
Two stations due South of a leaning tower which leans towards the North, are at distances a and b from its foot. If $\alpha $ and $\beta $ are the elevations of the top of the tower from these stations, then prove that its inclination $\theta $ to the horizontal is given by
$\cot \theta = \dfrac{{b\cot \alpha - a\cot \beta }}{{b - a}}$
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint:
First draw the diagram carefully with observation of the question. Then we can see three right angled triangles. Assume the unknown lengths with some variables. Apply suitable trigonometry ratios in all triangles. Do, needed manipulations to get the desired expression given in the question.
Complete step by step solution:
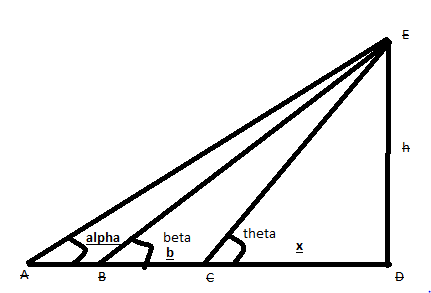
Three triangles are AED , BED and CED.
Let us assume that height of the tower DE = h
Also, assume CD is x
Then distance between first station to foot of tower AD = a+x
and distance between second station to foot of tower BD = b+x
As given in the question, we know that $\alpha $, $\beta $ are the angle of elevation two stations to the top of the tower. Thus we have
$
\angle EAD = \alpha \\
\angle EBD = \beta \\
\angle ECD = \theta \\
$
In $\vartriangle $CDE ,
$\cot \theta = \dfrac{x}{h}$ …(1) ( as cot ratio = $\dfrac{{base}}{{perpendicular}}$ )
In $\vartriangle $BDE ,
$\cot \beta = \dfrac{{x + b}}{h}$ …(2) ( as cot ratio = $\dfrac{{base}}{{perpendicular}}$ )
Similarly in In $\vartriangle $ADE ,
$\cot \alpha = \dfrac{{x + a}}{h}$ …(2) ( as cot ratio = $\dfrac{{base}}{{perpendicular}}$ )
From equation (1) , we have x = h cot$\theta $ , . Using this value in equation (2) and (3) , we get
$\cot \beta = \dfrac{{h\cot \theta + b}}{h}$ …(4)
And $\cot \alpha = \dfrac{{h\cot \theta + a}}{h}$ …(5)
Now by multiplying equation (4) by a on both sides we get
$a\cot \beta = a\cot \theta + \dfrac{{ba}}{h}$ …(6)
Similarly, by multiplying equation (5) by b on both sides we get
$b\cot \alpha = b\cot \theta + \dfrac{{ab}}{h}$ …(7 )
We subtract equation (6) from (7) , we get,
$
b\cot \alpha - a\cot \beta = b\cot \theta - a\cot \theta \\
\Rightarrow (b - a)\cot \theta = b\cot \alpha - a\cot \beta \\
\Rightarrow \cot \theta = \dfrac{{b\cot \alpha - a\cot \beta }}{{b - a}} \\
$
Hence we have proved the expression given in the problem.
Note:
Height and distance problems are very much solvable through the proper use of trigonometry ratios and obviously proper use of algebraic manipulations. Careful visualization of the problem and diagram will make the task easier.
First draw the diagram carefully with observation of the question. Then we can see three right angled triangles. Assume the unknown lengths with some variables. Apply suitable trigonometry ratios in all triangles. Do, needed manipulations to get the desired expression given in the question.
Complete step by step solution:

Three triangles are AED , BED and CED.
Let us assume that height of the tower DE = h
Also, assume CD is x
Then distance between first station to foot of tower AD = a+x
and distance between second station to foot of tower BD = b+x
As given in the question, we know that $\alpha $, $\beta $ are the angle of elevation two stations to the top of the tower. Thus we have
$
\angle EAD = \alpha \\
\angle EBD = \beta \\
\angle ECD = \theta \\
$
In $\vartriangle $CDE ,
$\cot \theta = \dfrac{x}{h}$ …(1) ( as cot ratio = $\dfrac{{base}}{{perpendicular}}$ )
In $\vartriangle $BDE ,
$\cot \beta = \dfrac{{x + b}}{h}$ …(2) ( as cot ratio = $\dfrac{{base}}{{perpendicular}}$ )
Similarly in In $\vartriangle $ADE ,
$\cot \alpha = \dfrac{{x + a}}{h}$ …(2) ( as cot ratio = $\dfrac{{base}}{{perpendicular}}$ )
From equation (1) , we have x = h cot$\theta $ , . Using this value in equation (2) and (3) , we get
$\cot \beta = \dfrac{{h\cot \theta + b}}{h}$ …(4)
And $\cot \alpha = \dfrac{{h\cot \theta + a}}{h}$ …(5)
Now by multiplying equation (4) by a on both sides we get
$a\cot \beta = a\cot \theta + \dfrac{{ba}}{h}$ …(6)
Similarly, by multiplying equation (5) by b on both sides we get
$b\cot \alpha = b\cot \theta + \dfrac{{ab}}{h}$ …(7 )
We subtract equation (6) from (7) , we get,
$
b\cot \alpha - a\cot \beta = b\cot \theta - a\cot \theta \\
\Rightarrow (b - a)\cot \theta = b\cot \alpha - a\cot \beta \\
\Rightarrow \cot \theta = \dfrac{{b\cot \alpha - a\cot \beta }}{{b - a}} \\
$
Hence we have proved the expression given in the problem.
Note:
Height and distance problems are very much solvable through the proper use of trigonometry ratios and obviously proper use of algebraic manipulations. Careful visualization of the problem and diagram will make the task easier.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which country won the ICC Men's ODI World Cup in 2023?

In cricket, how many legal balls are there in a standard over?

Explain the Treaty of Vienna of 1815 class 10 social science CBSE

A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

What does "powerplay" mean in limited-overs cricket?

What is the "Powerplay" in T20 cricket?




