




An Introduction to Flowering Plant
You all must have seen flowers, haven’t you? What’s your favourite flower? So, let’s learn something new about flowering plants today. All plants that produce flowers are flowering plants or angiosperms. Angiosperm plants come in a wide range of shapes and sizes, from 40-foot dogwood trees to 8-inch dandelions.
Flowers are beautiful and a normal part of people's lives. However, it can be confusing to know all the different parts of a flower and how they work together. What do you call the different parts of a plant? Do you know what the stamen of a flower is? In this article, we will explore the different parts of the flower diagram and some flowering plants' names.
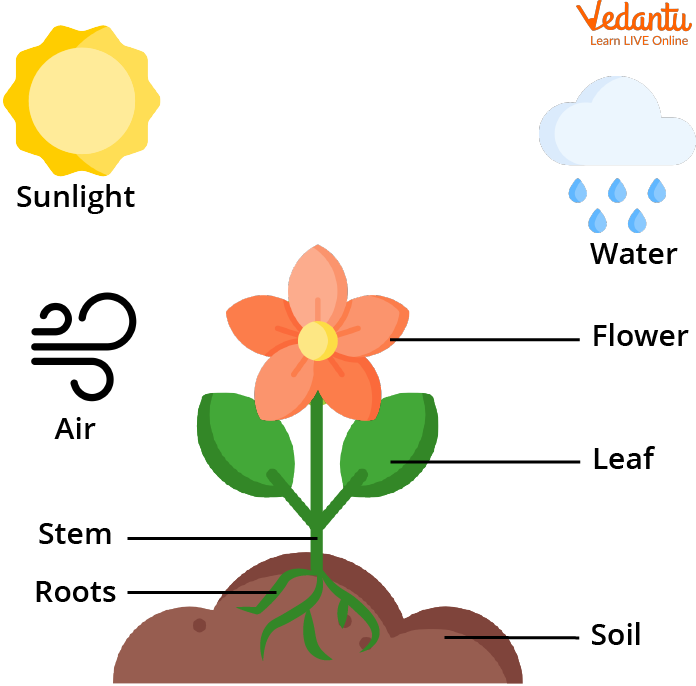
Parts of a Plant And Things That Help it Grow
What is a Flowering Plant?
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits and form the clade Angiospermae, commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words angeion and sperma, and refers to those plants that produce their seeds enclosed within a fruit. Angiosperms have male and female reproductive structures present in a flower. It is a characteristic feature of angiosperms.
Parts of the Flower Diagram
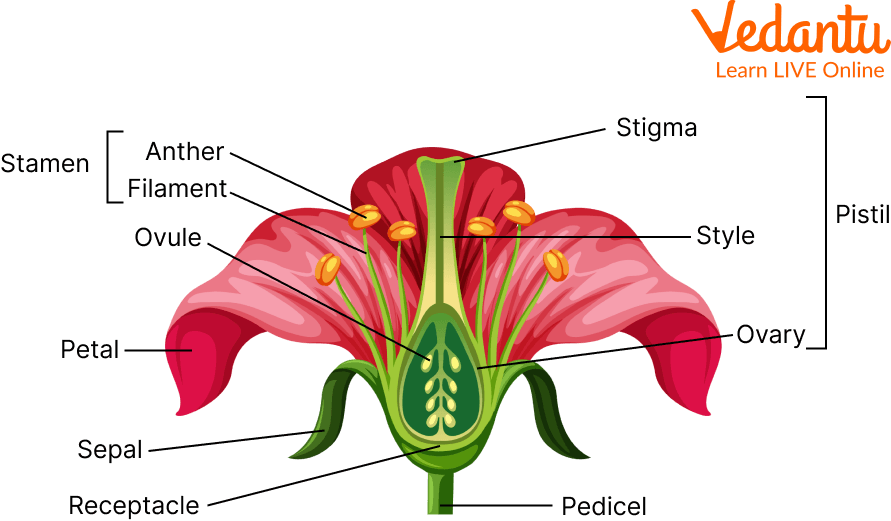
Parts of the Flower
According to the flower definition, the flower is the seed-bearing part of the plant and it contains reproductive organs like the stamen and carpel. Now, let’s move on to the parts of the flower. The four primary elements of most flowers are:
sepals,
petals,
stamens, and
carpels.
The stamen of a flower is the male component of the flower, while the carpels are the female part. The majority of flowers are hermaphrodites, meaning they have both male and female parts. Others may have one of the two parts and be either male or female. An example of the unisexual plant is the Papaya and an example of the bisexual flower is Datura.
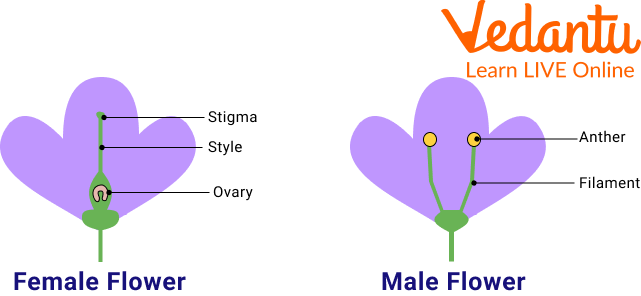
Unisexual Flowers
Peduncle: The flower stem is known as a peduncle.
Receptacle: The flower's receptacle is the section to which the stem is attached. It is small and located in the centre of the flower's base.
Sepals: The tiny, leaf-like components that sprout at the base of the petals. They make up the flower's outermost whorl.
Calyx: The calyx is the grouping of sepals. The calyx and its sepals' primary role is to protect the flower before it blooms (in the bud stage).
Petals: This layer is located just above the sepal layer. They are frequently brightly coloured since their primary function is to attract pollinators such as insects and butterflies to the bloom. The petals are referred to collectively as the corolla.
Stamen of a Flower : Stamens are the male components of flowers. The androecium is the collection of stamens.
They are grouped into two sections structurally
Filament: The long and slender portion that connects the anther to the flower.
Anthers: The stamen's head, responsible for manufacturing pollen that is delivered to the pistil or female portions of the same or another flower to fertilise it.
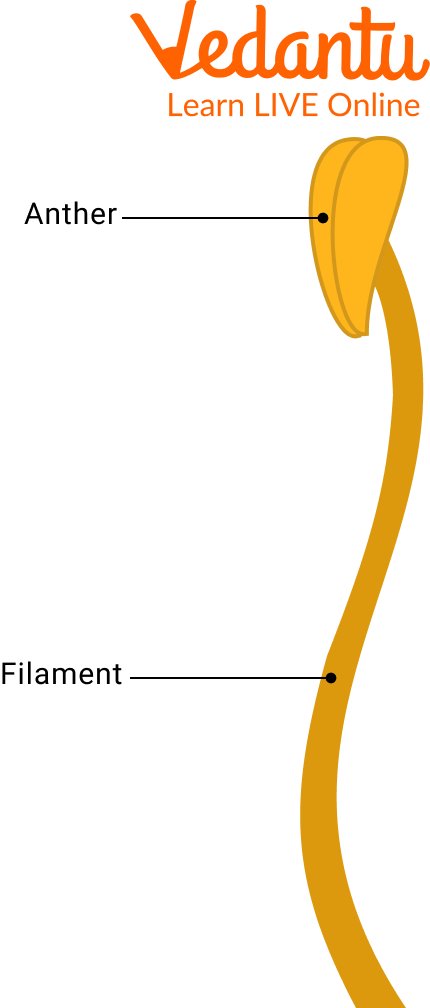
Stamen
Pistils: The female portions of a flower are formed by the pistil. A gynoecium is a group of pistils.

Carpel
Four Parts of the Pistil
Style: The stigma is held by the style, which is a long, slender stalk. When pollen reaches the stigma, the style begins to hollow out and forms a tube called the pollen tube, which transports pollen to the ovaries to allow fertilisation.
Stigma: This is situated at the style's tip. It serves as the pistil's head. The stigma carries a sticky material that attracts pollen grains from various pollinators or those distributed by the wind. They are in charge of starting the fertilisation process.
Ovary: The ovary is the base of the pistil. The ovules are held in the ovary.
Ovules: These are a flower's egg cells. They are kept in the ovary. When suitable pollen reaches the stigma and subsequently reaches the ovary to fuse with the ovules, this fertilised product produces the fruit, and the ovules create the fruit's seeds.
Life Cycle of a Flowering Plant
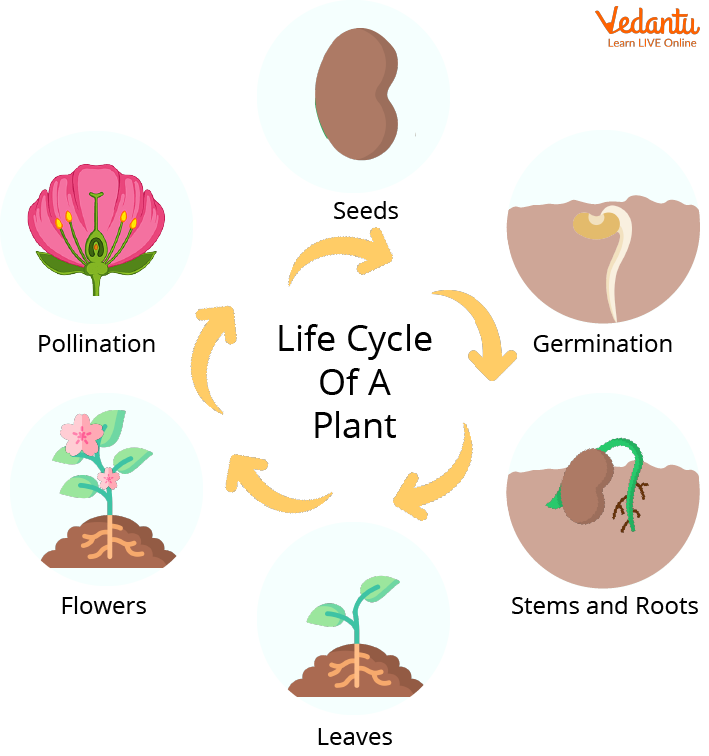
Life cycle of a Plant
In plants, reproduction is handled by the female and male reproductive organs. Now let's get started with the life cycle of flowering plants.
The life cycle of a flowering plant is very specific
Seeds are the beginning of their lives. Plants are born from seeds. In addition to having a hard outer shell, seeds have an embryo inside that is protected by that shell.
As soon as the seed is planted, it germinates. Air, water, and soil are necessary for its growth. Germination is the process by which a seed begins to grow. There are usually some small roots growing at the beginning of the process. As stems grow, they will grow into leaves.
As soon as life begins to appear above soil, it is referred to as a sprout or seedling.
As the seedling grows, it will become a fully mature plant with leaves, roots, and stems.
Plants that have reached maturity will flower. As a result of pollination, seeds will be produced by the flowers. The cycle will begin again once the seeds fall to the ground.
Summary
The part of the flower that blooms is called a flower. Seeds are produced by flowers that give rise to new plants. The main parts of the flower include the sepal, petal, stamen and carpel. The parts of stamen are anther and filament. The parts of the carpel are stigma, style, ovary and ovule.
Flowering plants are those plants that reproduce and produce flowers. They produce seeds inside the fruits. Angiosperm is the scientific name for flowering plants. In this article, we have discussed the flower definitions and flowering plants names.
FAQs on Flowering Plants: A Comprehensive Guide
1. What are the uses of flowers in our daily lives?
Flowers have many important uses beyond their beauty. They are widely used for decoration in homes and for celebrations like weddings. Many cultures use specific flowers for worship and religious ceremonies. Flowers are also given as gifts to express emotions. Furthermore, some flowers like rose and jasmine are used to create perfumes, while others such as saffron and clove are used as valuable spices in cooking.
2. Can you give some examples of common flowering plants?
Yes, there are many thousands of flowering plants. Some of the most common and easily recognisable examples include:
Rose (Gulab): Known for its fragrance and variety of colours.
Sunflower (Surajmukhi): A large flower that turns to face the sun.
Marigold (Genda): Often used in garlands and decorations.
Lotus (Kamal): India's national flower, an aquatic plant.
Jasmine (Chameli): A small, white flower famous for its strong, sweet scent.
Hibiscus (Gudhal): A large, trumpet-shaped flower common in tropical regions.
3. What are the main parts of a typical flower?
A typical flower consists of four main whorls or parts, each with a specific function:
Sepals: These are the green, leaf-like structures at the base of the flower that enclose and protect the developing bud.
Petals: These are the brightly coloured parts that attract pollinators like bees and butterflies.
Stamen: This is the male reproductive part of the flower. It consists of the anther (which produces pollen) and the filament (the stalk).
Pistil (or Carpel): This is the female reproductive part, located in the centre. It includes the stigma (receives pollen), style (connects the stigma to the ovary), and the ovary (contains ovules).
4. What are the key characteristics of flowering plants?
Flowering plants, technically known as angiosperms, are distinguished by a few key characteristics. Their most defining feature is the presence of flowers, which serve as their reproductive organs. After reproduction, they produce seeds that are enclosed within a protective fruit. They also have well-developed vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) for transporting water and nutrients.
5. What is the main difference between flowering and non-flowering plants?
The primary difference lies in their method of reproduction. Flowering plants (like sunflowers and apple trees) use flowers to produce seeds, and these seeds are protected inside a fruit. Non-flowering plants (like ferns, mosses, and pine trees) do not produce flowers. They reproduce using other methods, such as spores (in ferns and mosses) or bare seeds without a fruit (in gymnosperms like pine trees).
6. Why are flowers so colourful and fragrant?
The vibrant colours and sweet scents of flowers are strategic tools for survival and reproduction. Their main purpose is to attract pollinators—animals like bees, butterflies, birds, and bats. These animals are drawn to the flower in search of nectar, a sugary reward. As they feed, they inadvertently transfer pollen from one flower to another, enabling the plant to produce seeds.
7. How does a flower turn into a fruit?
A flower transforms into a fruit through the processes of pollination and fertilisation. First, pollen must be transferred from the male part (stamen) to the female part (pistil) of a flower. Once the pollen lands on the stigma, it grows a tube down to the ovary and fertilises the ovules inside. After fertilisation, the flower's petals wither and fall off as they are no longer needed. The ovary at the base of the pistil then begins to swell and develops into the fruit, while the fertilised ovules inside become the seeds.
8. How are flowering plants classified based on their life cycle?
Based on their life span, flowering plants are generally classified into three groups:
Annuals: These plants complete their entire life cycle, from seed germination to producing new seeds, within one growing season or year (e.g., marigold, wheat).
Biennials: These plants require two years to complete their life cycle. They typically grow foliage in the first year and produce flowers and seeds in the second year (e.g., carrot, cabbage).
Perennials: These plants live for more than two years, often flowering and producing seeds for many seasons (e.g., rose, mango tree).









