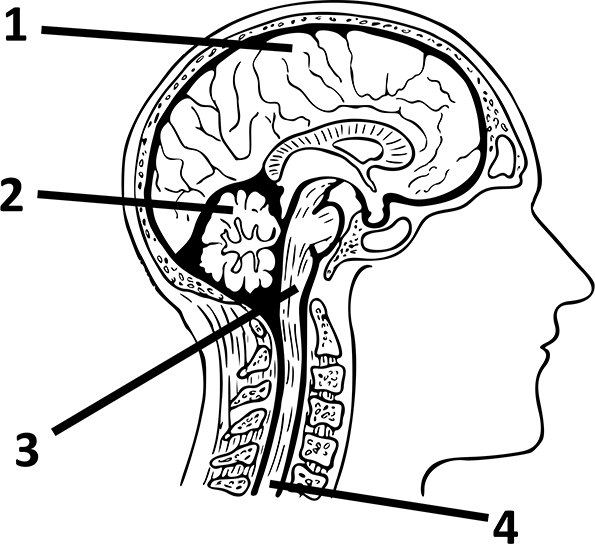
Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 10 - The Nervous System explains the brain and its parts in detail that helps students understand what are the parts of the brain well along with being able to understand how each of them has their own functions that keep the brain running. The parts as specified in Selina Concise Biology solutions can be provided as follows:
Cerebrum: which has the main function of interpreting touch, speech, vision, and reasoning
Cerebellum: which has the main function to coordinate the muscles movements, maintain a proper posture of body and balance
Brainstem: this part connects the cerebrum and cerebellum to the spinal cord which helps in regulating the performance of involuntary functions such as heart rate, breathing, body temperature, etc.
3. What does CNS mostly control according to Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 10 - The Nervous System?
According to Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 10 - The Nervous System the CNS mostly controls the function of the brain and the spinal cord. This in turn controls the entire body and the functions performed by the body. With each part of the brain responsible for different actions. Your response to a particular situation and ability to judge a particular situation is all done with the help of the CNS controlling your bodily functions. If the CNS fails, it is seen that most of the functions performed in the body are also stopped. This makes it one of the most important systems in the body.
4. What are the subtopics that are of importance in Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 10 - The Nervous System?
The subtopics that are deemed to be important in the Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 10 - The Nervous System can be provided as follows:
Need of the nervous system in the human body
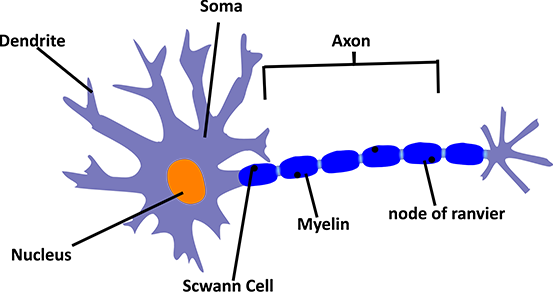
The function of the neuron is the unit of the nervous system. The neuron is also called the nerve cell.
Nerves are connected to the brain, the spinal cord, and the entire body which transfers the body function commands.
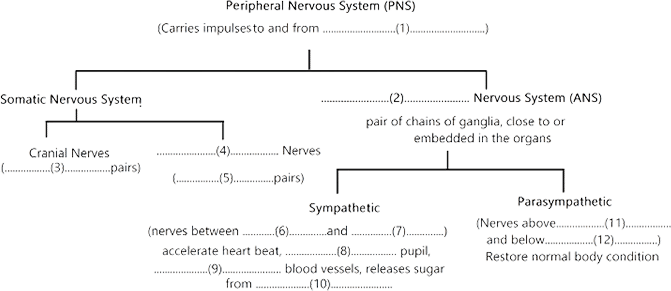
Two major divisions of the nervous systems and their functions respectively
Peripheral nervous system and what it controls.
Reflexes that are involuntary in natures and the circumstances under which it occurs
All of these topics once you understand will provide a detailed idea about the CNS and its main functioning in the body.
5. Why access the Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 10 - The Nervous System via Vedantu?
Vedantu provides a free downloadable version of Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 10 - The Nervous System which otherwise needs to be paid for or you need to either subscribe or login. Apart from this one facility, Vedantu also provides free live classes where the students of Class 10 can learn all about their syllabus and how to effectively study for their 10th board exams. The Selina Concise Biology Class 10 ICSE Solutions for Chapter 10 - The Nervous System via Vedantu which is structured according to the latest syllabus also provides an insight on the latest study patterns and how to follow them along.