
The orthocenter of the triangle with vertices $\left( {2,\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{2}} \right)$, $\left( {\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)$, $\left( {2,\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)$ is
A. $\left( {\dfrac{3}{2},\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 3}}{6}} \right)$
B. $\left( {2,\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)$
C. $\left( {\dfrac{5}{4},\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 2}}{4}} \right)$
D. $\left( {\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)$
Answer
553.2k+ views
Hint: Orthocenter of a triangle is defined as the point where perpendiculars drawn from the vertices to the opposite side will intersect each other. For a right-angled triangle, the orthocenter lies at the vertex containing the right angle.
Step By Step Solution:
Let us assume the points as
A = $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ = $\left( {2,\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{2}} \right)$
B = $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ = $\left( {\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)$
C = $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)$ = $\left( {2,\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)$
Firstly, we calculate the slope of the line AC using the formula,
Slope of AC = $\dfrac{{{y_3} - {y_1}}}{{{x_3} - {x_1}}}$
$\Rightarrow$ Slope of AC = $\dfrac{{\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2} - \left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{2}} \right)}}{{2 - 2}}$
$\Rightarrow$ Slope of AC = $\infty$
As slope of the line is infinity, the line AC will be perpendicular to the X-axis
Then we calculate the slope of the line BC using the formula
Slope of BC = $\dfrac{{{y_3} - {y_2}}}{{{x_3} - {x_2}}}$
$\Rightarrow$ Slope of BC = $\dfrac{{\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2} - \left( {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)}}{{2 - \dfrac{1}{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow$ Slope of BC = 0
As the slope of the line is equal to zero, the line BC will be parallel to X-axis.
Therefore $\Delta ABC$ will be a right angle triangle with $C = 90^\circ$
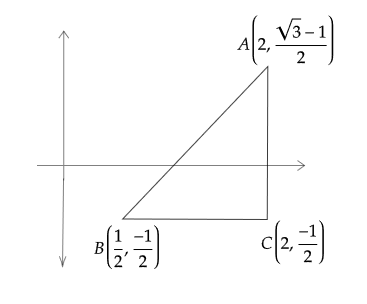
For a right-angled triangle, the orthocenter will be the vertex having an angle of 90 degrees.
$\therefore$ The point $\left( {2,\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)$ will be the orthocenter of the
triangle formed by the given vertices.
Therefore the correct answer is Option (B)
Note:
After finding the lines with slope equal to infinity and slope equal to zero, the common point from both the lines should be selected as the vertex containing the right angle. In the above calculation, the slope of AC is infinite and the slope of BC is zero. So point C is selected as a vertex having the right angle.
Step By Step Solution:
Let us assume the points as
A = $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ = $\left( {2,\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{2}} \right)$
B = $\left( {{x_2},{y_2}} \right)$ = $\left( {\dfrac{1}{2},\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)$
C = $\left( {{x_3},{y_3}} \right)$ = $\left( {2,\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)$
Firstly, we calculate the slope of the line AC using the formula,
Slope of AC = $\dfrac{{{y_3} - {y_1}}}{{{x_3} - {x_1}}}$
$\Rightarrow$ Slope of AC = $\dfrac{{\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2} - \left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 - 1}}{2}} \right)}}{{2 - 2}}$
$\Rightarrow$ Slope of AC = $\infty$
As slope of the line is infinity, the line AC will be perpendicular to the X-axis
Then we calculate the slope of the line BC using the formula
Slope of BC = $\dfrac{{{y_3} - {y_2}}}{{{x_3} - {x_2}}}$
$\Rightarrow$ Slope of BC = $\dfrac{{\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2} - \left( {\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)}}{{2 - \dfrac{1}{2}}}$
$\Rightarrow$ Slope of BC = 0
As the slope of the line is equal to zero, the line BC will be parallel to X-axis.
Therefore $\Delta ABC$ will be a right angle triangle with $C = 90^\circ$

For a right-angled triangle, the orthocenter will be the vertex having an angle of 90 degrees.
$\therefore$ The point $\left( {2,\dfrac{{ - 1}}{2}} \right)$ will be the orthocenter of the
triangle formed by the given vertices.
Therefore the correct answer is Option (B)
Note:
After finding the lines with slope equal to infinity and slope equal to zero, the common point from both the lines should be selected as the vertex containing the right angle. In the above calculation, the slope of AC is infinite and the slope of BC is zero. So point C is selected as a vertex having the right angle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




