
The inradius of a regular tetrahedron of side length a is
A. $ \sqrt {\dfrac{2}{3}a} $
B. $ \sqrt {\dfrac{3}{2}a} $
C. $ \dfrac{a}{{\sqrt 6 }} $
D. $ \dfrac{a}{{2\sqrt 6 }} $
Answer
565.5k+ views
Hint: In the problem they have asked to find the inradius of a regular tetrahedron. Let the side length of a tetrahedron be $ a $ , and let its base lie in the plane $ z = 0 $ with one vertex lying along the positive $ x $ axis. Thereafter, assuming the inradius and the circumference to be $ r $ and $ R $ respectively.
Complete step-by-step answer:
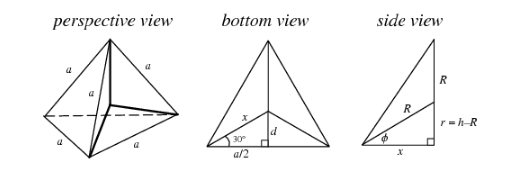
ording to the given information, we have,
Side length of a tetrahedron is $ a $ .
Let its base lie in the plane $ z = 0 $ with one vertex lying along the positive $ x $ axis. Assuming the inradius and the circumference to be $ r $ and $ R $ respectively and also the height and area to be $ h $ and $ A $ respectively.
Then the polyhedron vertices of this tetrahedron are located at ( $ x,0,0 $ ), ( $ - d, \pm \dfrac{a}{2},0 $ ), and ( $ 0,0,h $ ), where,
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{\dfrac{a}{2}}}{{\cos (\dfrac{\pi }{6})}}\] $ = \dfrac{1}{3}\sqrt {3}a $
Thereafter on simplifying ‘ $ d $ ’ we get,
$ \Rightarrow d = \sqrt {{x^2} - {{(\dfrac{1}{2}a)}^2}} $ $ = \dfrac{1}{6}\sqrt {3}a $
This further gives the area of the base as,
$ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2}a(R + x) $ $ = \dfrac{1}{4}\sqrt 3 {a^2} $
Therefore we get the height of the tetrahedron to be,
\[ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {{a^2} - {x^2}} \] $ = \dfrac{1}{3}\sqrt 6 a $
Further, the circumference of the tetrahedron is calculated from,
$ {x^2} + {(h - R)^2} = {R^2} $
$ {x^2} + {h^2} - 2hR + {R^2} = {R^2} $
Now on substituting the values already calculated in the above given equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{{x^2} + {h^2}}}{{2h}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{4}\sqrt 6 a $
Finally, we calculate the inradius $ r $ from,
$ r = h - R $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{12}}\sqrt 6 a $ $ = \dfrac{a}{{2\sqrt 6 }} $
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Tetrahedron is the simplest of the entire ordinary convex polygon and the only one which has fewer than five faces (four faces). The tetrahedron has 7 axes of symmetry: $ ^4{C_3} $ (axes connecting vertices with the centers of the opposite faces) and $ ^3{C_2} $ (the axes connecting the midpoints of opposite sides).
Complete step-by-step answer:

ording to the given information, we have,
Side length of a tetrahedron is $ a $ .
Let its base lie in the plane $ z = 0 $ with one vertex lying along the positive $ x $ axis. Assuming the inradius and the circumference to be $ r $ and $ R $ respectively and also the height and area to be $ h $ and $ A $ respectively.
Then the polyhedron vertices of this tetrahedron are located at ( $ x,0,0 $ ), ( $ - d, \pm \dfrac{a}{2},0 $ ), and ( $ 0,0,h $ ), where,
\[ \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{{\dfrac{a}{2}}}{{\cos (\dfrac{\pi }{6})}}\] $ = \dfrac{1}{3}\sqrt {3}a $
Thereafter on simplifying ‘ $ d $ ’ we get,
$ \Rightarrow d = \sqrt {{x^2} - {{(\dfrac{1}{2}a)}^2}} $ $ = \dfrac{1}{6}\sqrt {3}a $
This further gives the area of the base as,
$ \Rightarrow A = \dfrac{1}{2}a(R + x) $ $ = \dfrac{1}{4}\sqrt 3 {a^2} $
Therefore we get the height of the tetrahedron to be,
\[ \Rightarrow h = \sqrt {{a^2} - {x^2}} \] $ = \dfrac{1}{3}\sqrt 6 a $
Further, the circumference of the tetrahedron is calculated from,
$ {x^2} + {(h - R)^2} = {R^2} $
$ {x^2} + {h^2} - 2hR + {R^2} = {R^2} $
Now on substituting the values already calculated in the above given equation we get,
$ \Rightarrow R = \dfrac{{{x^2} + {h^2}}}{{2h}} $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{4}\sqrt 6 a $
Finally, we calculate the inradius $ r $ from,
$ r = h - R $
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{12}}\sqrt 6 a $ $ = \dfrac{a}{{2\sqrt 6 }} $
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: Tetrahedron is the simplest of the entire ordinary convex polygon and the only one which has fewer than five faces (four faces). The tetrahedron has 7 axes of symmetry: $ ^4{C_3} $ (axes connecting vertices with the centers of the opposite faces) and $ ^3{C_2} $ (the axes connecting the midpoints of opposite sides).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




