
The three vertices of a parallelogram $ABCD$ are $A(3,-4),B(-1,-3)$ and $C(-6,2)$. Find the coordinates of vertex $D$ and find the area of $ABCD$.
Answer
593.7k+ views
Hint: We are given the three vertices of a parallelogram $ABCD$ are $A(3,-4),B(-1,-3)$ and $C(-6,2)$. By using midpoint $O$ find vertex $D$. After that, to find the area used, Area of parallelogram $ABCD$ $=$ Area of $\Delta ABC$ $+$ Area $\Delta ADC$.
Complete step-by-step answer:
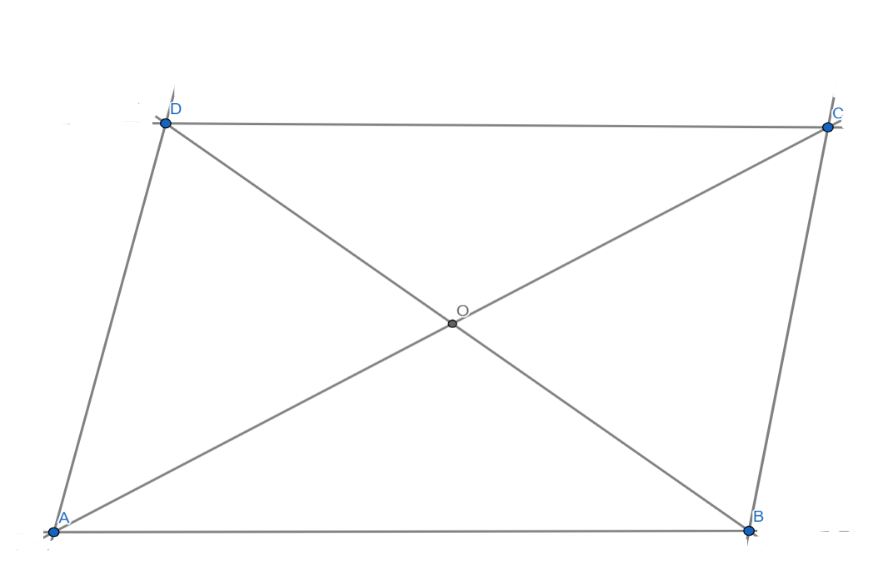
Now we are given the three vertices of a parallelogram $ABCD$ are $A(3,-4),B(-1,-3)$ and $C(-6,2)$.
$O$ is midpoint of $AC$$=(\dfrac{3-6}{2},\dfrac{-4+2}{2})$
Simplifying we get,
$O$ is midpoint of $AC$$=(\dfrac{-3}{2},-1)$ ……… (1)
In similar way,
$O$ is the midpoint of $BD$$=(\dfrac{-1+a}{2},\dfrac{-3+b}{2})$ …………. (2)
Now equating (1) and (2), we get,
$(\dfrac{-3}{2},-1)=(\dfrac{-1+a}{2},\dfrac{-3+b}{2})$
So, $-\dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{-1+a}{2}$
$a=-2$
Now, $\dfrac{-3+b}{2}=-1$
$b=1$
Therefore, $D(-2,1)$.
Now,
Area of parallelogram $ABCD$ $=$ Area of $\Delta ABC$ $+$ Area $\Delta ADC$
Area of parallelogram $ABCD$ $=$ $2$Area of $\Delta ABC$
Let us find Area of $\Delta ABC$ ,
Area of $\Delta ABC$ $=\dfrac{1}{2}[{{x}_{1}}({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{3}})+{{x}_{2}}({{y}_{3}}-{{y}_{1}})+{{x}_{3}}({{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}})]$
Area of $\Delta ABC$ \[=\dfrac{1}{2}[3(1-2)-2(2+4)-6(-4-1)]\]
Simplifying we get,
Area of $\Delta ABC$ \[=\dfrac{15}{2}\]sq. units
So now,
Area of parallelogram $ABCD$ $=$ $2$Area of $\Delta ABC$$=2\times \dfrac{15}{2}=15$ sq. units
Therefore, the area of parallelogram is $15$ square. units.
Additional information:
A parallelogram is a two-dimensional geometrical shape, whose sides are parallel with each other. It is a polygon having four sides, where the pair of parallel sides are equal in length. Also, the interior opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal to each other. The area of parallelogram depends on the base and height of it. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. The opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal in length, and the opposite angles are equal in measure. Also, the interior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary.
Note: A square and a rectangle are two shapes which have similar properties of a parallelogram. The opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal in length, and the opposite angles are equal in measure. The area of a parallelogram is the region bounded by the parallelogram in a given two-dimension space. To recall, a parallelogram is a special type of quadrilateral which has four sides, and the pair of opposite sides are parallel.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Now we are given the three vertices of a parallelogram $ABCD$ are $A(3,-4),B(-1,-3)$ and $C(-6,2)$.
$O$ is midpoint of $AC$$=(\dfrac{3-6}{2},\dfrac{-4+2}{2})$
Simplifying we get,
$O$ is midpoint of $AC$$=(\dfrac{-3}{2},-1)$ ……… (1)
In similar way,
$O$ is the midpoint of $BD$$=(\dfrac{-1+a}{2},\dfrac{-3+b}{2})$ …………. (2)
Now equating (1) and (2), we get,
$(\dfrac{-3}{2},-1)=(\dfrac{-1+a}{2},\dfrac{-3+b}{2})$
So, $-\dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{-1+a}{2}$
$a=-2$
Now, $\dfrac{-3+b}{2}=-1$
$b=1$
Therefore, $D(-2,1)$.
Now,
Area of parallelogram $ABCD$ $=$ Area of $\Delta ABC$ $+$ Area $\Delta ADC$
Area of parallelogram $ABCD$ $=$ $2$Area of $\Delta ABC$
Let us find Area of $\Delta ABC$ ,
Area of $\Delta ABC$ $=\dfrac{1}{2}[{{x}_{1}}({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{3}})+{{x}_{2}}({{y}_{3}}-{{y}_{1}})+{{x}_{3}}({{y}_{1}}-{{y}_{2}})]$
Area of $\Delta ABC$ \[=\dfrac{1}{2}[3(1-2)-2(2+4)-6(-4-1)]\]
Simplifying we get,
Area of $\Delta ABC$ \[=\dfrac{15}{2}\]sq. units
So now,
Area of parallelogram $ABCD$ $=$ $2$Area of $\Delta ABC$$=2\times \dfrac{15}{2}=15$ sq. units
Therefore, the area of parallelogram is $15$ square. units.
Additional information:
A parallelogram is a two-dimensional geometrical shape, whose sides are parallel with each other. It is a polygon having four sides, where the pair of parallel sides are equal in length. Also, the interior opposite angles of a parallelogram are equal to each other. The area of parallelogram depends on the base and height of it. A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. The opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal in length, and the opposite angles are equal in measure. Also, the interior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary.
Note: A square and a rectangle are two shapes which have similar properties of a parallelogram. The opposite sides of a parallelogram are equal in length, and the opposite angles are equal in measure. The area of a parallelogram is the region bounded by the parallelogram in a given two-dimension space. To recall, a parallelogram is a special type of quadrilateral which has four sides, and the pair of opposite sides are parallel.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Find the sum of series 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + + 100 class 9 maths CBSE

Distinguish between Conventional and nonconventional class 9 social science CBSE

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

Describe the 4 stages of the Unification of German class 9 social science CBSE

What is the role of Mahatma Gandhi in national movement

What was the Treaty of Constantinople of 1832 class 9 social science CBSE




