
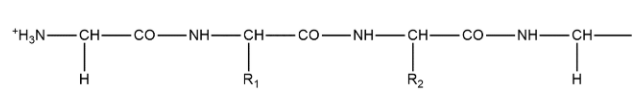
The substituents \[{{R}_{1}}\], and \[{{R}_{2}}\] for nine peptides are listed in the table given below. How many these peptides are positively charged at pH = 7.0?
Peptide \[{{R}_{1}}\] \[{{R}_{2}}\] I \[H\] \[H\] II \[H\] \[C{{H}_{3}}\] III \[C{{H}_{2}}COOH\] \[H\] IV \[C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}\] \[{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}N{{H}_{2}}\] V \[C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}\] \[C{{H}_{2}}CON{{H}_{2}}\] VI \[{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}N{{H}_{2}}\] \[{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}N{{H}_{2}}\] VII \[C{{H}_{2}}COOH\] \[C{{H}_{2}}CON{{H}_{2}}\] VIII \[C{{H}_{2}}OH\] \[{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}N{{H}_{2}}\] IX \[{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}N{{H}_{2}}\] \[C{{H}_{3}}\]
A. 4
B. 6
C. 8
D. 9
| Peptide | \[{{R}_{1}}\] | \[{{R}_{2}}\] |
| I | \[H\] | \[H\] |
| II | \[H\] | \[C{{H}_{3}}\] |
| III | \[C{{H}_{2}}COOH\] | \[H\] |
| IV | \[C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}\] | \[{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}N{{H}_{2}}\] |
| V | \[C{{H}_{3}}CON{{H}_{2}}\] | \[C{{H}_{2}}CON{{H}_{2}}\] |
| VI | \[{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}N{{H}_{2}}\] | \[{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}N{{H}_{2}}\] |
| VII | \[C{{H}_{2}}COOH\] | \[C{{H}_{2}}CON{{H}_{2}}\] |
| VIII | \[C{{H}_{2}}OH\] | \[{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}N{{H}_{2}}\] |
| IX | \[{{(C{{H}_{2}})}_{4}}N{{H}_{2}}\] | \[C{{H}_{3}}\] |

Answer
577.2k+ views
Hint: Peptides are short chains of two to fifty amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide that contains more than fifty amino acids are known as proteins.
Complete step by step solution:
A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain of up to approximately fifty amino acids and peptides are short chains of amino acids in which peptide bonds are present. A peptide bond is a type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from carbon number one of one and nitrogen number two along a peptide or protein chain. Peptides can be easily absorbed by the body as compared to proteins because they are smaller and more broken down than proteins. They can more easily penetrate through the skin and intestines which helps them to enter the bloodstream more quickly. Peptides which are of basic nature are positively charged while \[C{{H}_{2}}OH\], \[CON{{H}_{2}}\] and \[C{{H}_{3}}\] are neutral in nature which means it does not carry any positive charge. Thus out of the nine arrangements only 4 are positively charged at pH 7.0.
So, we can say that option A is correct in this case.
Note: Peptides like proteins are very important for us. The main supplements of peptides are eggs, milk, meat, beans, soy, oats and fish etc.
Complete step by step solution:
A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain of up to approximately fifty amino acids and peptides are short chains of amino acids in which peptide bonds are present. A peptide bond is a type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from carbon number one of one and nitrogen number two along a peptide or protein chain. Peptides can be easily absorbed by the body as compared to proteins because they are smaller and more broken down than proteins. They can more easily penetrate through the skin and intestines which helps them to enter the bloodstream more quickly. Peptides which are of basic nature are positively charged while \[C{{H}_{2}}OH\], \[CON{{H}_{2}}\] and \[C{{H}_{3}}\] are neutral in nature which means it does not carry any positive charge. Thus out of the nine arrangements only 4 are positively charged at pH 7.0.
So, we can say that option A is correct in this case.
Note: Peptides like proteins are very important for us. The main supplements of peptides are eggs, milk, meat, beans, soy, oats and fish etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




