




How Does Force Affect Objects? Explore with Real-Life Examples
Hey kids, today we are going to shed light on a very significant concept that we apply and use in daily life but fail in paying attention to it. Let’s try to understand this with an example. For example, When you push your refrigerator in a specific direction, you use a great amount of energy and power in doing so. There’s a term for this action, and it is known as Force. On that note, let’s go further and try to understand and study what is force for kids - the meaning, types of forces for kids, uses of forces and much more.
What is Force for Kids?
In simplified terms, the force can be defined as a pull or a push we exert on an object or a person to complete a certain task. A force is said to have occurred when two different objects come in direct contact and one object has impacted the other object. When both the objects expand or move away, the force stops too.
Force is always taking place around us even when we are pushing a table for better adjustment. Look at the picture below to understand the concept effectively.
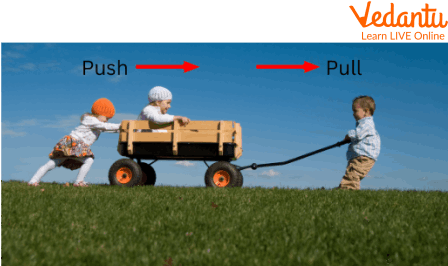
A Visual of Applied Force
Types of Forces for Kids
Now that we have studied force, let’s jump on its types. Force is divided into two major types: Contact forces and Field forces.
Contact Forces - This occurs when two objects touch or connect. It can also be applied differently. For example, contact forces occur when a person is pulling a wagon, kicking a football and dropping the ball.
Field Forces - This occurs when two objects contract or interact without being in contact with each other. This type of force can create a push or pull effect even from a distance. Gravity and Magnetism are field forces. Field force examples - The gravitational force pulls the apple towards the ground when it is falling from a tree. Similarly, a magnet placed near paper clips attracts the clips because of magnetic force.
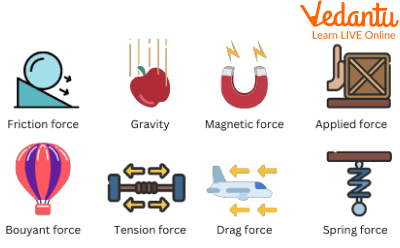
Types of Forces
Uses of Forces and Measurement Aspect - How are Forces Measured?
Uses:
Force can cause movement.
Change the shape of an object and accelerate or fluctuate the speed of an object.
It is useful as it can give us an approximate idea of the amount of intensity or effort while applying force.
Measurement: Newton is a unit used by scientists around the world to measure and evaluate force. This unit measures the force required to accelerate, fluctuate or speed up objects. Pound force is a unit also used to measure force.
Laws of Motion Associated with Force
A renowned English Scientist, Issac Newton discovered and developed a theory revolving three laws of motion and force. Let’s study these three basic Laws as they are mentioned below as follows:
1st Law - The First Law of motion states that the motion of an object is unchangeable until it is pushed or pulled by a force.
2nd Law - It states that when force is applied to an object, it would make the object accelerate and speed up in the same direction as the force is moving.
3rd Law - When a particular force is applied to an object, known as action, the object will exert an equal and opposite force, known as a reaction.
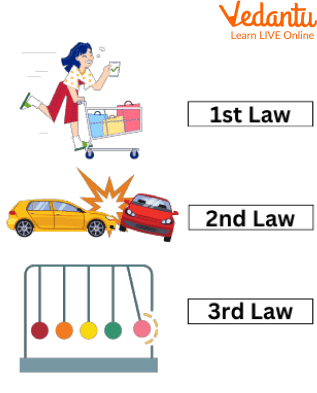
Laws of Motion by Newton
Summary
From the article What is force for kids, we have learnt various aspects revolving around the force. We learnt about force, which is a push or a pull we apply on an object. Then we learnt about two types of forces - Contact and Field force with appropriate examples. We have covered the major uses of force and how it is beneficial in our daily lives. We discovered that Force is measured by Newton. Lastly, we studied the three major laws of motion proposed by Issac Newton which was a significant contribution to Physics as a discipline. We hope you enjoyed reading this article, in case of any other doubts feel free to ask in the comments.
FAQs on Forces Made Easy for Kids: Definitions, Examples & Practice
1. What is force in simple words for kids?
In the simplest terms, a force is just a push or a pull on an object. You use force all day long! For example, when you kick a football, you are pushing it. When you pull a toy wagon, you are using a pulling force. Force is what makes things move, stop, or change direction.
2. What are the different things a force can do?
Applying a force can cause several changes to an object. The main effects of force are:
It can make a stationary object move (like pushing a swing).
It can stop a moving object (like catching a cricket ball).
It can change the direction of a moving object (like a badminton racket hitting a shuttlecock).
It can change the shape of an object (like squeezing a lemon or a sponge).
3. What are the main types of forces?
Forces are mainly divided into two types based on whether the objects need to touch each other. These are Contact Forces (which require touching) and Non-Contact Forces (which can act from a distance). Examples include friction (contact) and gravity (non-contact).
4. What is an example of a contact force?
A great example of a contact force is frictional force, or friction. This is the force that slows things down when they rub against another surface. For instance, when you roll a toy car on a carpet, the friction between the wheels and the carpet makes it stop. This force only works when the two surfaces are in contact.
5. How can a magnet pull an iron pin without even touching it?
This happens because of a non-contact force called magnetic force. A magnet creates an invisible force field around itself. When an object like an iron pin comes close enough, this field pulls the pin towards the magnet without any physical contact. This is why magnets are a perfect example of forces that can act from a distance.
6. Why does a ball thrown up in the air always come back down?
A ball always comes back down because of Earth's gravitational force, or gravity. Gravity is a powerful non-contact force that pulls every object towards the centre of the Earth. It's the same force that keeps you on the ground and prevents you from floating away into space. No matter how high you throw the ball, gravity will pull it back down.
7. If I push a big wall and it doesn't move, does that mean I'm not using any force?
No, you are definitely applying a force! The wall doesn't move because it is also pushing back on you with an equal amount of force in the opposite direction. When two forces are equal and opposite like this, they are called balanced forces. Balanced forces cancel each other out, so there is no change in the object's motion. An object only starts to move when the force is unbalanced, meaning one force is stronger than the other.









