




Key Human Body Systems Explained for Young Learners
We all only get one body, and we must keep it healthy if we are going to have long and happy lives. The human body is a complex system of cells, tissues, organs and organ systems that work together to support life. The human body is composed of numerous parts. Human anatomy is the study of these parts. Each part of the body serves a certain purpose or performs a specific function.
One of the most essential things to understand about the body is that it's made up of many different organs and parts. Every parent must introduce a few concepts of the human body to preschoolers, to develop interest. In this article, we'll go over some of the basic parts of the human body according to science.
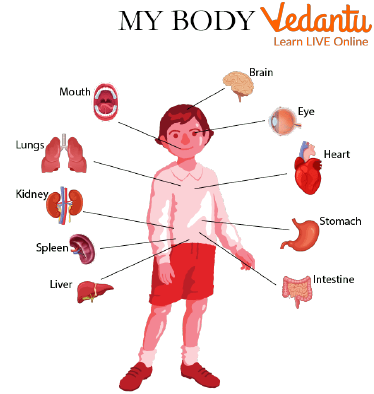
Human Anatomy for kids
Human Anatomy for Kids
Each system in the biology of a human body has a specific purpose. Your skeletal system provides support and structure to your body, allowing you to stand. By fighting off diseases, your immune system keeps you healthy. Each of these systems interacts with the others. For example, your skeletal system's bones would be useless without the muscular system to help them move.
Organ Systems in the Human Body
Given below are the various organ systems in the human body.
The Musco-skeletal System
Bones and muscles are found throughout the body. In addition to walking and running, the human body can crawl, jump, and climb. The number of bones in a human body for kids can reach 300 at birth. Age, however, leads to the fusion of bones. Adults have 206 bones in total. Locomotion is assisted by muscles, which are specialised tissues. Contraction and relaxation of muscles in that region cause limbs to move. In addition to joints, muscles are what allow bones to bend and stretch.
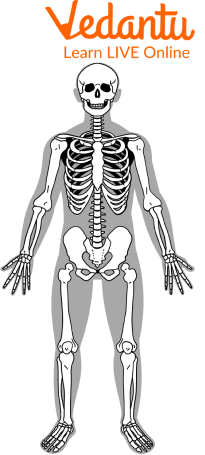
The Musco-skeletal System
The Circulatory System
Your circulatory system is made up of your heart and blood arteries. The heart's function is to circulate blood throughout your body. The left side of the heart transports oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to various regions of the body. The right side of the heart circulates blood to the lungs, where it is oxygenated.
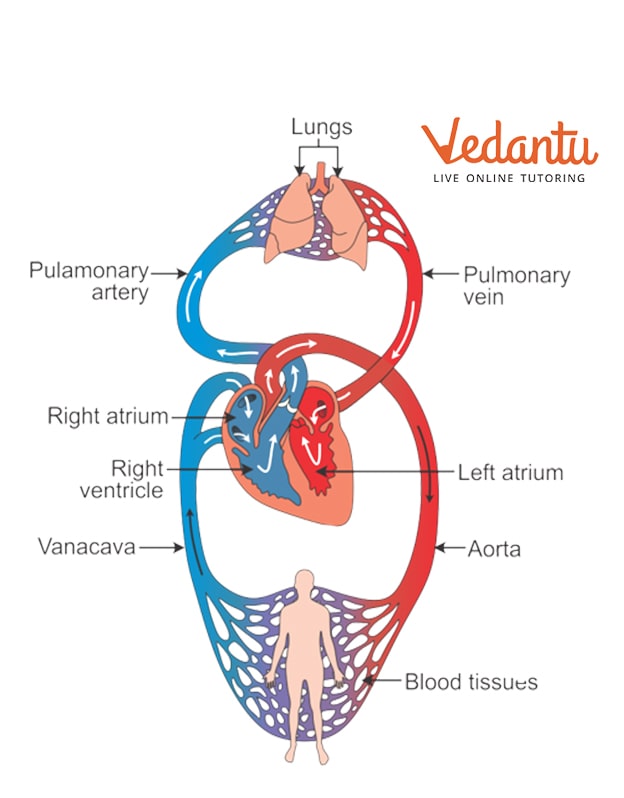
The Circulatory System
The Nervous System
The body has a long and complex path of nerves in the arm, neck, and brain. The nerves relay information to your brain so that you can process it and react. The human nervous system is made up of two parts-the central nervous systems (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Coordination and control in body systems are regulated by the nervous system. It helps us to respond to stimuli/information received from the outside and react to it. For example, whenever we touch any hot object, we immediately pull our hands away from it because our nervous system informs us that the object is hot and harmful to us.
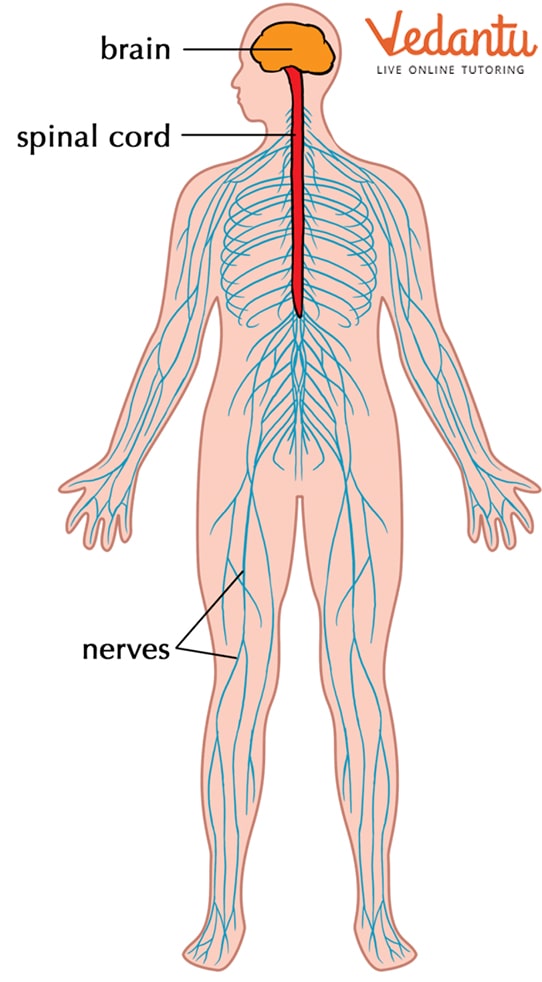
The Human Nervous System
The Respiratory System
The lungs are the most important part of the respiratory system. The lung's purpose is to move air into and out of the body. Oxygen from the air you breathe enters the bloodstream via small blood vessels. It then attaches itself to red blood cells and travels throughout the body. Carbon dioxide is present in the blood and is also removed by the lungs. When you exhale, you are removing carbon dioxide from your body that it no longer requires.
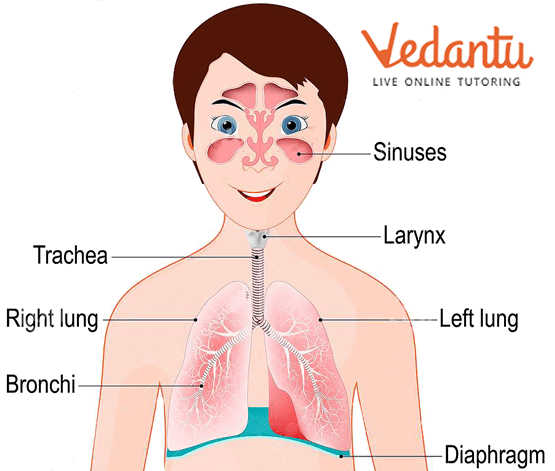
The Respiratory System
The Digestive System
Digestion begins when we break food down into small pieces in our mouth using our teeth, tongue, and saliva. Food then passes via the oesophagus and into the stomach, where stomach acids further break it down. It travels from the stomach to the small intestine. Here, your body extracts nutrients from food and transports them to different body parts via the circulatory system. Finally, the digested food is sent to the large intestine, where it exits your body and beyond.
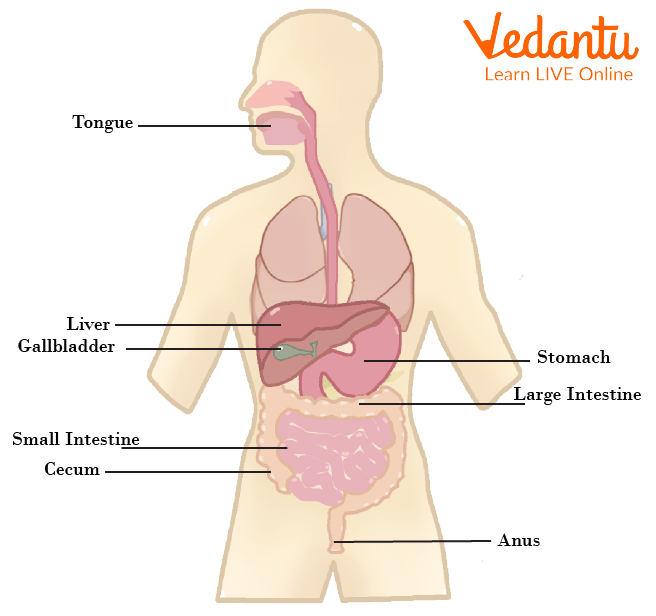
The Digestive System
The Excretory System
The excretory system is a group of organs that have to do with getting rid of the waste products from our bodies, such as urine, faeces, and sweat. The waste excreted by each organ is different. Faeces are mainly made up of bacteria, dead cells, hormones, mucus (snot), water, and weight-bearing chemicals. Urine contains urea and chloride
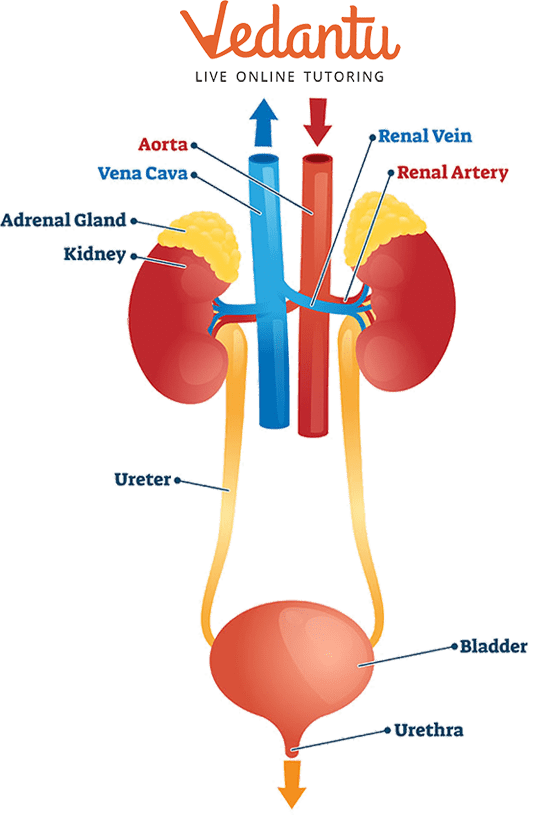
The Excretory System
The Reproductive System
The reproductive system of a human is made up of organs that include: the ovaries, fallopian tubes, testes, prostate gland and some other organs. The birth canal leads into the vaginal canal which in turn leads into the vulva where external genitals can be found as well as an opening to the cervix.
Interesting Facts for Kids
The following are some of the human body facts for kids:
Nearly 37 trillion cells make up the body system.
Approximately 39 trillion cells make up the microbial biome of our bodies, including bacteria and fungi.
Every day, the average body system breathes 22,000 times.
An average kidney filters out about 2 quarts of waste and water every day based on 200 quarts of blood (50 gallons).
The organs and body systems of kids develop up to 80% within three years of age.
Summary
From the article human body for kids, we have now understood that the body is a highly complex machine. There are many different organ systems in the body, each one with its distinct purpose. The major organ systems in the human body include the musculoskeletal system, circulatory system, nervous system, respiratory system, digestive system, excretory system and reproductive system.
The organ systems of the human body work together to keep humans alive and healthy. Like the respiratory system helps us to breathe, the digestive system helps in the digestion of food and the excretory system helps in the removal of waste products. We hope that you have enjoyed learning some facts about the human body with us. Approximately 100 billion nerve cells are found in the human brain.
FAQs on Fascinating Human Body Facts Every Kid Should Know
1. What is the most important organ in the human body and why?
The brain is often considered the most important organ. It acts as the body's control centre, managing thoughts, memory, speech, and movement. It also controls the function of many other organs, including the heart and lungs, making it essential for survival.
2. What is the main job of the heart?
The main job of the heart is to pump blood throughout the body. This is a vital function because blood carries oxygen and nutrients to all our cells, and it carries away waste products like carbon dioxide. Without the heart's constant pumping, our body wouldn't get the fuel it needs to work.
3. How many bones are in an adult's body compared to a baby's?
An adult human has 206 bones. Interestingly, a baby is born with around 300 bones. As the baby grows, some of these smaller bones, which are made of soft cartilage, fuse together to form the stronger, larger bones of the adult skeleton.
4. Why do our bodies need lungs?
Our bodies need lungs to perform the essential task of breathing. When we breathe in, our lungs take in oxygen from the air, which our body needs to create energy. When we breathe out, the lungs help us get rid of a waste gas called carbon dioxide. This process is called gas exchange.
5. What is the difference between the largest bone and the smallest bone in the human body?
The difference highlights the amazing variety in our skeletal system.
- The largest bone is the femur, or thigh bone. It is incredibly strong and supports our body weight for activities like walking and running.
- The smallest bone is the stapes, located in the middle ear. It is only about 3x2.5 millimetres and plays a crucial role in transmitting sound vibrations, allowing us to hear.
6. How does our stomach help us get energy from food?
The stomach acts like a mixer, churning food with powerful digestive juices and acids. This process breaks down complex food particles into a simpler, liquid-like substance. From there, the nutrients can be absorbed by the intestines and converted into the energy our body needs to function, play, and grow.
7. Why is it important for kids to learn about the human body?
Learning about the human body is important because it helps kids understand how to stay healthy. Knowing what different organs do, like the heart and lungs, explains the importance of exercise and a balanced diet. It also fosters curiosity and a deeper appreciation for how their own bodies work every day.









