
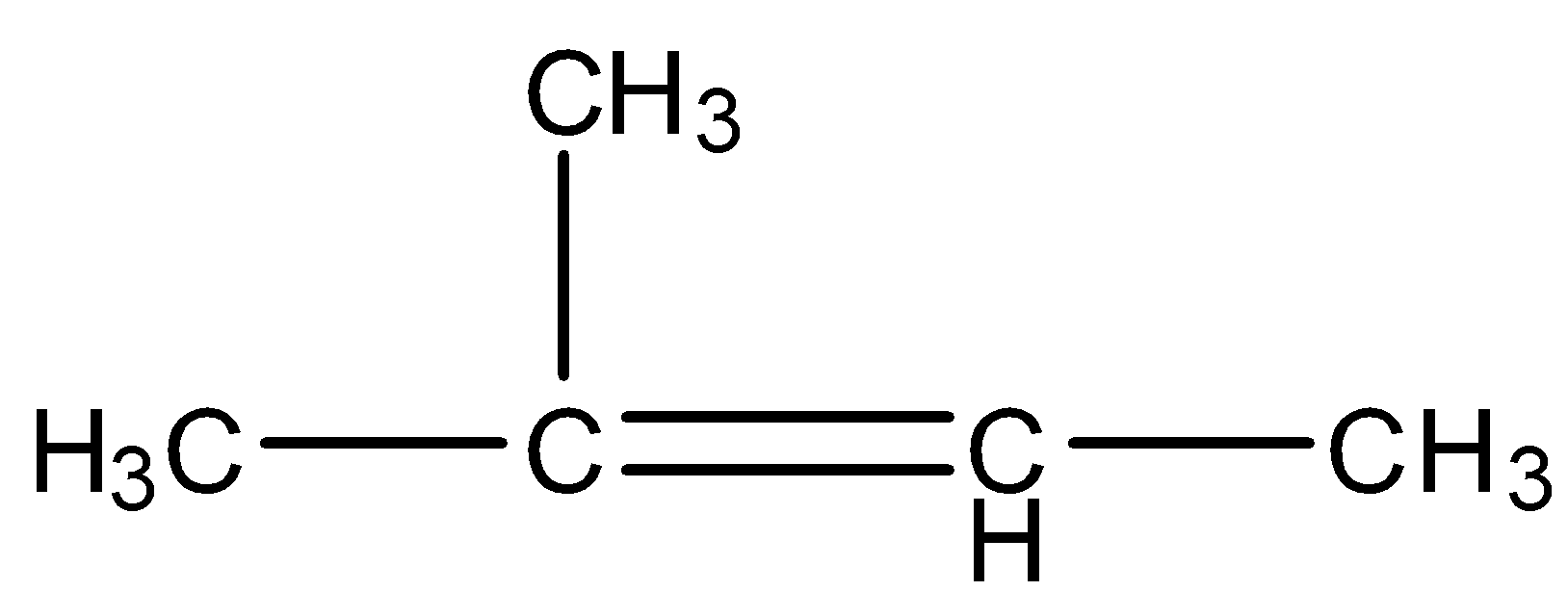
The compound ${{2 - methyl - 2 - butene}}$ on reaction with \[NaI{O_4}\] in the presence of \[KMn{O_4}\] gives:
A.\[C{H_3}COOH\]
B.\[C{H_3}COC{H_3} + C{H_3}COOH\]
C.\[C{H_3}COC{H_3} + C{H_3}CHO\]
D.\[C{H_3}CHO + C{O_2}\]

Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: Alkenes are a class of hydrocarbons (containing carbon and hydrogen) with at least one carbon-carbon double bond. They are also known as olefins and are more reactive due to the presence of the double bond. They undergo additional reactions which take place across the double bond where the weaker pi bond is broken in favor of the formation of stronger sigma bonds. They serve as feedstock for the petrochemical industry because they can participate in a wide variety of reactions.
Complete step by step answer:
When ${{2 - methyl - 2 - butene}}$ reacts within the presence of \[KMn{O_4}\] then the double bond between the two carbon atoms will break and the carbon atoms attached by this bond will be oxidized to form acetone and acetic acid since the reaction takes place in the presence of an oxidizing agent.
The balanced chemical reaction for the above equation is:
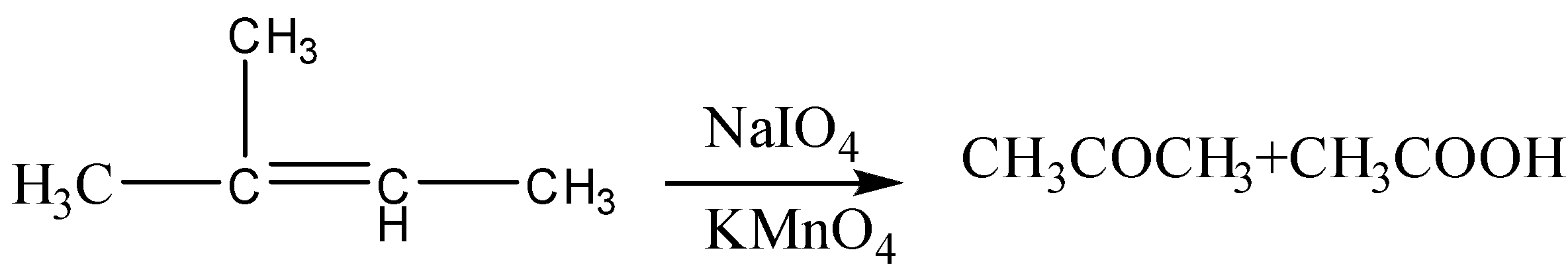
The oxidative cleavage \[KMn{O_4}\] starts with an addition to the pi bond-forming a cyclic intermediate which eventually breaks down into aldehyde and ketone. The aldehyde further oxidizes to the carboxylic acid by potassium permanganate. Since potassium permanganate is such a strong oxidizing agent the end product is often a carboxylic acid.
Note:
Alkenes are generally more reactive than alkanes due to the presence of more electron density in their pi bonds.
Alkenes can be oxidized into an acid and a ketone by strong oxidizing agents.
Initially, an aldehyde and ketone is formed which is further converted into acid and ketone (Aldehyde is oxidized into acid)
The molecular formula of alkene is ${{{C}}_{{n}}}{{{H}}_{{{2n}}}}$
Complete step by step answer:
When ${{2 - methyl - 2 - butene}}$ reacts within the presence of \[KMn{O_4}\] then the double bond between the two carbon atoms will break and the carbon atoms attached by this bond will be oxidized to form acetone and acetic acid since the reaction takes place in the presence of an oxidizing agent.
The balanced chemical reaction for the above equation is:

The oxidative cleavage \[KMn{O_4}\] starts with an addition to the pi bond-forming a cyclic intermediate which eventually breaks down into aldehyde and ketone. The aldehyde further oxidizes to the carboxylic acid by potassium permanganate. Since potassium permanganate is such a strong oxidizing agent the end product is often a carboxylic acid.
Note:
Alkenes are generally more reactive than alkanes due to the presence of more electron density in their pi bonds.
Alkenes can be oxidized into an acid and a ketone by strong oxidizing agents.
Initially, an aldehyde and ketone is formed which is further converted into acid and ketone (Aldehyde is oxidized into acid)
The molecular formula of alkene is ${{{C}}_{{n}}}{{{H}}_{{{2n}}}}$
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




