




What is a Hydrometer?
A hydrometer is made up of two words, hydro + meter, where hydro means water (or liquid) and meter means a scale. So, a hydrometer is used to measure some characteristics of liquids, i.e., specific gravity or relative density (density of liquid divided by the density of water). Hydrometers are filled with liquids like mercury (as in thermometers) or lead. During its use, it is placed in a container containing the liquid.
Definition: An instrument used to measure specific gravity or relative density of liquids which works on the principle that a solid body displaces its weight when placed in water and hence floats, also known as buoyancy, is called a hydrometer.
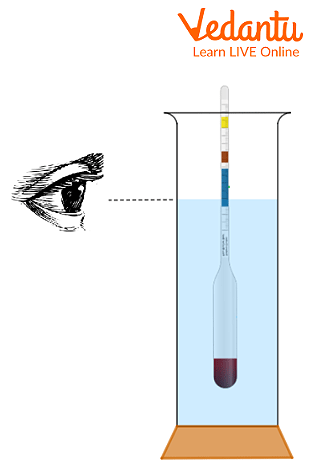
A Hydrometer Placed in a Liquid
The value at the surface of the liquid provides the specific density of the liquid. The value of specific gravity is unitless and expressed in decimals or percentages.
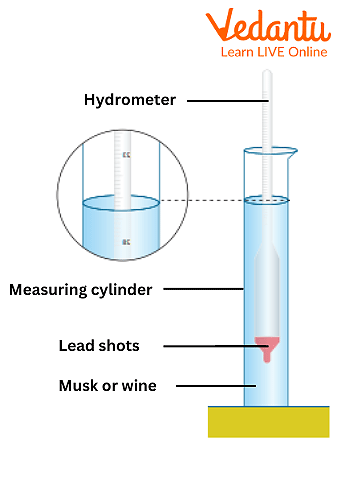
Diagram of Hydrometer
Types of Hydrometers and their Uses
Lactometer is used for milk.
Alcoholometer for wines and alcohols.
Saccharometer for sugar.
A barometer for tanning liquids in leather-making.
Acidometer for acids.
Salinometer for liquids with salt content.
Urinometer for urine analysis.
Thermo Hydrometer for fuel oils like petroleum.
Battery hydrometer for lead-acid battery.
Application of Hydrometer in Engineering
Use in Food Industry
Use in winemaking- A saccharometer and a thermometer is used to check the amount of sugar in wine or beer. The amount of sugar that is needed to put in can be determined by its specific gravity because it increases the density of solution. The alcohol content of the end product is determined by alcoholometer.

An Alcoholometer
Hydrometers are also used in making ice-creams and brewers.
Use in Soil Analysis
In the engineering field, the analysis of soil involves another important use of hydrometers. It is used in determining the distribution of soil particles.
Hydrometer Uses in Laboratory
Different types of specialised hydrometers are employed in different matters. All research is first done in laboratories, so the use of hydrometers in laboratories is varied.
Solved Questions
1. What is the special type of hydrometer which is used in checking the alcohol content in wine or beer?
Ans: The specialised hydrometer used for checking alcohol content is alcoholometer.
2. What do you understand about the relative density of a liquid?
Ans: Relative density of a liquid means density of liquid divided by density of water.
3. In what units is the specific gravity measured?
Ans: Specific gravity does not have any unit, it is unitless.
Conclusion
A hydrometer is an instrument used to measure the relative density or specific gravity of a liquid. It is of great importance for our day-to-day life as it is used in various industries which are crucial for our health. There are different types of specialised hydrometers which are named after their use.
FAQs on Uses of Hydrometer
1. What is the primary use of a hydrometer?
A hydrometer is an instrument primarily used to measure the relative density or specific gravity of a liquid. This measurement compares the density of a given liquid to the density of a reference liquid, which is typically water.
2. What is the scientific principle on which a hydrometer works?
A hydrometer operates based on Archimedes' principle. This principle states that a solid body suspended in a fluid is buoyed up by a force equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the body. A hydrometer will sink deeper in less dense liquids (displacing more fluid to match its weight) and float higher in more dense liquids.
3. What are some common examples of a hydrometer's use in various fields?
Hydrometers have several specialised applications. Some common examples include:
Lactometer: Used in dairies to check the purity and richness of milk.
Saccharometer: Used in winemaking and brewing to measure the sugar content in a solution.
Acidometer (Battery Hydrometer): Used to measure the specific gravity of the sulfuric acid in a lead-acid battery to determine its state of charge.
Salinometer: Used to measure the salt concentration in a solution, for example, in aquariums.
4. How is a hydrometer different from a hygrometer?
Although their names sound similar, these instruments have very different functions. A hydrometer measures the specific gravity or density of liquids. In contrast, a hygrometer is used to measure the amount of water vapour, or humidity, in the air.
5. Why does a hydrometer float higher in a liquid with greater density, like saltwater?
According to Archimedes' principle, the hydrometer floats when the buoyant force acting on it equals its total weight. In a denser liquid (like saltwater), a smaller volume of the liquid needs to be displaced to produce a buoyant force equal to the hydrometer's weight. Therefore, less of the hydrometer submerges, and it floats higher.
6. Can any hydrometer be used for any liquid?
No, hydrometers are often calibrated for specific ranges of density. For instance, an alcoholometer used for spirits has a different scale than a lactometer for milk. Using the wrong type of hydrometer would give inaccurate or meaningless readings as the scale would not be appropriate for the liquid's density range.
7. Why does the measurement on a hydrometer scale have no units?
A hydrometer measures specific gravity, which is a ratio of the density of a substance to the density of a reference substance (water). Since it is a ratio of two identical units (e.g., g/cm³ ÷ g/cm³), the units cancel each other out. This makes specific gravity a dimensionless quantity.
8. Can a hydrometer be used to test antifreeze in a car's cooling system?
Yes, this is a very common and important use. A specific type of hydrometer, often called an antifreeze tester, is used to measure the specific gravity of the coolant. This measurement helps determine the concentration of ethylene glycol in the water, which in turn indicates the freezing point and boiling point of the mixture, ensuring the engine is protected in extreme temperatures.









