
The length of the diagonals of a rhombus are $6cm$ and $8cm$ . Find the length of each side of the rhombus.
(a) $2cm$
(b) $3cm$
(c) $4cm$
(d) $5cm$
Answer
552.6k+ views
Hint: In the above question, we are given a rhombus with the length of the both diagonals. Now, we know that rhombus is a quadrilateral which has all the sides equal and the opposite angles are equal. Now, we know that the radius is half of diameter. We will use this to find the lengths of some sides. Later we will use the pythagoras theorem to find the length of the sides.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now, the given figure denotes the rhombus
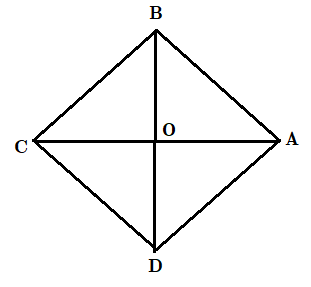
So,\[AC=8cm\] and \[BD=6cm\]
Now, we know that the diagonals of rhombus divide each other in two equal halves.
Hence, \[AO=4cm\] and \[OD=6cm\]
Now, we know that diagonals of rhombus bisect each other perpendicularly.
So, we can say that \[\angle AOD=90{}^\circ \]
In right \[\Delta AOD\] ,
We know that, \[AO=4cm\] and \[OD=3cm\]
So, by using the Pythagoras Theorem,
$\Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}=A{{O}^{2}}+O{{D}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}={{\left( 4 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow AD=5cm$
So, \[AD\] is \[5cm\]
So, the sides of the rhombus are of length \[5cm\]
Hence, the correct option is \[d\].
Note: Remember the properties of Rhombus:
All sides of the rhombus are equal.
The opposite sides of rhombus are parallel.
Opposite angles of rhombus are equal.
In a rhombus, diagonals bisect each other at right angles.
Diagonals bisect the angles of a rhombus.
The sum of two adjacent angles is equal to \[180\] degrees.
Diagonals of rhombus divide each other in two equal halves.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now, the given figure denotes the rhombus

So,\[AC=8cm\] and \[BD=6cm\]
Now, we know that the diagonals of rhombus divide each other in two equal halves.
Hence, \[AO=4cm\] and \[OD=6cm\]
Now, we know that diagonals of rhombus bisect each other perpendicularly.
So, we can say that \[\angle AOD=90{}^\circ \]
In right \[\Delta AOD\] ,
We know that, \[AO=4cm\] and \[OD=3cm\]
So, by using the Pythagoras Theorem,
$\Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}=A{{O}^{2}}+O{{D}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow A{{D}^{2}}={{\left( 4 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}$
$\Rightarrow AD=5cm$
So, \[AD\] is \[5cm\]
So, the sides of the rhombus are of length \[5cm\]
Hence, the correct option is \[d\].
Note: Remember the properties of Rhombus:
All sides of the rhombus are equal.
The opposite sides of rhombus are parallel.
Opposite angles of rhombus are equal.
In a rhombus, diagonals bisect each other at right angles.
Diagonals bisect the angles of a rhombus.
The sum of two adjacent angles is equal to \[180\] degrees.
Diagonals of rhombus divide each other in two equal halves.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

What is the Full Form of ISI and RAW

How do you find the valency of chlorine sulphur and class 9 chemistry CBSE

What are the major achievements of the UNO class 9 social science CBSE

Explain the importance of pH in everyday life class 9 chemistry CBSE

Differentiate between parenchyma collenchyma and sclerenchyma class 9 biology CBSE




