NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science - Heredity and Evolution - Free PDF Download
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 - Heredity and Evolution solved by expert Science teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines. All Chapter 9 - Heredity and Evolution exercise questions with solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
The NCERT Solutions are always beneficial in your exam preparation and revision. Download NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths from Vedantu, which are curated by master teachers. Science Students who are looking for Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions will also find the Solutions curated by our Master Teachers really Helpful.
NCERT Exemplar Solutions For Grade 10 Science(Biology) Chapter 10. - Heredity and Evolution
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. Exchange of genetic material takes place in
(a) vegetative reproduction
(b) asexual reproduction
(c) sexual reproduction
(d) budding
Ans. Option C is correct.
Explanation - Asexual reproduction involves single parents. Vegetative reproduction and budding are the types of asexual. In Asexual reproduction, single parents contribute the genes. Thus, no exchange of genetic material takes place.
Whereas in sexual reproduction, genes are contributed by two parents. Hence, the exchange of genetic material takes place.
2. Two pink colored flowers on crossing resulted in 1 red, 2 pink and 1 white flower progeny. The nature of the cross will be
(a) double fertilization
(b) self-pollination
(c) cross fertilization
(d) no fertilization
Ans. Option C is correct.
Explanation - The term ‘cross’ in the question indicates cross fertilization. When a pollen grain is transferred from one flower to another of the same species. This is called cross fertilization.
This is an example of incomplete dominance in which both alleles express themselves.
3. A cross between a tall plant (TT) and short pea plant (tt) resulted in progeny that were all tall plants because
(a) tallness is the dominant trait
(b) shortness is the dominant trait
(c) tallness is the recessive trait
(d) height of pea plant is not governed by gene ‘T’ or ‘t’
Ans. Option C is correct.
Explanation - In monohybrid cross, dominant character is the only character expressed in the first generation of progeny. In other words, recessive allele expressions are suppressed by the dominant alleles.
4. Which of the following statement is incorrect?
(a) For every hormone there is a gene.
(b) For every protein there is a gene.
(c) For production of every enzyme there is a gene.
(d) For every molecule of fat there is a gene
Ans. Option D is correct.
Explanation - Hormone and enzymes are made up of proteins and formation of any particular protein is also controlled by a particular gene. But fat formation does not depend on genes. Hence, all other options are correct.
5. If a round, green seeded pea plant (RR yy) is crossed with wrinkled, yellow seeded pea plant, (rr YY) the seeds produced in F1 generation are
(a) round and yellow
(b) round and green
(c) wrinkled and green
(d) wrinkled and yellow
Ans. Option A is correct.
Explanation - The roundness and yellow color are dominant characters. These will be fully expressed in the F1 generation.
6. In human males all the chromosomes are paired perfectly except one. This/ these unpaired chromosomes is/are
(i) large chromosome
(ii) small chromosome
(iii) Y-chromosome
(iv) X-chromosome
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (iii) only
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans. Option C is correct.
Explanation - These are sex chromosomes determining the gender of the offspring. In human, the male contains XY sex chromosomes which is heterogametic.
7. The maleness of a child is determined by
(a) the X chromosome in the zygote
(b) the Y chromosome in zygote
(c) the cytoplasm of germ cell which determines the sex
(d) sex is determined by chance
Ans. Option B is correct.
Explanation - If a sperm with Y chromosome fertilizes the egg, the resulting zygote would develop into a male child.
8. A zygote which has an X-chromosome inherited from the father will develop into
(a) boy
(b) girl
(c) X- chromosome does not determine the sex of a child
(d) either boy or girl
Ans. Option B is correct.
Explanation - As X-chromosome from the father will mate the X-chromosome of the mother resulting in XX-chromosome of the child as the 23rd pair. Thus, the child will be a girl.
9. Select the incorrect statement
(a) Frequency of certain genes in a population change over several generations resulting in evolution
(b) Reduction in weight of the organism due to starvation is genetically controlled
(c) Low weight parents can have heavy weight progeny
(d) Traits which are not inherited over generations do not cause evolution
Ans. Option B is correct.
Explanation - Weight loss/gain depends on external factors and are not carried genetically. This is an acquired trait.
10. New species may be formed if
(i) DNA undergoes significant changes in germ cells
(ii) chromosome number changes in the gamete
(iii) there is no change in the genetic material
(iv) mating does not take place
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i), (ii) and (iii)
Ans. Option A is correct.
Explanation - Evolution takes place due to change in genetic material which means no change in genetic material, no evolution would occur.
Sexual reproduction cannot occur without mating which means no exchange of genetic material would occur. Hence, (iii) and (iv) are incorrect.
DNA undergoes significant changes in germ cells along with time and change in number of chromosomes which could be due to deletion and deletion resulting in mutation. These two play significant role in the rise of new species.
11. Two pea plants, one with round green seeds (RRyy) and another with wrinkled, yellow (rrYY) seeds produce F1 progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds. When F1 plants are selfed, the F2 progeny will have new combination of characters. Choose the new combination from the following
(i) Round, yellow
(ii) Round, green
(iii) Wrinkled, yellow
(iv) Wrinkled, green
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Ans. Option C is correct.
Explanation - Result obtained after selfing of F1 progeny- The new combination formed in F2 progeny is Round, green (RRyy) and Wrinkled, yellow (rrYY)
Punnett square- Selfing of F1 progeny
GAMETES | Ry | RY | rY | ry |
Ry | RRyy | RRYy | RrYy | Rryy |
RY | RRYy | RRYY | RrYY | RrYy |
rY | RrYy | RrYy | rrYY | rrYy |
ry | Rryy | RrYy | rrYy | rryy |
12. A basket of vegetables contains carrot, potato, radish and tomato. Which of them represent the correct homologous structures?
(a) Carrot and potato
(b) Carrot and tomato
(c) Radish and carrot
(d) Radish and potato
Ans. Option C is correct.
Explanation - Homologous structures are those which are same in origin and structure but perform similar or different functions in organisms.
Radish and Carrot are homologous structures because both perform the function of food storage and both are modified roots.
Potato is a modified stem whereas tomato is a fruit.
13. Select the correct statement
(a) Tendril of a pea plant and phylloclade of Opuntia are homologous
(b) Tendril of a pea plant and phylloclade of Opuntia are analogous
(c) Wings of birds and limbs of lizards are analogous
(d) Wings of birds and wings of bat are homologous
Ans. Option A is correct.
Explanation- Homologous structures are those which are same in origin and structure but perform similar or different functions in organisms.
Tendril of a pea plant and phylloclade of Opuntia are modified leaves which means they are similar in origin. Tendril wraps around the anchor and provides support to pea plants whereas phylloclades help in photosynthesis in opuntia.
14. If the fossil of an organism is found in the deeper layers of earth, then we can predict that
(a) the extinction of organism has occurred recently
(b) the extinction of organism has occurred thousands of years ago
(c) the fossil position in the layers of earth is not related to its time of extinction
(d) time of extinction cannot be determined
Ans. Option B is correct.
Explanation - Fossils are the remaining non-degraded parts of living beings found deposited within the rocks. The layer of rocks helps in deciding the age of fossils. The fossils found in deeper layers are older compared to the ones found in the upper layers.
15. Which of the following statements is not true with respect to variation?
(a) All variations in a species have equal chance of survival
(b) Change in genetic composition results in variation
(c) Selection of variants by environmental factors forms the basis of evolutionary processes.
(d) Variation is minimum in asexual reproduction
Ans. Option A is correct.
Explanation - Nature only selects the fittest variation among all kinds of variations which are useful for survival of organisms.
16. A trait in an organism is influenced by
(a) paternal DNA only
(b) maternal DNA only
(c) both maternal and paternal DNA
(d) neither by paternal nor by maternal DNA
Ans. Option C is correct
Explanation - Since DNA in an organism is contributed by two parents during reproduction, hence traits are influenced by both maternal and paternal DNA.
17. Select the group which shares maximum number of common characters
(a) two individuals of a species
(b) two species of a genus
(c) two genera of a family
(d) two genera of two families
Ans. Option C is correct.
Explanation - Species is the lowest taxon and hence members of the same species share the maximum number of common characters.
18. According to the evolutionary theory, formation of a new species is generally due to
(a) sudden creation by nature
(b) accumulation of variations over several generations
(c) clones formed during asexual reproduction
(d) movement of individuals from one habitat to another
Ans. Option B is correct.
Explanation - Whenever there is a variation in DNA a new species is formed. But making clones and movement from one habitat to another does not result in DNA variation. Moreover, the Theory of Sudden Creation was disapproved by the scientists.
19. From the list given below, select the character which can be acquired but not inherited
(a) color of eye
(b) color of skin
(c) size of body
(d) nature of hair
Ans. Option C is correct.
Explanation -A person can become fat or thin because of diet. A person can develop a muscular body through regular exercise. But these characters cannot be inherited in the next generation. A character is inherited when genetic variation accumulates in DNA.
20. The two versions of a trait (character) which are brought in by the male and female gametes are situated on
(a) copies of the same chromosome
(b) two different chromosomes
(c) sex chromosomes
(d) any chromosome
Ans. Option A is correct.
Explanation - Copies of the same chromosome contain the same alleles for a trait. When gamete is transferred from the male and female, gametes pair up to form a chromosomal pair which combines the two alleles of a trait from both the parents.
21. Select the statements that describe characteristics of genes
(i) genes are specific sequence of bases in a DNA molecule
(ii) a gene does not code for proteins
(iii) in individuals of a given species, a specific gene is located on a particular chromosome
(iv) each chromosome has only one gene
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans. Option B is correct.
Explanation - A gene codes for proteins and hence statement (ii) is incorrect. A chromosome can have several specific genes at particular loci. Thus, the statement (iv) is incorrect.
22. In peas, a pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with a short plant (tt). The ratio of pure tall plants to short plants in F2 is
(a) 1 : 3
(b) 3 : 1
(c) 1 : 1
(d) 2 : 1
Ans. Option C is correct.
Explanation - A cross between (TT) and (tt) would produce progenies with following genotypes -
In F2 generation- selfing of F1 progeny-
Gametes | T | t |
T | TT | Tt |
T | Tt | tt |
Pure tall (TT), Mixed tall (Tt) and Short (tt). The ratio of pure tall and pure short plant is 1 : 1.
23. The number of pair (s) of sex chromosomes in the zygote of humans is
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) four
Ans. Option A is correct.
Explanation - human contains 23 pair of chromosome in which 22 are autosomes where as 1 pair is sex chromosomes. In Zygote, one sex gamete is transferrer from male parent and other from female parent.
24. The theory of evolution of species by natural selection was given by
(a) Mendel
(b) Darwin
(c) Morgan
(d) Lamarck
Ans. Option B is correct.
Explanation- The theory of evolution of species by natural selection was given by Charles Darwin who was a naturalist. He stated that only organisms which are well adapted to their environment will survive, rest will be eliminated.
25. Some dinosaurs had feathers although they could not fly but birds have feathers that help them to fly. In the context of evolution this means that
(a) reptiles have evolved from birds
(b) there is no evolutionary connection between reptiles and birds
(c) feathers are homologous structures in both the organisms
(d) birds have evolved from reptiles
Ans. Option D is correct
Explanation- Birds have evolved from reptiles because dinosaurs are reptiles which develop feathers but could not use them for flying. It shows feathers developed later which were adapted by birds for flying.
Short Answer Questions
26. How is the sex of a newborn determined in humans?
Ans. The somatic cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes. The23rd chromosome pair in humans constitutes the sex chromosome.
The 23rd pair chromosome in a female is XX, whereas the genetic makeup of a male is XY. The female is homogametic, forms X - gamete while male is heterogametic, forms X - gamete and Y- gamete.
During fertilization, when sperm carrying X chromosome fuses with egg having X chromosome, results in female child
Whereas if sperm carries Y chromosome and fuses with egg, results in male child. The chromosome responsible for sex determination in a male is Y chromosome.
27. Do genetic combination of mothers play a significant role in determining the sex of a new born?
Ans. No
The 23rd chromosome pair in humans constitutes the sex chromosome.
The 23rd pair chromosome in a female is XX, whereas the genetic makeup of a male is XY. The female forms one gamete- X chromosomal gamete. Hence, All children will inherit an ‘X’ chromosome from their mother regardless of whether they are boys or girls.
The chromosome responsible for sex determination in a male is Y chromosome. The male contains XY sex chromosome in germ cells.
The transfer of X gametes from the father and X chromosome from mother fuse to form zygote with XX chromosome, is responsible for Femaleness in a child.
Thus, women are not responsible for giving birth to a girl child.
28. Mention three important features of fossils which help in the study of evolution.
Ans. (a) Fossils preserve the remaining part of ancient species which helps in study of their morphological structure.
(b) Fossils help in establishing evolutionary relationships among organisms and help in establishing the common ancestors among them.
(c) The fossil helps in determining the age of a species, giving information about the time period in which that species lived.
29. Why do all the gametes formed in human females have an X chromosome?
Ans. Human females have the two X chromosomes called sex chromosomes as 23rd pair of chromosome. During cell division, one X chromosome enters in each gamete. Thus, all female gametes contain X-chromosome.
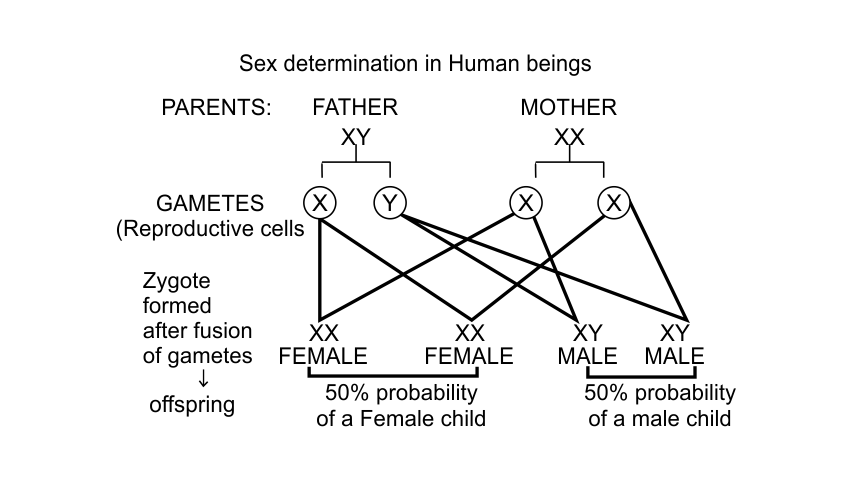
30. In human beings, the statistical probability of getting either a male or female child is 50 - 50. Give a suitable explanation.
Ans. The sex of an infant is determined by the type of sex chromosome contributed by the male gamete.
In male, sperm carries either X or Y chromosomes. Thus, the probability of sperm to carry each type of chromosome is 50%. Hence, the statistical probability of getting either male or female child is 50-50% which depends on the male gamete carrying X or Y chromosome. Let's understand this with cross.
31. A very small population of a species faces a greater threat of extinction than a larger population. Provide a suitable genetic explanation.
Ans. A small population of a species faces a greater threat of extinction than a larger population. Following are the reasons-
(a) Inbreeding - Inbreeding in a small population results in the least number of variations, weakening their adaptivity according to environment.
(b) Genetic drift - Any sudden changes in a small population i.e, loss of gene pool from a population is called genetic drift which has potential to cause the extinction of the entire small population.
(c) Inbreeding depression - It lowers the population survival rate and rate of reproduction, causing negative population growth which is further detrimental to the survival of the species.
32. What are homologous structures? Give an example. Is it necessary that homologous structures always have a common ancestor?
Ans. Structures which have a common basic structure but perform different functions are called homologous structures.
E.g.- The fore limbs of amphibians, reptiles, and mammals.
For example - the forelimbs of frogs and dogs are homologous structures, as they are composed of similar bones which are humorous, radio-ulna, carpal and metacarpals. The forelimbs of frogs are adapted for jumping movement, while the forelimbs of dogs are adapted for walking and running.
Yes, it is necessary that homologous structures always have a common ancestor, we can observe the morphological similarities among the homologous structures.
33. Does the occurrence of diversity of animals on earth suggest their diverse ancestry also? Discuss this point in the light of evolution.
Ans. The animals have a vast diversity in structures; they may not have a common ancestry, because common ancestry limits the extent of diversity. But we can group the animals into different groups and subgroups; on the basis of certain common characteristics. As many of these diverse animals are inhabiting the same habitat, their evolution by geographical isolation and speciation is also not likely. Thus, a common ancestor for all the animals is not the likely theory.
34. Give the pair of contrasting traits of the following characters in pea plant and mention which is dominant and recessive (i) yellow seed (ii) round seed.
Ans.
(a) yellow — dominant
green — recessive
(b) round — dominant
wrinkled — recessive
35. Why did Mendel choose pea plant for his experiments?
Ans.
(a) Easy to grow
(b) Short life span
(c) Easily distinguishable characters
(d) Larger size of flower
(e) Self pollinated
(f) Cross-Pollination can be done easily
36. A woman has only daughters. Analyze the situation genetically and provide a suitable explanation.
Ans. The woman produces an ova with ‘X’ chromosome.
The male produces sperms with X and Y chromosome which determines the sex of the child. The statistical probability of getting either male or female child is 50-50% which depends on the male gamete carrying X or Y chromosome.
Here, the X-chromosome of sperm combines with the X-chromosome of egg resulting in daughters. This proves that only X chromosomal gamete is transferred from father during fertilization.
Long Answer Questions
37. Does geographical isolation of individuals of a species lead to formation of a new species? Provide a suitable explanation.
Ans. Yes, geographical isolation leads to speciation i.e formation of new species due to development of unique characteristics when separated from a group within a species.
The geographical isolation imposes limits to sexual reproduction due to separation from the group. It gradually leads to genetic drift.
Geographical isolation encourages inbreeding among themselves and generates new variations. The accumulation of these variations through one generation to next generations may ultimately lead to speciation.
38. Bacteria have a simpler body plan when compared with human beings. Does it mean that human beings are more evolved than bacteria? Provide a suitable explanation.
Ans. Evolution is defined as the accumulation of variations along the period of time. It is a point of debate which depends on the way we evaluate evolution. If Body complexity is a parameter to study evolution then humans are more evolved than bacteria. Bacteria are unicellular and have cellular level organization whereas humans are multicellular and have organ level organization.
But complexity is not the only measure to take into consideration, the ability of survival is also considered. According to which, bacteria are more evolved. Human beings are living only on land, but adapt to live on other places by taking artificial facilities. Moreover, in extreme environmental conditions, human beings are not adapted to withstand extreme climatic conditions. On the other hand, bacteria are known to be found in extreme environmental conditions such as Sulphur spring, hydrothermal vents, crater of volcano, etc. From this point of view, bacteria can be considered as more evolved than human beings.
39. All the human races like Africans, Asians, Europeans, Americans and others might have evolved from a common ancestor. Provide a few evidences in support of this view.
Ans. All the human races have a large number of common characters. The list of common characters can be very long but we can make a shorter list -Similar size of brain,
Bipedal locomotion,
Hair of body.
Ability to handle tools.
Ability to communicate using language.
Highly complex social behaviour.
Same body design.
All these characters show a common ancestor for all human races. Moreover, all human beings are able to interbreed and keep them under the same species.
40. Differentiate between inherited and acquired characters. Give one example for each type.
Ans.
Inherited Characters | Acquired characters |
Inherited characteristics are those which affect genetic material of an organism and these changes are accumulated in genetic material. These characteristics can be transferred from parent to offspring in next generations. Example- Colors of eye, color of skin and nature of hair | Acquired characteristics are those characteristics which are acquired during lifetime by experiences and adaptations. These changes do not affect genetic material of an organism and can not be passed onto offspring. Example- Size of the body, Muscle size |
41. Give reasons why acquired characters are not inherited.
Ans. Acquired characteristics are those characteristics which are acquired during lifetime by experiences and adaptations. Let us take the example of a certain cricketer who is an excellent batsman. He may become an excellent batsman because of various reasons like his keen interest in the game, timely support from his family and friends, proper coaching at the right age and timely selection in the cricket team. The cricketing ability could be acquired by the batsman the way he responded to all the challenges and opportunities. But all this training will not change his genetic makeup. Hence, his cricketing skills would not be passed onto the next generation.
In fact, acquired characters alter phenotypes of an individual. It has no effect on genetic makeup. A character can only be inheritable when it changes the genotype of an individual. Hence, acquired characters are not inherited.
42. Evolution has exhibited a greater stability of molecular structure when compared with morphological structures. Comment on the statement and justify your opinion.
Ans. The visible structures in an organism are called morphological structures.
Morphological structures can be observed physically by us. Molecular structures are the structure of biomolecules such as DNA, protein and carbohydrates are the integral components of organisms.
This diversity is possible because of diversity in morphological structures in organisms which shows the morphological structures are least stable.
Over the course of time, the biomolecular structure has not changed in organisms but the morphological changes have been observed. The DNA is the same in a human and in e rodents such as rats . The structure of protein is the same in a bird and in a fungi.
This shows that evolution has exhibited a greater stability of molecular structure when compared with morphological structure.
43. In the following crosses write the characteristics of the progeny-
Cross | Progeny |
(a) RRYY ✖ RRYY Round, yellow ; Round, yellow (b) RrYy✖RrYy Round, yellow ; Round, yellow (c) rryy✖rryy Wrinkled, green ; Wrinkled, green (d) RRYY ✖rryy Round, yellow ; Wrinkled, green | ……………………. ……………………. ……………………. ……………………. ……………………. ……………………. ……………………. ……………………. |
Ans.
(a) Round, yellow (RRYY)
(b) RrYy✖RrYy
GAMETES | Ry | RY | rY | Ry |
Ry | RRyy | RRYy | RrYy | Rryy |
RY | RRYy | RRYY | RrYY | RrYy |
rY | RrYy | RrYy | rrYY | rrYy |
ry | Rryy | RrYy | rrYy | Rryy |
Round yellow (RRYY), Round yellow (RrYy), Round green (RRyy), Round green (Rryy), wrinkled yellow (rrYY), wrinkled yellow (rrYy), wrinkled green (rryy).
(c) Wrinkled green (rryy)
(d) Parent - RRYY ✖rryy
Round, yellow Wrinkled, green
F1 generation - RrYy( Round, yellow )
Result - Round yellow (RrYy)
44. Study the following cross and showing self-pollination in F1, fill in the blank and answer the question that follows-
Parents RRYY ✖ rryy
Round, yellow Wrinkled, green
F1 RrYy ✖ ?
Ans. Parents - RRYY ✖ rryy
Round, yellow Wrinkled, green
F1 - RrYy (Round, yellow )
F2 - Selfing of F1
RrYy ✖ RrYy
Round, yellow Round, yellow
GAMETES | Ry | RY | rY | Ry |
Ry | RRyy | RRYy | RrYy | Rryy |
RY | RRYy | RRYY | RrYY | RrYy |
rY | RrYy | RrYy | rrYY | rrYy |
Ry | Rryy | RrYy | rrYy | Rryy |
45. In question 44, what are the combinations of characters in the F2 progeny? What are their ratios?
Ans. Round yellow (RRYY), Round yellow (RrYy), Round green (RRyy), Round green (Rryy), wrinkled yellow (rrYY), wrinkled yellow (rrYy), wrinkled green (rryy).
This can be shown by following Punnett Square -
GAMETES | Ry | RY | rY | Ry |
Ry | RRyy | RRYy | RrYy | Rryy |
RY | RRYy | RRYY | RrYY | RrYy |
rY | RrYy | RrYy | rrYY | rrYy |
Ry | Rryy | RrYy | rrYy | Rryy |
Ratio- 9:3:3:1 (round-yellow : wrinkled-yellow : round-green : wrinkled-green pea seeds)
46. Give the basic features of the mechanism of inheritance.
Ans.
(i) Characters are controlled by genes.
(ii) Each gene controls one character
(iii) There are two alternate forms of a gene which are called alleles.
(iv) One allele is dominant over the other, the suppressed allele is called recessive allele.
(v) Genes are present on chromosomes
(vi) An individual contains two forms of the gene which are either similar or dissimilar
(vii) Alleles segregate during cell division to form gametes.
(viii) The segregated alleles unit at the time of fertilization.
47. Give reasons for the appearance of new combinations of characters in the F2 progeny.
Ans. During Mendel’s experiment with dihybrid cross, it was seen that all the plants in the F1 generation produced round and yellow seeds. However, in the F2 generation, phenotypes of different seeds were different. This shows a new combination of characters in the F2 generation.
Out of round and wrinkled texture, round texture is the dominant character. Similarly, out of yellow and green colors, yellow color is the dominant character. In the F1 generation, all the plants produced round yellow seeds because of the dominance of characters. But the genotype of all plants was of mixed characters, i.e..RrYy. This happened because of the Law of Independent Assortment. The gene for seed texture behaved independently of the gene for seed color.
Due to this, the F2 generation showed different combinations of genotypes, viz. RRYY, RRYy, RrYY, RrYy, rrYY, rrYy, rryy. This can be shown by following punnett square
GAMETES | Ry | RY | rY | ry |
Ry | RRyy | RRYy | RrYy | Rryy |
RY | RRYy | RRYY | RrYY | RrYy |
rY | RrYy | RrYy | rrYY | rrYy |
Ry | Rryy | RrYy | rrYy | rryy |
Ratio- 9:3:3:1 (round-yellow : wrinkled-yellow : round-green : wrinkled-green pea seeds)
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 - Heredity and Evolution (Book Solutions)
A fossil is a preserved thing of any once-living thing from a past geological age. There are three important features of fossils that are mentioned below:
- Fossils are the preserved ancient species.
- Fossils help calculate the evolutionary differences between organisms and their ancestors.
- Fossils determine the lifespan of specific species.
Register online science tuitions on Vedantu.com to clear your doubts and download all the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 to prepare for Board Examinations.
Chapter 9 is all about fossils. Fossils are not the remains of the organism itself! They formed as rocks. A single fossil can preserve an entire organism or just part of one. Bones, shells, feathers, and leaves are a few examples of fossils. The topics which are important according to NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 9 pdf are
1. Accumulation Of Variation During Reproduction
2. Heredity Sex Determination
3. Evolution
4. Speciation
5. Evolution And Classification
6. Human Evolution.
There are many reasons to say that Vedantu’s Chapter 9 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science helps students in their preparation. The first reason is these solutions are explained simply and understandably to help students with their exam preparation. This pdf has detailed answers for all the questions present in the Class 10 science textbook. These solutions are available in PDF format which can be easily downloaded from the Vedantu website or app. Students can also improve their confidence levels towards the preparation.
To make your preparation easier, the experts at Vedantu have prepared the NCERT Solutions to help Vedantu students score more marks in Class 10 Final exams. Vedantu’s Chapter 9 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science covers some topics. They are listed below.
History of evolution and different theories of evolution.
NCERT Exemplar Class 10 science solutions Chapter 9 discusses different experiments done by the famous scientists of the time such as Griffith and Mendel.






































