
The plane wall of an oven is of thickness L = 0.05m and is exposed to the surrounding at 3000K. The outer surface of the oven exposed to the surrounding is at temperature 320K in a steady state. The energy radiated (in $\dfrac{W}{{{m^2}}}K$) by the outer surface is proportional to the temperature difference between the surface and the surrounding with proportionality constant $20\dfrac{W}{{{m^2}}}K$. Find the difference in the temperature of the inner surface and outer surface of the theorem in steady state. The wall has thermal conductivity of $K = 5\dfrac{W}{{{m^2}}}$
(a) 4
(b) 8
(c) 12
(d) 20
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: As this question includes the two different temperatures one of the outside and the other of inside as well as the thermal conductivity state of the wall of the oven so, to solve this question we are going to use the formula of thermal conductivity.
Formula used:
$K = \dfrac{{ql}}{{A\Delta T}}$
$\dfrac{{T.C. \times {\text{A}}}}{{\text{t}}}{\text{ }}\left( {{T_{{\text{inner}}}} - {T_{{\text{outer}}}}} \right) = p\left( {{T_{outer\,surface}} - {T_{{\text{exposed}}\,{\text{to}}\,{\text{surrounding}}}}} \right)$
Complete answer:
Thermal conductivity: In simple language one can define thermal conductivity as the direct transfer of energy in the form of heat and energy through any particle or substance to another. Such transference can only happen if there is a difference between two substances. It is used for measuring the capacity of up to how much any object can conduct heat. The formula of thermal conductivity is $K = \dfrac{{ql}}{{A\Delta T}}$ .
According to the question, the diagram of the question can be as follows.
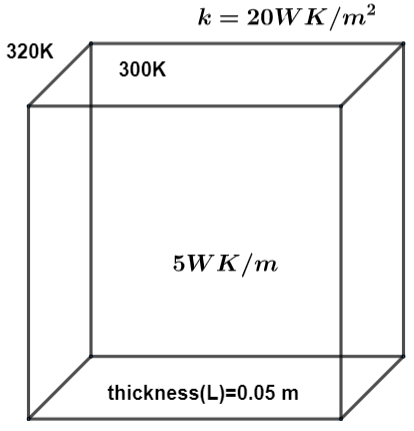
Let us suppose that the inner temperature of the wall is ${T_{inner}}$ and the outer temperature is ${T_{outer}}$. So, under the state of steadiness, the measurement of net heat flow of current is going to be 0.
Therefore,
$\dfrac{{T.C. \times {\text{A}}}}{{\text{t}}}{\text{ }}\left( {{T_{{\text{inner}}}} - {T_{{\text{outer}}}}} \right) = p\left( {{T_{{\text{outer}}\,{\text{surface}}}} - {T_{{\text{exposed}}\,{\text{to}}\,{\text{surrounding}}}}} \right)$
Where T.C. is called thermal conductivity of wall and t is thickness of oven
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{{5A}}{{0.05}}\left( {\Delta T} \right) = 20A\left( {320 - 300} \right) \cr
& \Rightarrow \Delta T = {4^{\text{o}}}C \cr} $
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Note:
Whenever we get numerical we will find out the words that will be helpful in applying the formula to solve it. As in this question, it includes thermal conductivity as a clue so, we will use the formula of it and get the answer. While solving we need to focus on the values of the temperatures. As they are defining different temperatures so, we will also use the temperature differently. If we substitute wrong values in the formula then we will lead towards the wrong answer and hence, the wrong option. The value of temperature may either be in Celsius or Kelvin but here, it is not an issue.
Formula used:
$K = \dfrac{{ql}}{{A\Delta T}}$
$\dfrac{{T.C. \times {\text{A}}}}{{\text{t}}}{\text{ }}\left( {{T_{{\text{inner}}}} - {T_{{\text{outer}}}}} \right) = p\left( {{T_{outer\,surface}} - {T_{{\text{exposed}}\,{\text{to}}\,{\text{surrounding}}}}} \right)$
Complete answer:
Thermal conductivity: In simple language one can define thermal conductivity as the direct transfer of energy in the form of heat and energy through any particle or substance to another. Such transference can only happen if there is a difference between two substances. It is used for measuring the capacity of up to how much any object can conduct heat. The formula of thermal conductivity is $K = \dfrac{{ql}}{{A\Delta T}}$ .
According to the question, the diagram of the question can be as follows.

Let us suppose that the inner temperature of the wall is ${T_{inner}}$ and the outer temperature is ${T_{outer}}$. So, under the state of steadiness, the measurement of net heat flow of current is going to be 0.
Therefore,
$\dfrac{{T.C. \times {\text{A}}}}{{\text{t}}}{\text{ }}\left( {{T_{{\text{inner}}}} - {T_{{\text{outer}}}}} \right) = p\left( {{T_{{\text{outer}}\,{\text{surface}}}} - {T_{{\text{exposed}}\,{\text{to}}\,{\text{surrounding}}}}} \right)$
Where T.C. is called thermal conductivity of wall and t is thickness of oven
$\eqalign{
& \dfrac{{5A}}{{0.05}}\left( {\Delta T} \right) = 20A\left( {320 - 300} \right) \cr
& \Rightarrow \Delta T = {4^{\text{o}}}C \cr} $
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Note:
Whenever we get numerical we will find out the words that will be helpful in applying the formula to solve it. As in this question, it includes thermal conductivity as a clue so, we will use the formula of it and get the answer. While solving we need to focus on the values of the temperatures. As they are defining different temperatures so, we will also use the temperature differently. If we substitute wrong values in the formula then we will lead towards the wrong answer and hence, the wrong option. The value of temperature may either be in Celsius or Kelvin but here, it is not an issue.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




