
The temperature inside and outside of a refrigerator are $275 $ K and $300$ K, respectively. Assuming that the refrigerator cycle is ideal reversible, for every joule of work done the heat delivered to the surroundings is nearly.
a) $10 J$
b) $11 J$
c) $14 J$
d) $12 J$
Answer
533.1k+ views
Hint: The working substance absorbs some amount of heat from the sink which is at the lower temperature, then W is the work which is done on the working substance and then some amount of heat rejected by the working substance to the surroundings. This is the basic principle of refrigerators.
Complete step by step answer:
Given inside temperature (sink temperature), $T_{2}=275 K$
Outside temperature (source temperature), $T_{1}=300K$
Work done = $1 J$
R is the refrigerator.
Assume: Refrigerator is ideal and reversible. So, we can write:
$\dfrac{ Q_{1}}{ Q_{2}} = \dfrac{ T_{1}}{ T_{2}}$
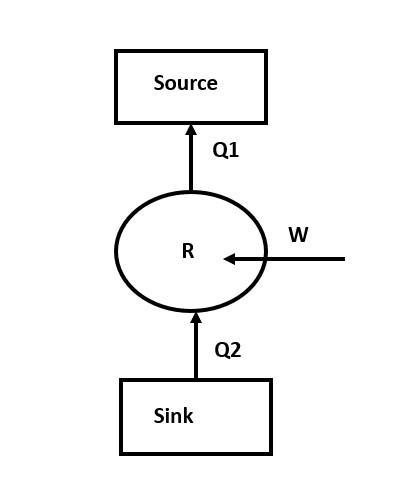
We have to find the heat lost to the surroundings, $ Q_{1}$.
Coefficient of performance -
$B = \dfrac{ Q_{2}}{W}$
Now, we will write B in terms of the temperatures.
$B = \dfrac{ T_{2}}{ T_{1}- T_{2}}$
$B = \dfrac{ 275}{ 300- 275} =11$
By using, formula of coefficient of performance, we can evaluate: -
$B = \dfrac{ Q_{2}}{W}$
Now, we will put the value of W.
$10 = \dfrac{ Q_{2}}{1}$
$ Q_{2} = 10 j$
By using the value of work, we can calculate $ Q_{1}$.
$W = Q_{1} - Q _{2}$
$Q_{1} = W + Q _{2}$
$Q_{1} = 1 + 10 = 11 J$
So, the heat delivered to the surroundings = $11 J$.
So, the correct answer is “Option b”.
Note: The heat flow follows the first law of thermodynamics. Work has to be done, otherwise heat will not flow from low temperature to high temperature and violates the second law of thermodynamics. In the refrigerator, heat is rejected to surroundings and entropy is increased.
Complete step by step answer:
Given inside temperature (sink temperature), $T_{2}=275 K$
Outside temperature (source temperature), $T_{1}=300K$
Work done = $1 J$
R is the refrigerator.
Assume: Refrigerator is ideal and reversible. So, we can write:
$\dfrac{ Q_{1}}{ Q_{2}} = \dfrac{ T_{1}}{ T_{2}}$

We have to find the heat lost to the surroundings, $ Q_{1}$.
Coefficient of performance -
$B = \dfrac{ Q_{2}}{W}$
Now, we will write B in terms of the temperatures.
$B = \dfrac{ T_{2}}{ T_{1}- T_{2}}$
$B = \dfrac{ 275}{ 300- 275} =11$
By using, formula of coefficient of performance, we can evaluate: -
$B = \dfrac{ Q_{2}}{W}$
Now, we will put the value of W.
$10 = \dfrac{ Q_{2}}{1}$
$ Q_{2} = 10 j$
By using the value of work, we can calculate $ Q_{1}$.
$W = Q_{1} - Q _{2}$
$Q_{1} = W + Q _{2}$
$Q_{1} = 1 + 10 = 11 J$
So, the heat delivered to the surroundings = $11 J$.
So, the correct answer is “Option b”.
Note: The heat flow follows the first law of thermodynamics. Work has to be done, otherwise heat will not flow from low temperature to high temperature and violates the second law of thermodynamics. In the refrigerator, heat is rejected to surroundings and entropy is increased.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




