
Given below is the flow chart of sewage treatment. Identify A, B, C, and D and select the correct option.
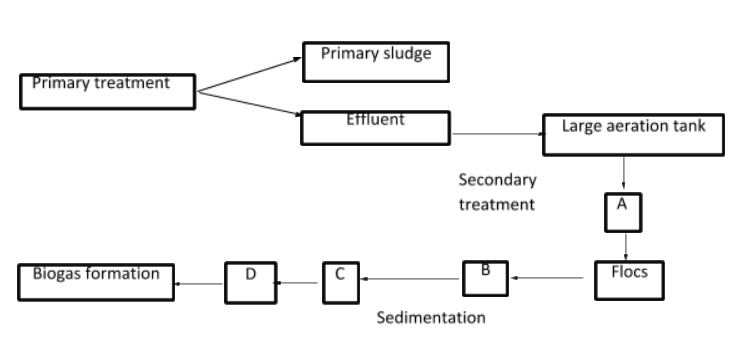
I. A- Mechanical agitation, B- increased BOD, C- Activated sludge, D- Aerobic Sludge digesters.
II. A- Mechanical agitation, B- reduced BOD, C- Activated sludge, D- Anaerobic, sludge digesters.
III. A- Microbial digestion, B- Activated sludge, C- Reduced BOD, D- Anaerobic sludge digesters.
IV. A- Microbial digestion, B- Mechanical agitation, C- Reduced BOD, D- Anaerobic sludge digesters.

Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: The process of removal of contaminants from municipal wastewater and industrial wastewater is called sewage treatment. Depending upon the type of removal of contaminants it is further categorized as primary and secondary sewage treatment.
Complete answer: Sewage treatment removes contaminants through physical, chemical, and biological processes. After undergoing these processes, the treated wastewater or effluent is safe enough to release into the environment. Sewage treatment is also referred to as wastewater treatment. The whole process includes five steps: pre – treatment, primary treatment, secondary treatment, tertiary treatment and fourth treatment stage. A physical process which involves the removal of large impurities from wastewater is termed as primary treatment. Heavy solid waste is allowed to settle at the bottom whereas oil, grease, and lighter solid waste float on the surface in primary treatment. After removal of settled and floating materials the remaining liquid waste may be discharged or subjected for secondary treatment. Dissolved and suspended biological matter are removed in secondary treatment. Water-borne microorganisms are responsible for the process of secondary treatment. The filtered effluent is sent to the large aeration tank where mechanical agitation takes place. The flocs produced by mechanical agitation have reduced biological oxygen demand (BOD). This is allowed to sediment to form activated sludge. The activated sludge is digested by microorganisms called anaerobic sludge digesters to produce biogas.
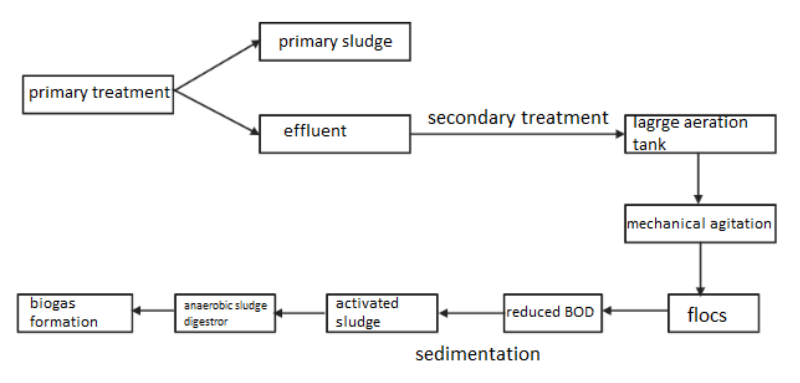
So, option II is the correct option.
Note: The main difference between primary and secondary treatment is that primary treatment is a physical process in which large impurities are removed whereas secondary treatment is a biological process performed using microbes. Biogas consists of methane, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen sulphite.
Complete answer: Sewage treatment removes contaminants through physical, chemical, and biological processes. After undergoing these processes, the treated wastewater or effluent is safe enough to release into the environment. Sewage treatment is also referred to as wastewater treatment. The whole process includes five steps: pre – treatment, primary treatment, secondary treatment, tertiary treatment and fourth treatment stage. A physical process which involves the removal of large impurities from wastewater is termed as primary treatment. Heavy solid waste is allowed to settle at the bottom whereas oil, grease, and lighter solid waste float on the surface in primary treatment. After removal of settled and floating materials the remaining liquid waste may be discharged or subjected for secondary treatment. Dissolved and suspended biological matter are removed in secondary treatment. Water-borne microorganisms are responsible for the process of secondary treatment. The filtered effluent is sent to the large aeration tank where mechanical agitation takes place. The flocs produced by mechanical agitation have reduced biological oxygen demand (BOD). This is allowed to sediment to form activated sludge. The activated sludge is digested by microorganisms called anaerobic sludge digesters to produce biogas.

So, option II is the correct option.
Note: The main difference between primary and secondary treatment is that primary treatment is a physical process in which large impurities are removed whereas secondary treatment is a biological process performed using microbes. Biogas consists of methane, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen sulphite.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




