




Easy DNA Definition, Structure, and Functions Explained for Students
DNA contains all of the instructions for a living thing's structure and behaviour. Human DNA, for example, affects things like the eyes' colour and the lungs' function. Different sections of the DNA carry each bit of information. These pieces are referred to as genes.
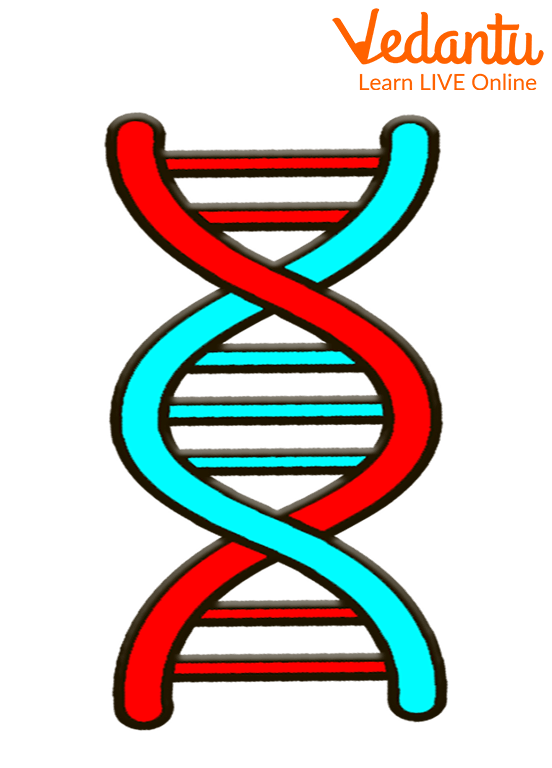

DNA
What does DNA Represent?
DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic acid.
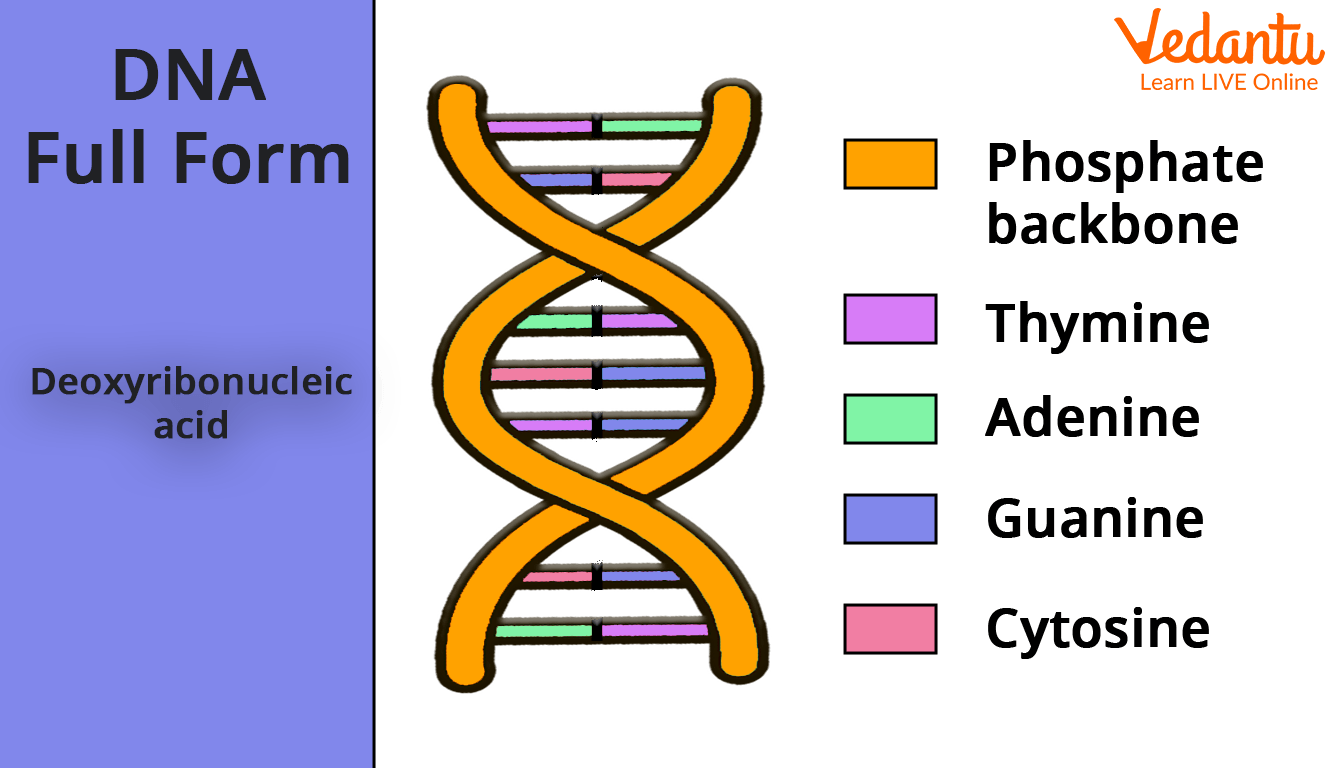
DNA Full Form
What is DNA composed of?
DNA is made up of long, thin molecules known as nucleotides. Adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine are the four types of nucleotides. Their first letter is typically used to represent them:
Adenine - A
Thymine - T
Cytosine - C
Guanine - G
A phosphate and deoxyribose backbone connects the nucleotides together. Sometimes, the nucleotides are referred to as "bases."
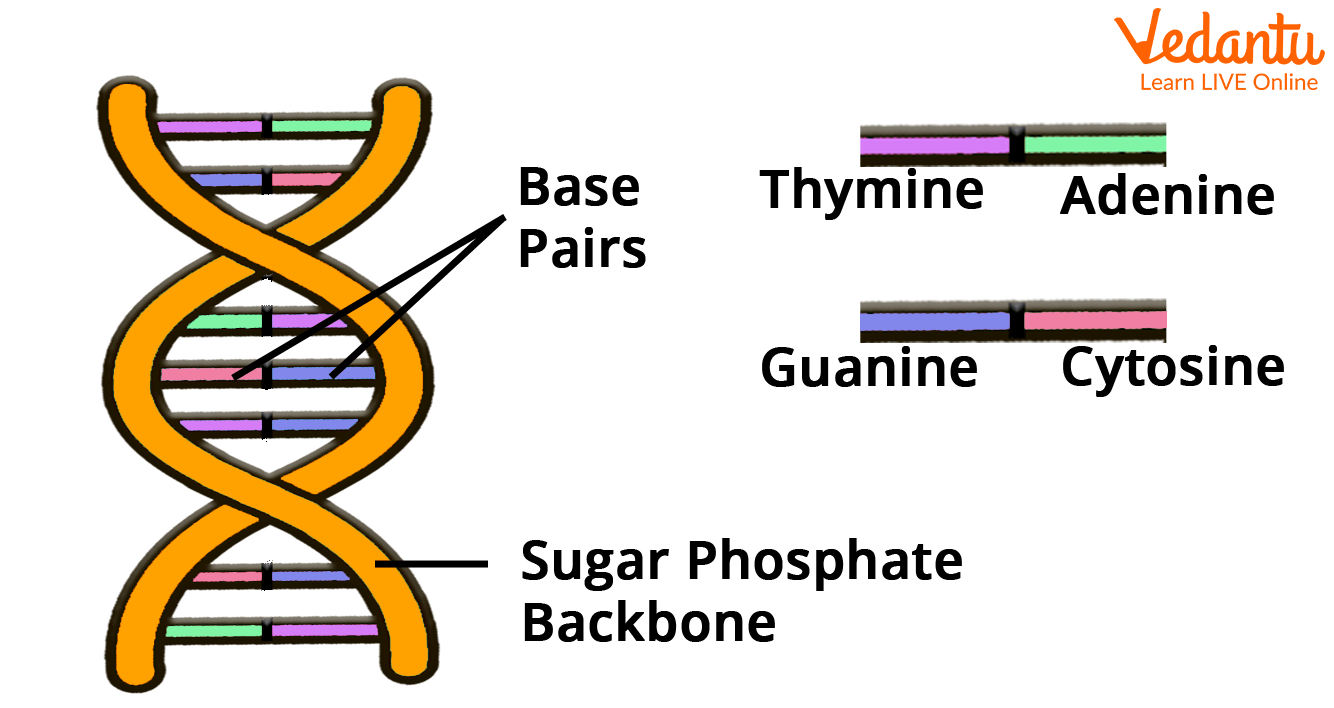
DNA Structure Diagram
Various Cell Types in the Body
There are over 210 different cell kinds in our bodies. Every cell contributes in another way to the operation of our body. For example, blood, bone, and muscle-building cells exist.
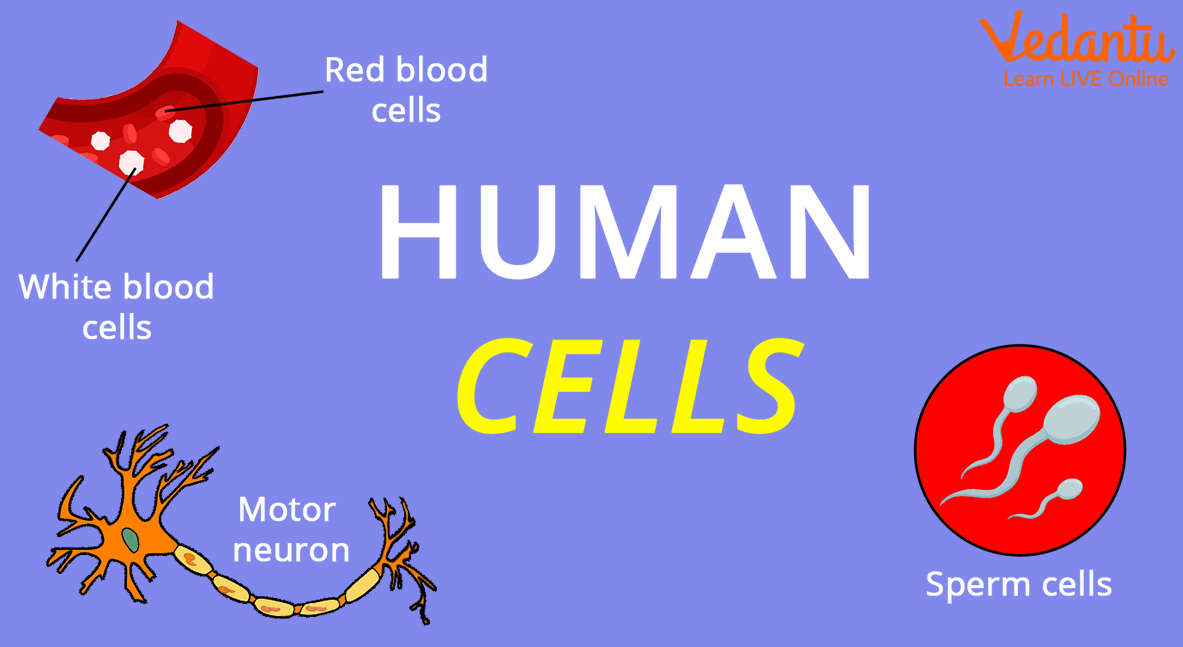
Types of Cells
How do Cells Decide Things?
DNA provides instructions to cells on what to do. Sort of like a computer program, DNA functions. DNA is the software or code, and the cell is the computer or the hardware.
The Genetic Code
The many letters of the nucleotides store the DNA code. The letters on the DNA that make the instructions are "read" by the cell. For example, a word called a codon is made up of three letters. The following is an example of a codon string:
ATC TGA GGA AAT GAC CAG
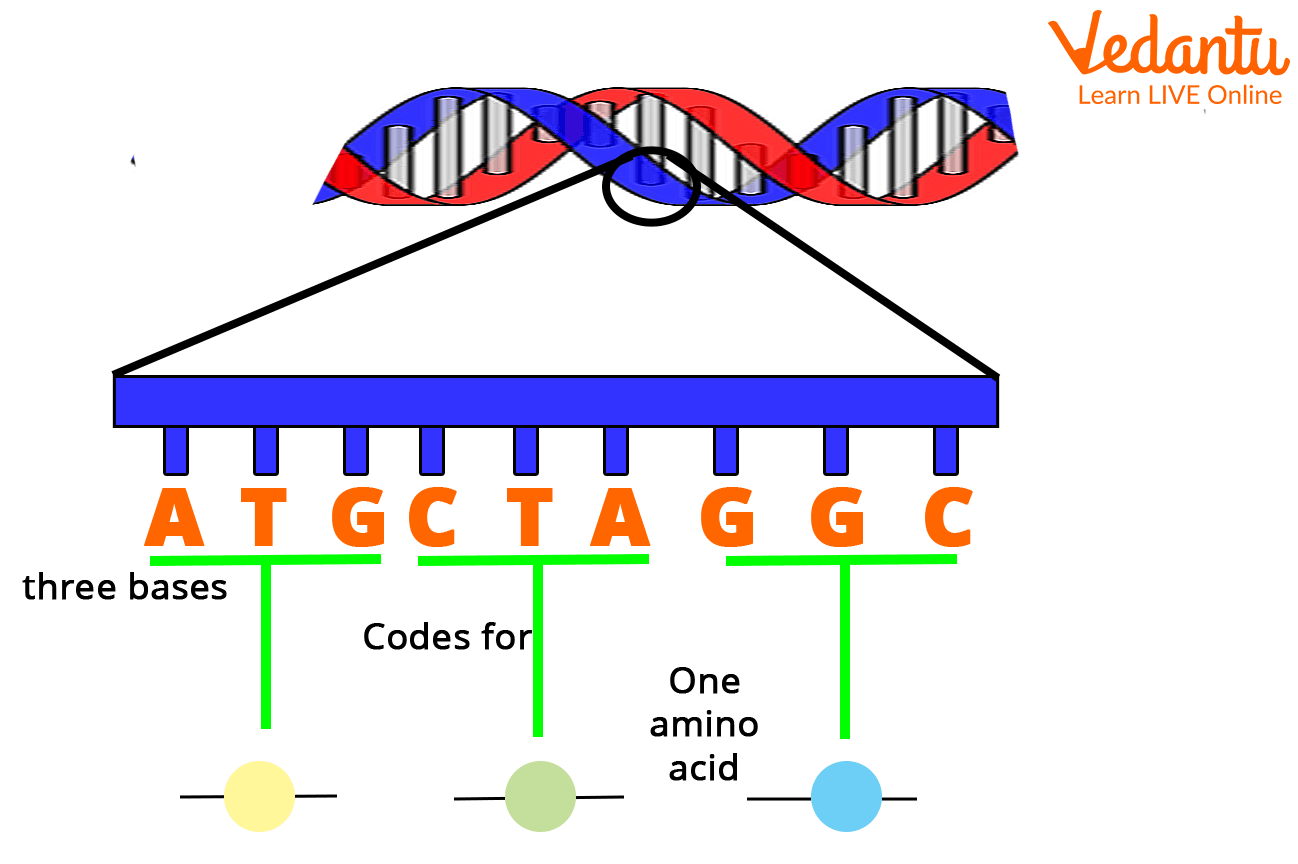
Genetic Code
Genes
Genes are collections of instructions found within each DNA strand. A gene instructs a cell on how to produce a certain protein. The cell uses proteins to carry out certain tasks, grow, and live.
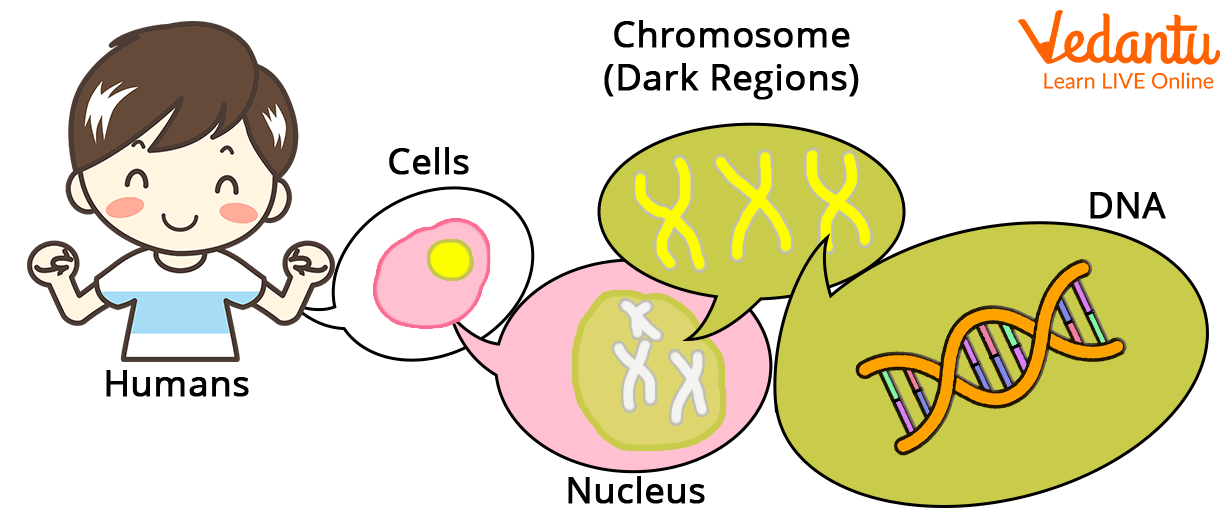
Genes
Functions of DNA
The proper functioning of DNA molecules contributes to the body's continued health. DNA aids in the production of proteins, which are essential for cell survival. DNA also enables the procreation of living beings. Biological characteristics are passed down from parents to offspring through DNA genes. Sometimes DNA contains errors. The term "mutations" refers to these errors. They can bring up illnesses and other issues.
DNA Molecules
Structure of DNA
DNA has a specific form, despite seeming to be very thin, lengthy strings under a microscope. It is known as a double helix. The backbone that binds the DNA together is outside the double helix. There are two sets of intertwined backbones. The nucleotides indicated by the letters A, T, C, and G are located between the backbones. Each backbone is connected by a separate nucleotide, which binds to another nucleotide in the centre. Nucleotides can only fit together in specific combinations. Therefore, they can be compared to puzzle pieces: G and A are the only connections they have with each other.
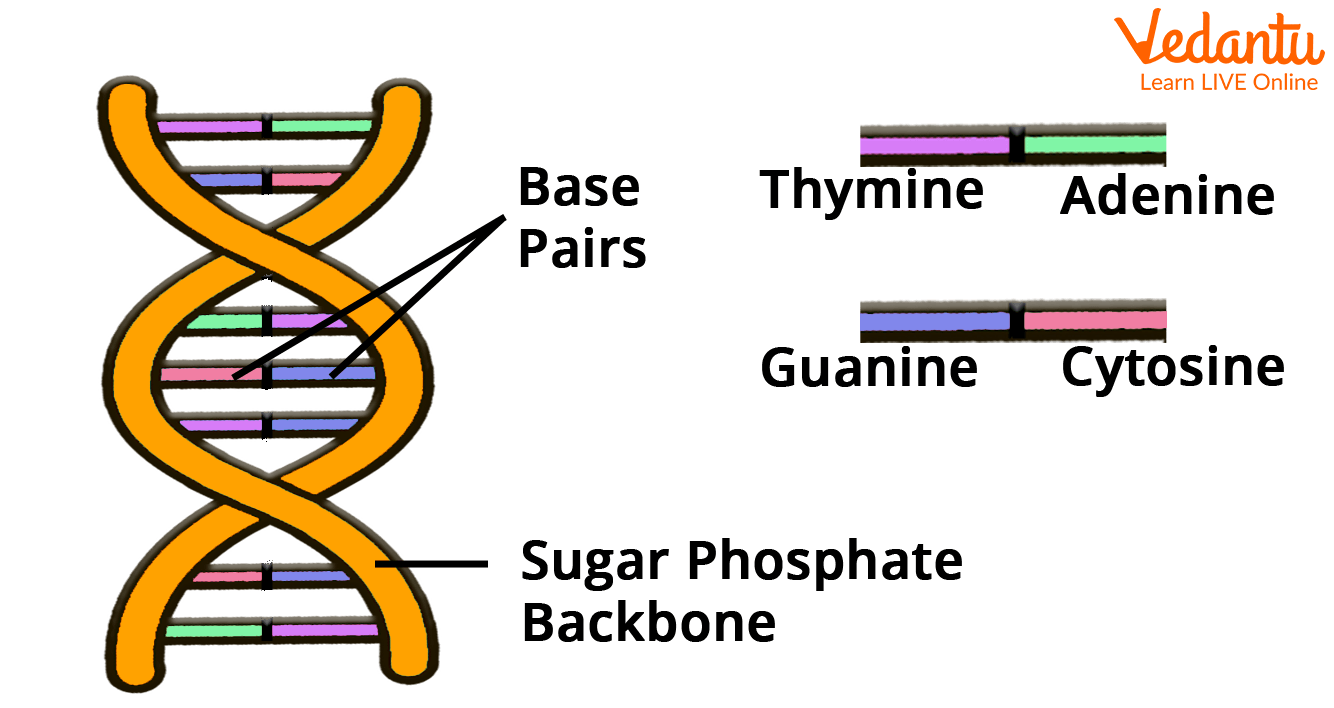
Basic DNA Structure
Interesting DNA-Related Facts
Everyone on the earth shares exactly the same 99.9% of their DNA. However, we are all different in that 0.1 percent of the population.
James Watson and Francis Crick, two scientists, discovered the double helix structure of DNA in 1953.
Your body contains enough DNA molecules to extend to the Sun and back multiple times if you were to unravel every single one of them.
Within the cell, DNA is arranged into things called chromosomes.
Friedrich Meischer, a Swiss researcher, discovered and isolated DNA for the first time in 1869.
Showing Chromosomes
Summary
All living things are built and maintained according to the genetic code found in DNA, a complicated, long-chained molecule. DNA, which is present in almost all cells, contains the instructions required to make proteins, specific molecules crucial to the body's growth and operation.
Sample Questions
1. What is the complete form of DNA?
Ans: Deoxyribonucleic acid is the full form of DNA.
2. The colour of eyes, hair, and height are all determined by________.
Ans: Genes.
3. Which of the following carries genetic information?
Cell wall b) DNA C) Golgi complex
Ans: b) DNA
FAQs on What is DNA? Definition, Structure & Importance for Kids
1. What is DNA in simple words?
DNA is like a giant instruction book found inside almost every cell of your body. It tells your body how to grow and work. These instructions decide things like your eye colour, hair colour, and how tall you might grow. The full name for DNA is Deoxyribonucleic Acid.
2. How is DNA like a recipe book for building a person?
Think of DNA as a huge recipe book where each recipe is a gene. A gene is a special instruction for one specific thing, like a recipe for baking a cake (making your eye colour blue) or a recipe for building a house (making you tall). Your body reads these gene-recipes to build and run everything about you.
3. What does the DNA structure look like?
DNA has a famous shape called a double helix. It looks like a twisted ladder. The two long sides of the ladder are called strands, and the steps connecting them are made of special chemicals called bases. It's this unique twisted shape that allows it to store so much information.
4. What are the 'steps' of the DNA ladder made of?
The steps of the DNA ladder are made of four chemical bases that always pair up in a specific way:
- Adenine (A) always pairs with Thymine (T).
- Guanine (G) always pairs with Cytosine (C).
This strict pairing rule (A-T and G-C) is very important for copying the DNA instructions correctly. These pairs are held together by weak bonds, like two sides of a zipper.
5. Why is my DNA different from my friend's DNA?
Your DNA is unique to you (unless you have an identical twin!). While all humans share about 99.9% of the same DNA, the tiny 0.1% difference is what makes you special. The order of the A, T, C, and G bases in your instruction book is slightly different from your friend's, leading to different traits like hair style, height, and other features.
6. Where do we get our DNA from?
You get your DNA from your biological parents. You receive half of your DNA instruction book from your mother and the other half from your father. This is why you might have your mother's eyes and your father's nose – it's a mix of their genetic instructions.
7. What happens if there is a small 'typo' or mistake in the DNA instructions?
A mistake in the DNA code is called a mutation. Most of the time, these small changes do nothing at all or are fixed by our cells. Sometimes, a mutation can cause a change in a trait, which can be harmless (like a unique eye colour), or it could lead to a health condition. Mutations are also a reason why there is so much variety among all living things.
8. Is the DNA in my hair the same as the DNA in my toes?
Yes, it is! Almost every single cell in your body, whether it's in your skin, hair, or toes, contains the exact same complete set of DNA instructions. The amazing part is that different cells only 'read' the parts of the instruction book they need. A hair cell reads the 'how to be hair' chapter, while a toe cell reads the 'how to be a toe' chapter.
9. What are some fun and interesting facts about DNA?
DNA is full of amazing secrets! Here are a few fun facts:
- If you could stretch out all the DNA from one human cell, it would be about 2 metres (6 feet) long.
- If you lined up all the DNA from all the cells in your body, it would reach to the Sun and back hundreds of times!
- Humans share about 98% of their DNA with chimpanzees and about 50% with bananas.
- The complete set of your DNA instructions is called your genome.
10. What is a DNA sample used for?
A DNA sample is any part of a person's body, like a drop of saliva, blood, or a piece of hair, that contains their cells. Scientists and doctors can study the DNA from these samples for many reasons. For example, it can be used to see if a person might have certain inherited health conditions, to find out who a person's relatives are, or by detectives to solve crimes.









