
The magnetic field at the centre of coil of $n$ turns, bent in the form of a square of side $2l$, carrying current $i$, is :
A. $\dfrac{\sqrt{2}{{\mu }_{0}}ni}{\pi l}$
B. $\dfrac{\sqrt{2}{{\mu }_{0}}ni}{2\pi l}$
C. $\dfrac{\sqrt{2}{{\mu }_{0}}ni}{4\pi l}$
D. $\dfrac{2{{\mu }_{0}}ni}{\pi l}$
Answer
563.1k+ views
Hint:Use the formula for the magnitude of the magnetic field at a point, which is at a perpendicular distance d from the straight conductor carrying some current. Make use of the symmetry of a square.Magnetic field is an invisible space around a magnetic object. A magnetic field is basically used to describe the distribution of magnetic force around a magnetic object.
Formula used:
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\pi d}\left( \sin {{\theta }_{1}}+\sin {{\theta }_{2}} \right)$
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that there is coil carrying current i, in the shape of a square. The coils have $n$ turns and the length of each side of the square is $2l$. Now, consider a straight conductor carrying current $i$ of length l. The magnitude of the magnetic field at a point, which is at a perpendicular distance d from the straight conductor (as shown in the figure) is given as $B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\pi d}\left( \sin {{\theta }_{1}}+\sin {{\theta }_{2}} \right)$ ….. (i).
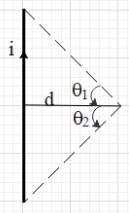
The direction of the magnetic field is given by the right hand thumb rule.
In the given case, the coil is in the form of a square.
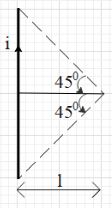
Due to symmetry, the magnitude of the magnetic field produced by each side of the square, at the centre of the coil is the same. From the right hand thumb rule, the direction of the four magnetic field fields will be inwards. Let us calculate the magnetic field due to any one side. In the figure we can see that for each side the angles ${{\theta }_{1}}$ and ${{\theta }_{2}}$ are equal to ${{45}^{\circ }}$ each. And the perpendicular distance of the centre from the side is l.
Now, substitute ${{\theta }_{1}}={{\theta }_{2}}={{45}^{\circ }}$ and $d=l$.
$\Rightarrow B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\pi l}\left( \sin {{45}^{\circ }}+\sin {{45}^{\circ }} \right)$
$\Rightarrow B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\pi l}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}\pi l}$.
This means that the magnetic field produced by each side of the square at the centre is equal to $B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}\pi l}$
Since the direction of all four magnetic fields is same, the magnetic field produced by one such coil at the centre is equal to $4B=4\left( \dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}\pi l} \right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}{{\mu }_{0}}i}{\pi l}$.
It is given that there are $n$ turns in the coil. Therefore, the net magnetic field at the centre of the coils is equal to $\dfrac{\sqrt{2}n{{\mu }_{0}}i}{\pi l}$.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:In case of a straight current carrying conductor, the right hand thumb rule says that if we point our thumb in the direction of the current flowing in the conductor, then in the direction in which we curl our other figures will give the direction of the magnetic field line.
Formula used:
$B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\pi d}\left( \sin {{\theta }_{1}}+\sin {{\theta }_{2}} \right)$
Complete step by step answer:
It is given that there is coil carrying current i, in the shape of a square. The coils have $n$ turns and the length of each side of the square is $2l$. Now, consider a straight conductor carrying current $i$ of length l. The magnitude of the magnetic field at a point, which is at a perpendicular distance d from the straight conductor (as shown in the figure) is given as $B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\pi d}\left( \sin {{\theta }_{1}}+\sin {{\theta }_{2}} \right)$ ….. (i).

The direction of the magnetic field is given by the right hand thumb rule.
In the given case, the coil is in the form of a square.

Due to symmetry, the magnitude of the magnetic field produced by each side of the square, at the centre of the coil is the same. From the right hand thumb rule, the direction of the four magnetic field fields will be inwards. Let us calculate the magnetic field due to any one side. In the figure we can see that for each side the angles ${{\theta }_{1}}$ and ${{\theta }_{2}}$ are equal to ${{45}^{\circ }}$ each. And the perpendicular distance of the centre from the side is l.
Now, substitute ${{\theta }_{1}}={{\theta }_{2}}={{45}^{\circ }}$ and $d=l$.
$\Rightarrow B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\pi l}\left( \sin {{45}^{\circ }}+\sin {{45}^{\circ }} \right)$
$\Rightarrow B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{4\pi l}\left( \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}} \right)=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}\pi l}$.
This means that the magnetic field produced by each side of the square at the centre is equal to $B=\dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}\pi l}$
Since the direction of all four magnetic fields is same, the magnetic field produced by one such coil at the centre is equal to $4B=4\left( \dfrac{{{\mu }_{0}}i}{2\sqrt{2}\pi l} \right)=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}{{\mu }_{0}}i}{\pi l}$.
It is given that there are $n$ turns in the coil. Therefore, the net magnetic field at the centre of the coils is equal to $\dfrac{\sqrt{2}n{{\mu }_{0}}i}{\pi l}$.
Hence, the correct option is A.
Note:In case of a straight current carrying conductor, the right hand thumb rule says that if we point our thumb in the direction of the current flowing in the conductor, then in the direction in which we curl our other figures will give the direction of the magnetic field line.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




