
Draw the diagram of the human sperm and label its parts. Describe it in a few sentences.
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: The sperm is the male gamete arising from the male reproductive system. It is a microscopic structure, motile in nature, and fertilizes the female gamete, the egg. In mammals, the motile sperm travels with the help of a fluid known as semen.
Complete step by step answer:
- The human sperm can be divided into the head, the neck, the middle piece, and the tail.
- The entire body is enveloped by a plasma membrane.
- The head contains an elongated haploid nucleus that encloses the genetic material. The anterior end of the head is covered with a cap- like structure known as the acrosome.
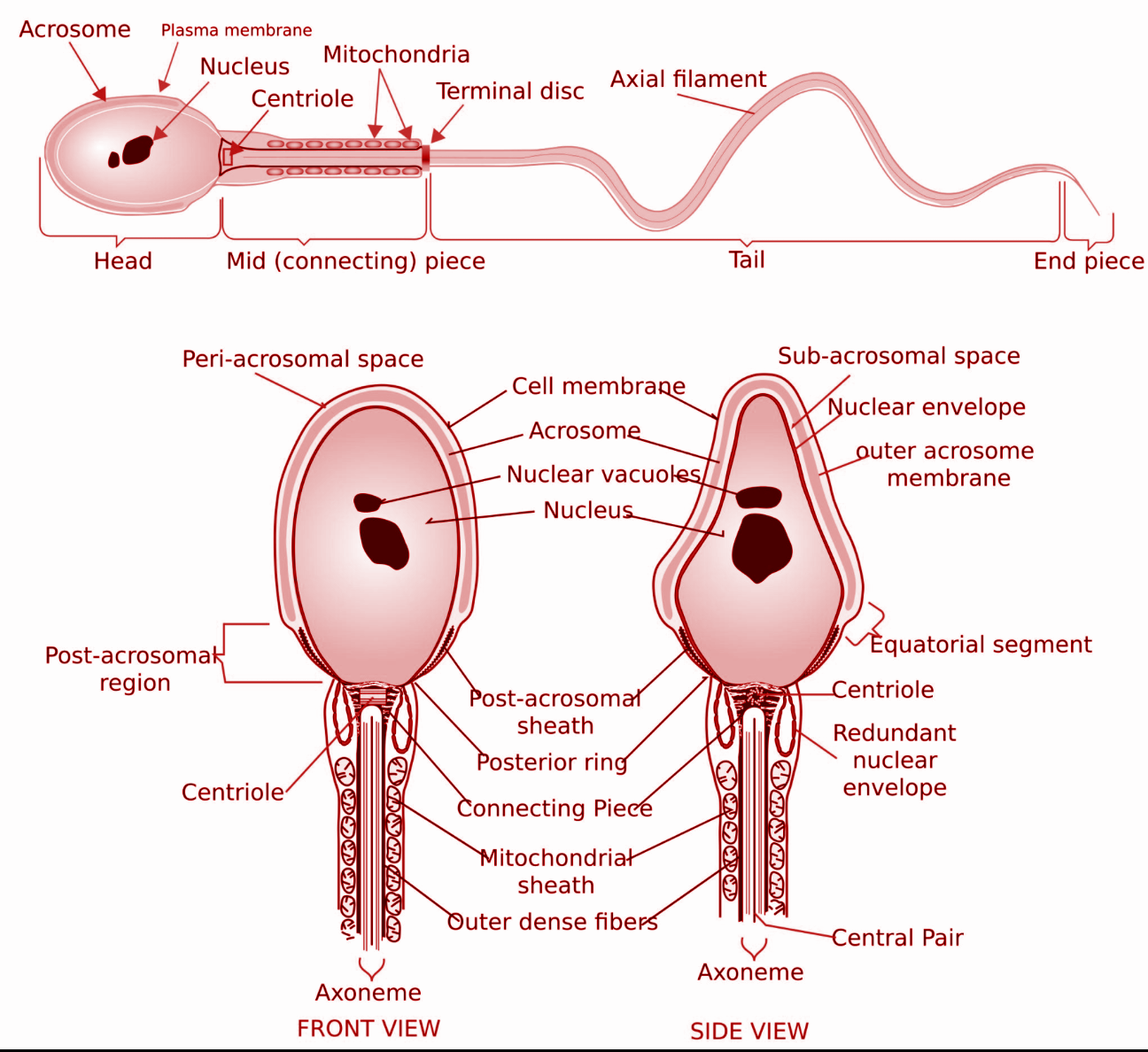
- The acrosome contains enzymes such as hyaluronidase that help in fertilization of the ovum.
- The middle piece contains mitochondria that are responsible for providing energy for the movement of the tail. This facilitates sperm motility that is essential for fertilization.
- The tail is the longest part and is also called the flagellum. Its wave- like motion propels the sperm forward and aids it in swimming and penetration of the egg.
Additional Information:
- Sperm cells are formed during a process called spermatogenesis. It takes place in the seminiferous tubules of testes in humans.
- The formation of sperm takes place by meiotic division.
- Semen, the fluid required to transport and provide nutrition to the sperm cells is produced in the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and urethral glands.
- During fertilization, the sperm activates the oocyte and provides the haploid paternal genome and the centriole.
Note:
- Sperm cells cannot divide and have a limited lifespan.
- The human male ejaculates 200-300 million sperm in one coitus. In normal fertility in a healthy human, at least $60\%$ of the sperms must have normal structure and size and at least $40\%$ of them must show rigorous motility.
- Sperm cells can survive inside the female reproductive tract for more than 5 days after coitus.
Complete step by step answer:
- The human sperm can be divided into the head, the neck, the middle piece, and the tail.
- The entire body is enveloped by a plasma membrane.
- The head contains an elongated haploid nucleus that encloses the genetic material. The anterior end of the head is covered with a cap- like structure known as the acrosome.

- The acrosome contains enzymes such as hyaluronidase that help in fertilization of the ovum.
- The middle piece contains mitochondria that are responsible for providing energy for the movement of the tail. This facilitates sperm motility that is essential for fertilization.
- The tail is the longest part and is also called the flagellum. Its wave- like motion propels the sperm forward and aids it in swimming and penetration of the egg.
Additional Information:
- Sperm cells are formed during a process called spermatogenesis. It takes place in the seminiferous tubules of testes in humans.
- The formation of sperm takes place by meiotic division.
- Semen, the fluid required to transport and provide nutrition to the sperm cells is produced in the seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and urethral glands.
- During fertilization, the sperm activates the oocyte and provides the haploid paternal genome and the centriole.
Note:
- Sperm cells cannot divide and have a limited lifespan.
- The human male ejaculates 200-300 million sperm in one coitus. In normal fertility in a healthy human, at least $60\%$ of the sperms must have normal structure and size and at least $40\%$ of them must show rigorous motility.
- Sperm cells can survive inside the female reproductive tract for more than 5 days after coitus.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




