




What Are Photocells? Definition, Working Principle & Examples
Photocells is an umbrella term for different types of photoelectric cells which mainly use the light energy or radiation emitted by the sun, absorb it and convert it into electrical energy. Their main work is based on a phenomenon known as photo electric effect, in which a light sensitive material absorbs light energy or photons and emits an electron thus generating electricity. These are used in various electrical devices. We will discuss these photocells, their types, significance, and uses in this article.
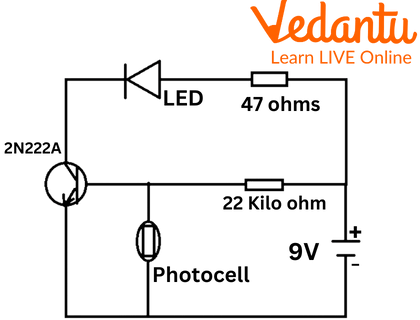
Circuit Diagram of Photocell
Types of Photocell
There are mainly three types of Photocell which are discussed in this section.
The Photoemissive Cell
The term photoemissive means a material which can emit electrons when energy in certain forms like radiation is supplied to the material. When the energy is provided to the material, the electrons in the material get excited and are thus emitted out of their original orbits.
A photoemissive cell is more commonly known as a Phototube. It is based on the photoelectric effect, which is a phenomenon which includes light energy bombarded on any light sensitive material which then emits out electrons.
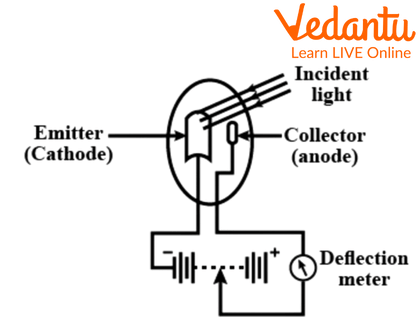
A Photoemissive Cell
The Photovoltaic Cell
A Photovoltaic cell also simply known as a Solar Cell. It is an electronic device which converts the solar energy falling on it into electricity. This is known as the photovoltaic effect which is essentially a physical and chemical phenomenon.
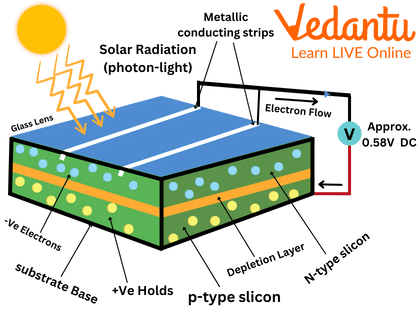
A Photovoltaic Cell
The Photoconductive Cell
It is an electrical device which is light sensitive and works as a resistor. The resistance decreases with an increase in the light intensity.
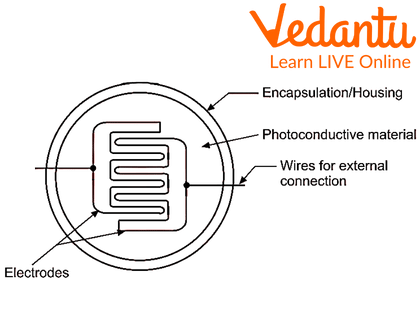
A Photoconductive Cell
What is the Importance of a Photocell?
In this section, we will talk about the significance of photocell. Photocells, nowadays, are being used in a lot of electrical appliances, which makes their use more eco-friendly since all type of photocells are majorly based on the photoelectric effect which takes energy mainly from the Sun, thus producing close to no pollution and even though it involves high initial investment but in later stages, it is very cost-effective.
Uses of Photocell
Some applications of photo electric cells are mentioned below.
They are used in various devices such as:
Sensors
Automatic Lights
Calculators
Lux Metres which is used to detect light intensity.
Switches
Robotics
Burglar Alarms
They are also used in sound reproduction while recording films, etc.
Sample Questions
State whether the statements mentioned below are true or not.
1. Photovoltaic cells and solar cells are the same thing.
Ans: True.
2. Photocells are an eco-friendly option.
Ans: True.
3. Does photocell cause pollution?
Ans: No, photocells do not cause any pollution because they mainly utilise sunlight and convert it into electrical energy.
Complete the following statements by filling in the blanks.
1. There are ______ types of photocells.
Ans: three.
2. Photocells mainly function based on ________
Ans: photoelectric effect.
3. Photoelectric effect most commonly uses _______ energy.
Ans: light
Summary
There are three types of photocells, Photoemissive, Photovoltaic, and Photoconductive. They are mainly based on the photoelectric effect, which is when energy in any form is supplied to a sensitive material, the material emits an electron, the energy can be in the form of light, heat, etc. and the target material will be respective to the form of energy. Photocells are usually used in a lot of electronics. They are eco-friendly and cause no pollution.
FAQs on Overview of Photocells
1. What is a photochemical cell and how does it generate electricity?
A photochemical cell, also known as a photoelectrochemical cell (PEC), is a device that directly converts light energy into electrical energy. It functions using a semiconductor photoelectrode that absorbs photons from a light source. This light energy excites electrons, causing them to move and create an electric current, a process based on the photoelectric effect. This is different from a standard battery, which uses stored chemical energy.
2. What is the working principle of a photochemical cell?
The working of a photochemical cell is based on the interaction of light with a semiconductor material immersed in an electrolyte. The process involves these key steps:
Light Absorption: A semiconductor photoelectrode absorbs photons from sunlight or another light source.
Electron Excitation: If a photon's energy is greater than the semiconductor's band gap, it excites an electron, creating an electron-hole pair.
Charge Separation and Flow: The electron is guided through an external circuit, creating a usable electric current. Simultaneously, the 'hole' participates in a redox reaction with the electrolyte, completing the circuit.
3. What types of materials are used to construct a photochemical cell?
The choice of material is crucial for a photochemical cell's efficiency. Key materials include:
Semiconductor Photoelectrodes: These are the core components that absorb light. Common examples include Silicon (Si), Titanium Dioxide (TiO₂), and Gallium Arsenide (GaAs).
Counter Electrodes: Often made of a stable and conductive material like platinum or carbon.
Electrolyte: A solution that allows ions to move between the electrodes, completing the electrical circuit.
4. How is a photochemical cell different from a standard galvanic cell?
The main difference lies in their source of energy. A galvanic cell (like a common battery) converts stored chemical energy from a spontaneous redox reaction into electrical energy. In contrast, a photochemical cell converts light energy into electrical energy. Its reaction is non-spontaneous and is driven entirely by the absorption of photons, meaning it only produces electricity when exposed to light.
5. What are some important real-world applications of photochemical cells?
Photochemical cells are fundamental to several modern technologies. Their primary applications include:
Solar Panels: The most widespread application, where arrays of photovoltaic cells convert sunlight into electricity for residential and commercial use.
Photoelectrolysis: An advanced application for splitting water (H₂O) into hydrogen and oxygen gas using sunlight, offering a pathway to clean hydrogen fuel.
Light Sensors: Used in devices like automatic street lamps, camera light meters, and motion detectors that respond to changes in light intensity.
6. Why does a photochemical cell only work with light of a certain minimum frequency?
This is due to a principle from quantum mechanics. For a cell to work, incoming photons must have enough energy to excite an electron across the semiconductor's band gap. This minimum required energy corresponds to a specific light frequency, known as the threshold frequency. If the light's frequency is below this threshold, its photons are not energetic enough to create an electron-hole pair, and no electricity will be generated, no matter how bright the light is.
7. Does a photochemical cell require an external power source like electricity to operate?
No, a photochemical cell does not require electricity to operate; its main purpose is to generate electricity. It is a self-contained energy converter. Its only essential external input is light energy. The absorbed light provides the energy needed to drive the internal processes that result in the flow of electric current.









