




What Is Energy? Definitions, Types & Everyday Applications
Has your mom ever told you you need to eat the right foods for energy? So why does she do that? This is because every task that needs to be done requires energy. To pick up a book, you need energy; to walk, you need energy; to climb stairs, you need energy. Otherwise, you won't be able to do so. All of these tasks are work, and all work requires energy to complete. So, let's learn about energy and some fascinating facts.
What is Energy?
Before going further into the types and facts related to energy, let us understand the scientific definition of energy. Energy can be defined as the ability to do work. As discussed above, everything that does any work needs the energy to do that work. But where do you get this energy from? Human beings get their energy from food. Similarly, machines get the energy to do work from fossil fuels like petrol, diesel, etc.
What is energy
Measurement Of Energy
Everything in this universe has a unit of measurement. Therefore, energy is also measured in units. In the international measurement system, energy is measured in joules or J. However, energy is also measured in kilowatt-hours, or kWh. This unit is usually used when calculating the electricity used in our homes.
Types of Energy
Energy is used whenever any work is done. Hence, there are many types of energy. However, the most beautiful aspect of energy is that it can be converted from one form to another. For example, the microphone converts electrical energy into sound energy, the bulb converts electrical energy into light, which is also a form of energy, the batteries convert chemical energy into electrical energy, and so on. Therefore, let us discuss these types of energy in detail.
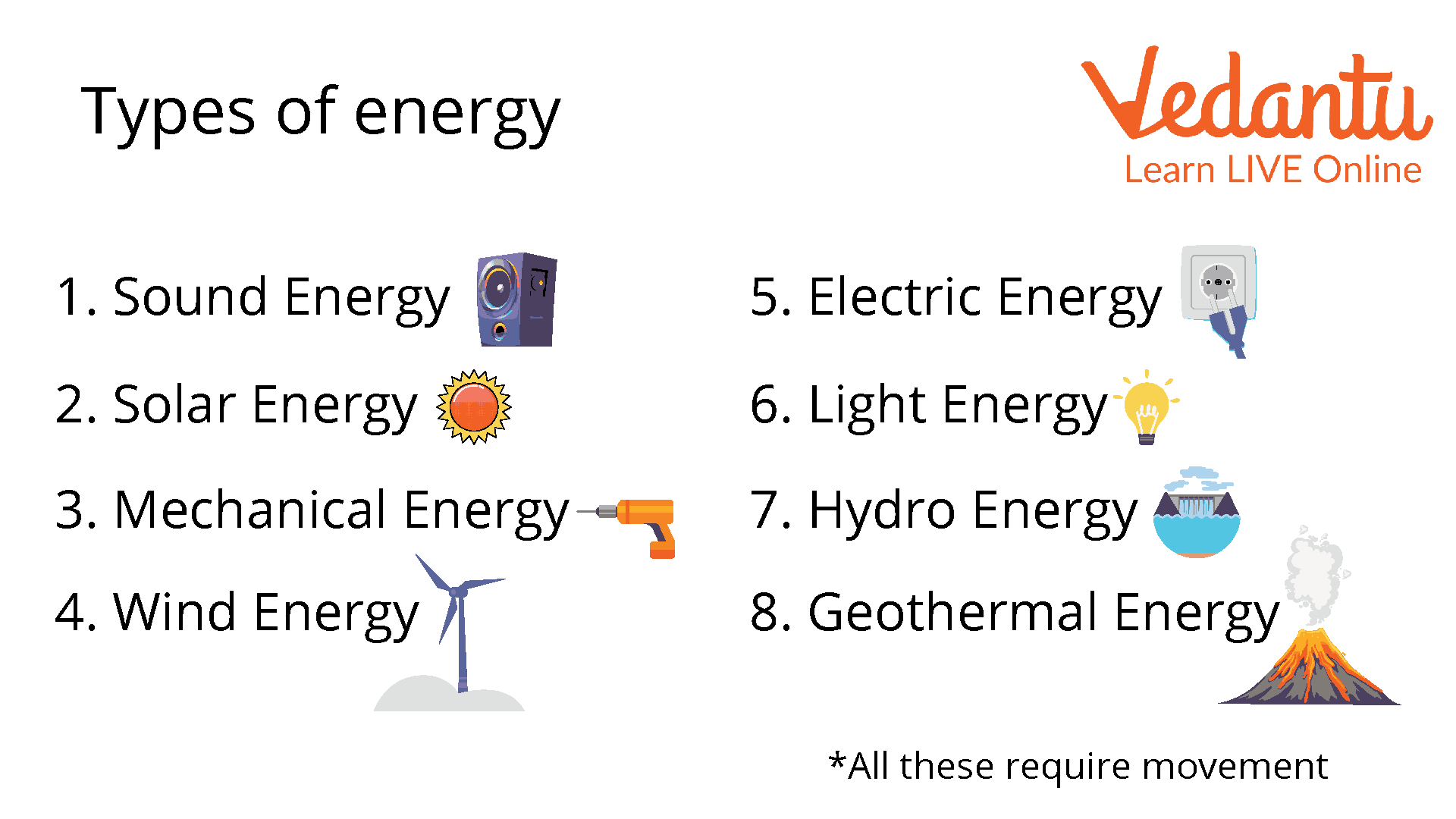
Types of Energy
Electrical Energy
Electrical energy is the most commonly used energy today. We use it every day and everywhere. You must have used your mobile phone or energy to switch on the TV. Electrical energy is obtained from various sources.
Low-intensity electrical energy is generated from batteries, while high-intensity electrical energy is obtained from hydroelectric dams. You may be surprised to know that flowing water can also be used to generate electricity, called hydroelectricity. You will learn about hydroelectricity in higher classes.
Chemical Energy
Chemical energy is energy that comes from various chemical reactions. This kind of energy is stored in specific molecules and releases energy only upon any chemical reaction. For example, the electrical energy we get from batteries results from the chemical reaction in batteries. Another example of chemical energy is the petroleum used to move vehicles.
Light Energy
Light energy is the type of energy that helps us see things. The sources of light energy are the sun, the electric bulbs used in our houses, lamps, etc. You will learn about the details of light production in the higher classes.
Heat Energy
You may have encountered heat energy in various forms, such as a warm glass of milk or hot parathas, which your mom may have served you. Have you ever wondered how these items become so warm or hot? They are hot because of the heat energy used to cook the food items. The heat energy comes from burning the gas in gas cylinders or electric induction heaters.
Kinetic Energy
The word “kinetic” means motion. Therefore, the energy of motion is known as kinetic energy. Therefore, when you run or walk, you are said to have kinetic energy. Similarly, any moving body is said to possess kinetic energy.
Potential Energy
Potential energy is also called stored energy. Have you ever heard your teacher say that a specific student has potential? What they mean by this is that the child has the capacity or ability to perform a particular task. Examples of potential energy include the energy stored in a spring when you compress it, objects placed at a height ready to fall under the force of gravity, etc.
Nuclear Energy
Nuclear energy is the energy released during nuclear fusion or fission. A huge amount of energy is released during these nuclear processes. Many nuclear plants derive energy from these nuclear processes in a very controlled manner. This is because these reactions are very explosive, and many things are taken care of while conducting them.
Renewable and Non-Renewable Energy
Although we learnt about many forms of energy, these forms can be classified into two types: renewable and non-renewable.
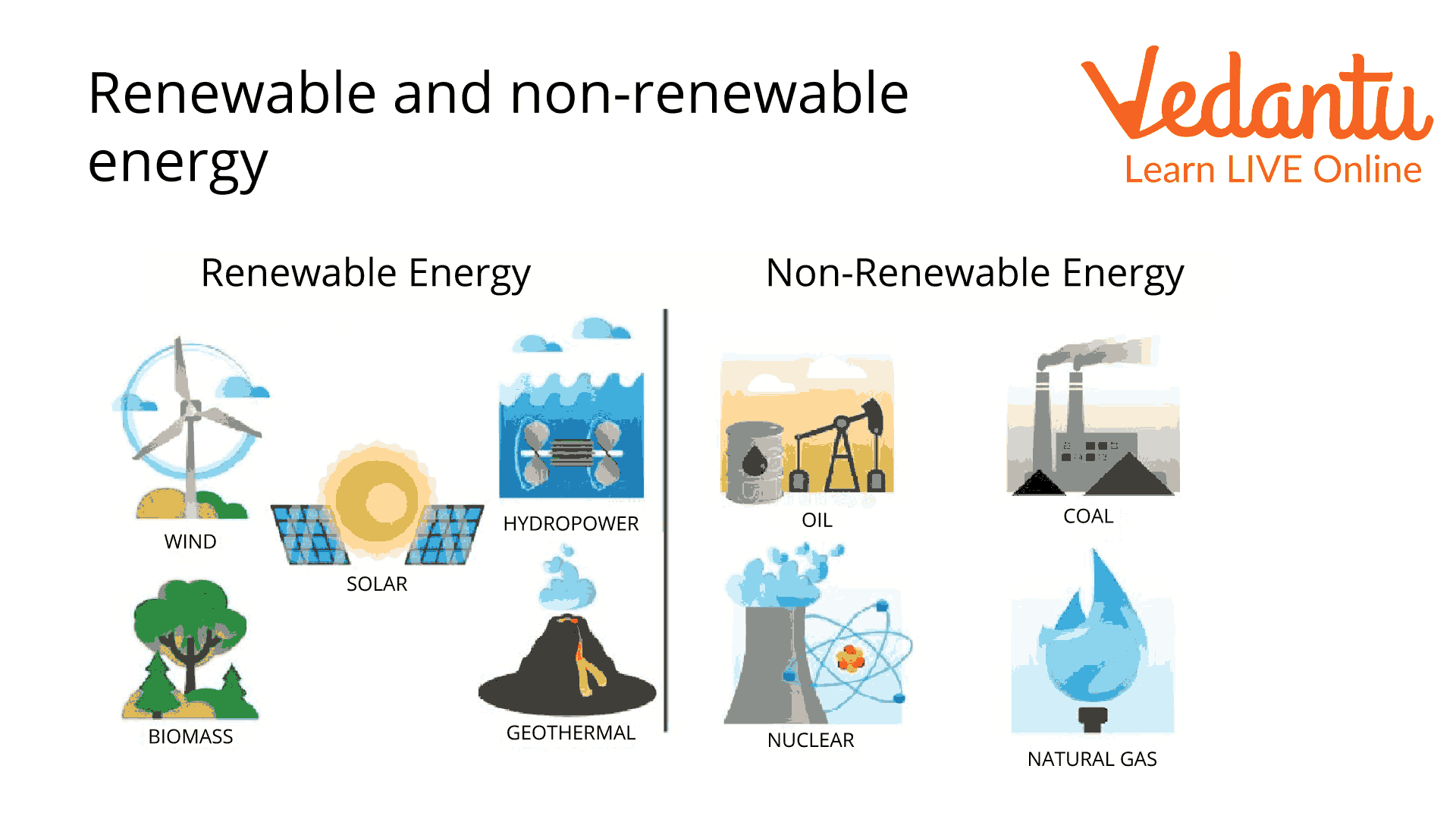
Renewable and non-renewable Energy
Renewable energy is the type of energy that can be recycled, and the sources of this type of energy are not quickly exhausted or used up. Examples of renewable energy include solar energy, wind energy, etc.
Non-renewable energy is the type of energy that cannot be recycled, and the sources of this energy are quickly exhausted. Examples of this type of energy are fossil fuels like petroleum, diesel, etc.
Science Facts About Energy
Fuels used in vehicles like diesel, petroleum, or CNG are forms of fossil fuel from the remains of fossilised animals.
Fossil fuels will get used up and finished one day.
Windmills are used to derive wind energy.
The water that flows through a dam or water reservoir is used to make energy.
The energy derived from the sun is called solar energy.
Energy can also be derived from geothermal spots, and this energy is called geothermal energy.
Conclusion
So, this is all about energy, its types, and some facts about it. In this article, you have learnt about the forms of energy and their sources, renewable and non-renewable energy, and facts related to energy. In higher classes, you will learn more about how different forms of energy can be converted into other forms. For example, heat energy is converted to light energy, etc.
FAQs on Essential Science Facts About Energy
1. What is the most important science fact about energy?
The most fundamental fact about energy is explained by the Law of Conservation of Energy. This law states that energy cannot be created or destroyed; it can only change from one form to another. For example, when you switch on a lamp, electrical energy is not used up but is converted into light energy and heat energy.
2. What are some common types of energy we see and use every day?
Energy exists in many forms around us. Some of the most common types you encounter daily include:
- Chemical Energy: Stored in batteries, food, and fuels like petrol. Our bodies use chemical energy from food to function.
- Electrical Energy: Powers our homes, schools, and gadgets. It flows through wires.
- Kinetic Energy: This is the energy of motion. A running child, a moving car, and a spinning fan all have kinetic energy.
- Thermal Energy (Heat): The energy that makes things warm. The Sun is a major source of thermal energy.
- Light Energy: A form of energy that our eyes can detect. It comes from the Sun, light bulbs, and screens.
3. How do our bodies get and use energy to live?
Our bodies work like amazing energy converters. We get energy by eating food, which contains stored chemical energy. Through a process called metabolism, our body breaks down the food and releases this energy. We then use it for everything we do: moving our muscles (kinetic energy), keeping our bodies warm (thermal energy), and even for thinking and sending signals through our nerves (electrical energy).
4. Where did the word 'energy' come from?
The word 'energy' wasn't invented but rather evolved. It comes from the ancient Greek word 'energeia', which was used by the philosopher Aristotle to mean activity or operation. However, it was the scientist Thomas Young who first introduced the term 'energy' in its modern scientific sense in the early 1800s.
5. If energy cannot be destroyed, why does a rolling ball eventually stop?
This is a great question that shows the law of conservation of energy in action! The ball’s motion energy (kinetic energy) doesn't just disappear. It is transformed into other forms of energy due to two main forces:
- Friction: As the ball rolls, it rubs against the ground, creating heat energy (thermal energy).
- Air Resistance: The ball also pushes against the air, which creates a tiny amount of sound energy and more heat.
6. What is the difference between renewable and non-renewable energy sources?
The main difference lies in how quickly they are replenished.
- Renewable energy sources come from natural resources that are constantly refilled, such as sunlight (solar energy), wind (wind energy), and moving water (hydroelectric energy). They are considered environmentally friendly.
- Non-renewable energy sources are finite and take millions of years to form. Once we use them up, they are gone for a very long time. Examples include coal, oil, and natural gas.
7. Can you give a simple example of energy changing forms?
A perfect example is a person eating an apple and then riding a bicycle. The apple contains chemical energy. When the person eats it, their body converts that chemical energy into kinetic energy to pedal the bicycle. The moving bicycle wheels then create heat energy due to friction with the road. In this one activity, energy has changed from chemical to kinetic to heat.





















