
The meiosis takes place in
A. Apical meristem
B. Intercalary meristem
C. Reproductive cells
D. Vegetative cells
Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: In sexually reproducing species used to generate gametes, such as sperm or egg cells, meiosis is a special form of cell division of germ cells. It requires two division rounds that eventually result in four cells with just one copy of each paternal and maternal chromosome. It requires two division rounds that eventually result in four cells with just one copy of each paternal and maternal chromosome.
Complete answer:
In apical meristem, intercalary meristem and vegetative cells mitosis occurs because tissues and organ development require constant cellular growth.
In reproductive cells, meiosis usually occurs. By undergoing one cycle of DNA replication followed by two divisions, meiosis ends in four haploid daughter cells: homologous chromosomes are divided in the first phase and sister chromatids are separated in the second division. Haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes are formed by Meiosis. The resulting zygote is diploid again when two gametes fuse.
Genetic material of each chromosome's paternal and maternal copies is crossed over, producing new code variations on each chromosome. Later, during fertilisation, the haploid cells from a male and female formed by meiosis can combine to form a cell again with two copies of each chromosome, the zygote.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
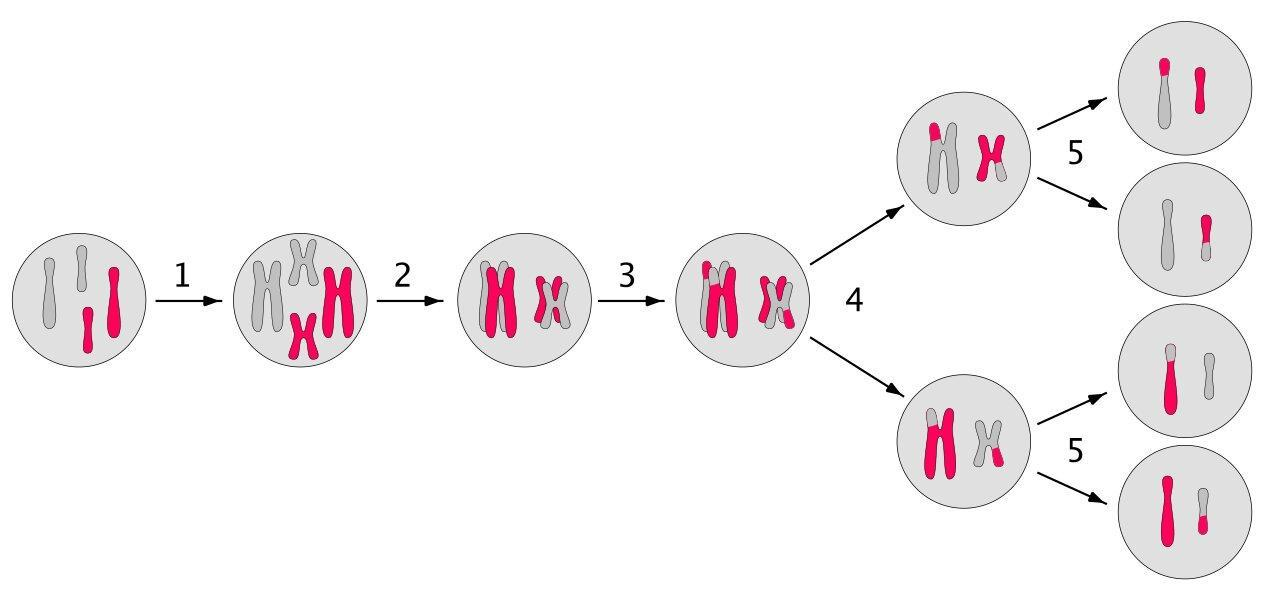
Note: Meiosis, in eukaryotes, is a central occurrence in the sexual cycle. Meiosis occurs in all single-celled and multicellular sexually reproducing species (which are all eukaryotes), including mammals, plants and fungi. For oogenesis and spermatogenesis, it is an important technique. The most known cause of miscarriage and the most common genetic cause of developmental defects are errors in meiosis that result in aneuploidy (an irregular number of chromosomes).
Complete answer:
In apical meristem, intercalary meristem and vegetative cells mitosis occurs because tissues and organ development require constant cellular growth.
In reproductive cells, meiosis usually occurs. By undergoing one cycle of DNA replication followed by two divisions, meiosis ends in four haploid daughter cells: homologous chromosomes are divided in the first phase and sister chromatids are separated in the second division. Haploid gametes with one set of 23 chromosomes are formed by Meiosis. The resulting zygote is diploid again when two gametes fuse.
Genetic material of each chromosome's paternal and maternal copies is crossed over, producing new code variations on each chromosome. Later, during fertilisation, the haploid cells from a male and female formed by meiosis can combine to form a cell again with two copies of each chromosome, the zygote.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.

Note: Meiosis, in eukaryotes, is a central occurrence in the sexual cycle. Meiosis occurs in all single-celled and multicellular sexually reproducing species (which are all eukaryotes), including mammals, plants and fungi. For oogenesis and spermatogenesis, it is an important technique. The most known cause of miscarriage and the most common genetic cause of developmental defects are errors in meiosis that result in aneuploidy (an irregular number of chromosomes).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




