




Why Is Helium Important? Key Facts Every Student Should Know
Kids, have you heard about the periodic table, which contains all the elements present in nature? Well, one such element is the inert gas Helium. It is an inert gas because helium is highly reluctant to combine with other elements to form compounds.
Helium is also called a noble gas and is the second most abundant gas after hydrogen. Noble gases like helium are also called inert gases because of their completely filled outermost valence shells. Today let us learn all about helium and some interesting facts about helium.
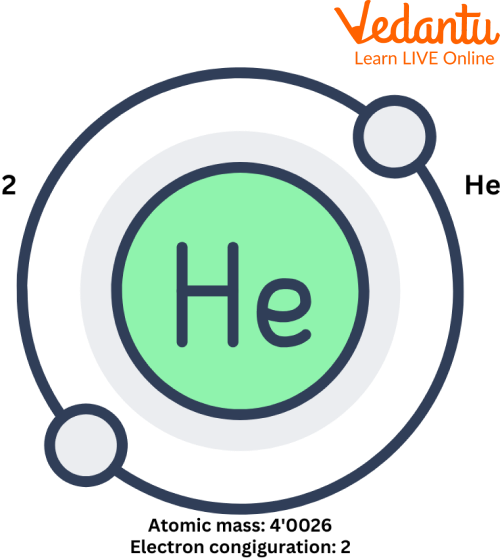
Helium Atom
All About Helium
Children, most of you know helium as the lighter-than-air gas that fills our party balloons. But to your surprise, helium is an irreplaceable element for industries as well as science.
Helium Element
Did you know that Helium is the second most abundant and lightest element in the universe? Second only to hydrogen. It is located on the top of the periodic table at atomic number 2. The atomic number 2 means that it has two protons in its core. Helium is usually found in gaseous form but turns into a liquid below negative 452 degrees Fahrenheit or negative 268 degrees celsius.
Created during the big ban and found in stars, planets, and even our own moon. However, helium is relatively rare on earth. It is formed as a gaseous byproduct of uranium that is decayed over billions of years and is trapped beneath the earth's surface. Helium is harvested from natural gas reserves and can’t be artificially produced. Due to this, helium has become a non-renewable resource on earth.
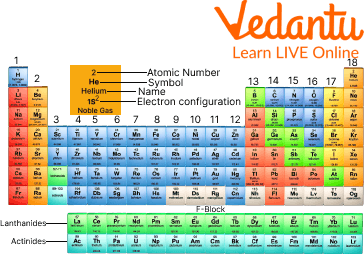
Helium Element on the Periodic Table
Helium Symbol
The official symbol of the helium element is ‘He.’ Helium is a very gas as it does not explode like hydrogen and does not corrode like oxygen. The slow decay of radioactive material produces helium in the earth's crust, and when it reaches the surface because it is lighter than air, it just floats up out of the atmosphere. But some of it gets trapped underground and is captured along with natural gas.

A Beaker Containing Helium
Properties of Helium
Let's know about some properties of helium:
Helium is odourless, colourless, tasteless, and non-toxic.
Helium is the first element in the noble gas group which is group 18 in the periodic table.
The boiling and melting point of helium is the lowest among all the elements in the periodic element. Helium has a slight weight.
The symbol of helium is He, and this inert gas's atomic mass is around 4u, and its atomic number is 2. It contains two electrons per shell.
10 Uses of Helium
There are many uses for helium. And some of the important uses are as below:
Due to the lightweight nature of helium, it is used to fill balloons at parties and events.
If taken in liquid form, helium acts as a cryogenic agent. It helps all the reactions at colder temperatures due to its cryogenic properties.
The solubility of helium in the blood is very low. Due to this special property, helium is used in artificial respiration.
The mixture of helium and oxygen is useful in the treatment of asthma, emphysema, and other respiratory disorders.
Helium is used to create an inert atmosphere while welding magnesium and aluminium.
Helium is responsible for the transferring of heat inside the gas-cooled atomic reactors hence is used as a heat transfer agent inside these reactors.
Helium gas is also used in filling aeroplane tires due to its lightweight and non-reacting nature.
Helium is used extensively in the medical, manufacturing, space, and defence industries due to its extraordinary chemical and physical properties.
Helium is used in medical applications like superconducting magnets in magnetic resonance imaging or MRI scanners in hospitals.
Helium plays a significant role in manufacturing fibre optic wire, semiconductors, and LCD panels. It cools parts and components quickly and controls the heat transfer rate to reduce defects and improve productivity. It functions as a carrier gas in the production process.
Interesting Facts About Helium
As we learned, Helium is a very interesting gas. Let us all look at some interesting facts about Helium:
Helium was discovered by scientists in the sun's atmosphere before it was found on earth. Helium is named after the Greek god of the sun ‘Helius.’
The oxygen tanks the divers take with them under the ocean are a mixture of 80% helium and 20% oxygen. This helps in creating an artificial atmosphere for divers under the water.
The United States of America eats up about half of the world's helium supply. More than 25% of helium in the United States is used in MRI machines.
An isotope of helium, Helium-3, is effectively used to detect radiation coming out of potentially dangerous nuclear materials.
Helium is also one of the major gases in the atmospheres of giant gas planets such as Jupiter and Saturn, which are made up of clouds of hydrogen and helium.
Summary
When we think of the second element of the periodic table, helium is what comes to our mind. Helium is the gas that makes balloons rise, but beyond that, helium has some extremely important uses in Science. In the above article, we read about helium gas, its properties of helium uses of helium and some interesting facts about helium.
We got to know that helium is the second, which we have discussed in the above article. Even though it is considered to be the most abundant gas in the universe, it is a non-renewable resource on earth. It does not react with other elements as is an inert gas.
FAQs on Helium Facts: Properties, Uses, and Surprising Insights
1. What is helium, and what are its key characteristics?
Helium (symbol He, atomic number 2) is the second lightest element in the universe. It is a noble gas, meaning it is part of a group of elements with very low chemical reactivity. Key characteristics include being colourless, odourless, tasteless, non-toxic, and significantly lighter than air.
2. Is helium classified as a metal or a non-metal?
Helium is a non-metal. It belongs to Group 18 of the periodic table, known as the noble gases. Its classification as a non-metal is due to its properties, including its gaseous state at room temperature and its inability to conduct electricity.
3. What makes helium's physical properties unique compared to all other elements?
Helium holds the distinction of having the lowest melting and boiling points of any known substance. It is the only element that cannot be solidified by cooling at normal atmospheric pressure; immense pressure must be applied. This is due to exceptionally weak forces between its atoms, a quantum mechanical effect.
4. What are some of the most important physical and chemical properties of helium?
The properties of helium make it useful for many applications. Key properties include:
- Low Density: It is much less dense than air, which gives it lifting power.
- Chemical Inertness: It has a full valence electron shell, making it extremely unreactive and non-flammable.
- High Thermal Conductivity: It transfers heat very effectively.
- Low Boiling Point: It exists as a liquid only at extremely low temperatures, making it an excellent coolant for cryogenics.
5. Why is helium considered a chemically inert or noble gas?
Helium is chemically inert because its outermost electron shell is completely full, containing two electrons (a configuration known as a duplet). This stable arrangement means helium has no tendency to lose, gain, or share electrons to form chemical bonds with other elements, making it highly unreactive under normal conditions.
6. What are some common real-world applications of helium gas?
Due to its unique properties, helium has several important applications, such as:
- Lifting Gas: For party balloons, weather balloons, and airships because it is light and non-flammable.
- Cryogenics: Liquid helium is used as a super coolant for MRI magnets and in scientific research.
- Welding: It provides an inert protective atmosphere during arc welding.
- Deep-Sea Diving: Mixed with oxygen to create a breathing gas (Heliox) that prevents nitrogen narcosis in deep-sea divers.
7. Why is helium used in balloons instead of hydrogen, which is even lighter?
Although hydrogen is lighter and provides more lift, it is highly flammable and explosive when mixed with air. Helium, being a noble gas, is completely inert and does not burn. This inherent safety makes it the preferred choice for all lifting applications where flammability is a risk, such as in party balloons and public airships.
8. How was helium first discovered, and how did it get its name?
Helium was discovered not on Earth, but in the sun. In 1868, French astronomer Pierre Janssen and English astronomer Norman Lockyer independently observed a new yellow line in the sun's spectral data during a solar eclipse. Lockyer concluded it was a new element and named it 'helium' after Helios, the Greek god of the sun.
9. Why is there a global concern about a potential helium shortage?
Helium is a non-renewable resource. On Earth, it is primarily formed by the slow radioactive decay of elements like uranium and thorium deep underground and is extracted from natural gas deposits. Once helium is released into the atmosphere, it is so light that it escapes Earth's gravity and is lost to space forever. Since we are consuming our limited reserves much faster than they are naturally replenished, there is a serious concern about future availability.









