
Explain sex determination in humans with line diagram.
Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint: A sex-determination system is a biological system that determines the development of sexual characteristics in an organism
Complete answer:
Sex determination in humans occur by XY sex-determination system. Complex mechanisms are responsible for the development of the phenotypic differences between male and female humans from an undifferentiated zygote. In the nucleus of a cell chromosomes are present. In humans, normally 23 pairs of chromosomes are present, out of which 22 pairs are autosomes and the last pair of chromosomes determines the sex of the individuals. Females have XX chromosomes and males have XY chromosome pairs.
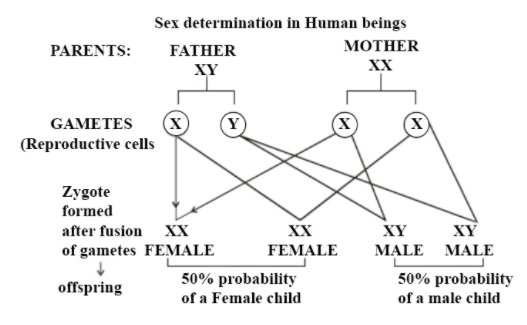
The sex of an individual is determined at the time of fertilization; a chromosome from the sperm cell, either X or Y, fuses with the X chromosome in the egg cell. Depending on which which sperm fertilizes the egg; the sex of the offspring is determined. If sperm containing X chromosome fertilizes the egg then the child will be a girl. If sperm containing Y chromosome fertilizes the egg then the child will be a boy.
Additional information: Females have XX chromosomes and are called homogametic. While males have XY chromosomes and are called heterogametic. Sex chromosomes are also called allosomes.
Note: Sex is influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Sexual differentiation in humans is the process of development of sex differences in humans. It is defined as the development of phenotypic structures consequent to the action of hormones produced following gonadal determination. Sexual differentiation includes development of different genitalia and the internal genital tracts and body hair plays a role in gender identification
Complete answer:
Sex determination in humans occur by XY sex-determination system. Complex mechanisms are responsible for the development of the phenotypic differences between male and female humans from an undifferentiated zygote. In the nucleus of a cell chromosomes are present. In humans, normally 23 pairs of chromosomes are present, out of which 22 pairs are autosomes and the last pair of chromosomes determines the sex of the individuals. Females have XX chromosomes and males have XY chromosome pairs.

The sex of an individual is determined at the time of fertilization; a chromosome from the sperm cell, either X or Y, fuses with the X chromosome in the egg cell. Depending on which which sperm fertilizes the egg; the sex of the offspring is determined. If sperm containing X chromosome fertilizes the egg then the child will be a girl. If sperm containing Y chromosome fertilizes the egg then the child will be a boy.
Additional information: Females have XX chromosomes and are called homogametic. While males have XY chromosomes and are called heterogametic. Sex chromosomes are also called allosomes.
Note: Sex is influenced by genetic and environmental factors. Sexual differentiation in humans is the process of development of sex differences in humans. It is defined as the development of phenotypic structures consequent to the action of hormones produced following gonadal determination. Sexual differentiation includes development of different genitalia and the internal genital tracts and body hair plays a role in gender identification
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




