




How Do These Human Body Facts Help You Learn Science in a Fun Way?
Humans are pretty awesome creatures. We are the only creatures with the 6th sense of self-awareness. We are capable of things no other species on this planet can possibly do. Understanding our complex body organisation and functions helps one appreciate the true beauty of nature itself. This article is to give you some unbelievably awesome and weird facts about this natural machinery of awesomeness. Let’s jump right in!

A Child Handling a Laptop
Let’s look into some amazing facts about our body in the following order, system-wise:
Brain, Spinal Cord, and Nerves
Special Senses (Comprises of eye, nose, ear, tongue)
Heart and Lungs
Stomach, Intestines, and Digestive Tract
Skin, Hair, and Nails
Blood, Blood Vessels, and Lymphatics
Brain, Spinal Cord, and Nerves
Also known as the central nervous system, this system fascinates us big time. The fact that you’re able to sense and realise your environment in a matter of milliseconds is a rather extraordinary phenomenon. Let’s look into some of the amazing facts!
The brain suspends in a special fluid known as the cerebrospinal fluid which produces a floating effect due to which we don't feel the complete weight of the brain on our neck. This special fluid also prevents the brain from shock and infections (what a magical fluid indeed!).
The spinal cord is capable of a phenomenon known as “reflex” where the information does not reach the brain. Reflex occurs during emergency situations when the sensation and response come from the spinal cord (the next time you withdraw your hand from a very hot object without hurting yourself, you must thank the reflex action of the spinal cord).
Nerves are made of super cool cells (neurons) that are capable of transmitting and receiving electrical impulses (little flow of electricity) due to which the brain is capable of its function.
Brain, Spinal Cord, and Nerve Cells
Special Senses
We would not be able to appreciate the beauty of existence without special senses. Our vision, hearing, taste, or smell without these important little organs.
The eyes have special muscles called the iris, which control the amount of light entering the eye. Iris contracts and relaxes during dark and light environments respectively so the retina (a light-sensitive part present in the eye) is protected from damage
The smallest bone in your body is placed in your ear, known as ‘Stapes’ it is around 3 mm in length.
The tongue has unique tongue prints just like fingerprints. Every human being possibly has a unique tongue print.
Special Senses
Heart and Lungs
There’s a special type of electrical impulse that is generated in your heart which helps in the pumping action of the heart by producing a contracting action.
The heart is responsible for pumping blood to every part of the body except the cornea of the eye
Surviving with one lung is possible in place of the normal 2 lungs. Thus, in case of lung disease and removal of a lung, the person can survive with just one lung.
Stomach, Intestines, and Digestive Tract
A person who has had a gastrectomy (complete removal of the stomach) can survive with smaller and frequent meals. These individuals have their oesophagus connected to their small intestine.
Your intestines have a huge surface area that, if laid out flat, could cover two tennis courts. (Do you know how big is one tennis court?)
As mentioned earlier, one can live without a stomach but not without intestines as they are the ‘sole point of food and water absorption’.
Stomach and Intestines
Skin, Hair, and Nails
The dust you see around the house might actually be dead skin cells (we shed a lot of dead skin on a daily basis).
Hair is the second fastest growing tissue in our body after the bone marrow.
‘Onychophagia’ is the proper medical name given to the biting of nails.

Skin, Hair, and Nails
Blood, Blood Vessels, and Lymphatics
A newborn baby is found to have only 1 cup of blood in circulation (around 240 mL).
Your blood vessels are super long (around 60,000 miles in length) and could cover the globe a little more than twice if laid out flat end to end.
The lymphatic system is an important circulatory system present in our body by circulating lymph (a clear tissue fluid). It is so widely spread that cancer cells often spread through this pathway.
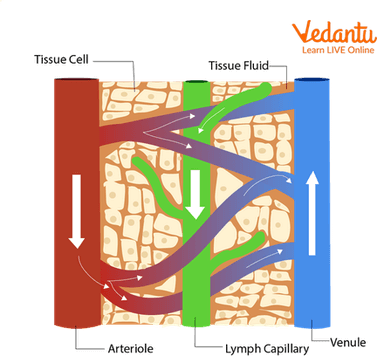
Blood Vessels and Lymph Vessels
Summary
Let’s quickly summarise what we’ve discussed up until now.
Your body has various structures put together in the form of organ systems like the Nervous system (Brain, Spinal Cord, and nerves), Cardiovascular system (Heart, blood, and blood vessels), Lymphatic system (Lymphatic vessels, lymph, and lymph nodes), Digestive System (Stomach, intestines, and digestive tract), Respiratory system (Lungs and blood vessels), Integumentary system (skin, hair, and nails) so on and so forth.
These systems work together in fascinating ways to ensure the healthy functioning of the body.
FAQs on Fascinating Facts About the Human Body Every Student Should Know
1. What are our five main senses and which organs are responsible for them?
The human body has five special senses that help us understand the world around us. Each sense is linked to a specific organ: the eyes for sight, the ears for hearing, the nose for smell, the tongue for taste, and the skin for touch.
2. What are some fun and surprising facts about human organs?
Our organs are full of surprises! Here are a few fun facts:
- The human brain doesn't have pain receptors, so it can't feel pain.
- Your heart beats over 100,000 times every single day.
- The liver is the only organ that can completely regrow itself from as little as 25% of its original mass.
- An adult's stomach can stretch to hold about 1.5 litres of food.
3. Why doesn't it hurt when you get a haircut or trim your nails?
It doesn't hurt to cut your hair or nails because the parts you trim are made of dead cells. These cells contain a protein called keratin but have no nerves or blood vessels. The living part of your hair and nails is under the skin (the hair follicle and nail bed), which is why it hurts if you pull a hair out from the root!
4. What is an organ system and what are some important examples?
An organ system is a group of organs that work together to perform a major function in the body. For example, the digestive system (including the stomach and intestines) breaks down food, while the respiratory system (including the lungs) helps us breathe. Other key systems are the circulatory, nervous, and skeletal systems.
5. How is the human skeleton both strong and lightweight at the same time?
The human skeleton's clever design makes it both strong and light. The outer layer of bone is dense and hard, providing strength. However, the inside has a honeycomb-like structure called trabecular bone, which is much lighter but still incredibly strong. This combination provides support for our body without making us too heavy to move.
6. If the brain controls everything, why can't we feel pain in the brain itself?
This is a fascinating fact! While the brain is the control centre that processes pain signals from all over the body, the brain tissue itself lacks the specific nerve endings called nociceptors that detect pain. This is why surgeons can perform brain surgery on patients who are awake without causing them any pain in the brain.
7. What are some of the most mind-blowing facts about the human body?
The human body is truly amazing. Here are a few mind-blowing facts:
- Your body contains enough iron to make a 3-inch nail.
- If you stretched out all the blood vessels from an adult, they would circle the Earth about four times.
- The acid in your stomach is strong enough to dissolve razor blades.
- Humans are the only animals known to blush.
- Every minute, you shed over 30,000 dead skin cells.
8. How does our body digest different types of food?
Our body's digestive system is like a smart factory. Digestion starts in the mouth with saliva. In the stomach, strong acids and enzymes break down proteins. The small intestine does most of the work, using different enzymes to break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins into small molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream for energy and growth.









