
The area of the quadrilaterals, the coordinates of whose vertices are (1,2), (6,2), (5,3) and (3,4) are
A.$\dfrac{9}{2}$
B.5
C.$\dfrac{{11}}{2}$
D.11
Answer
580.8k+ views
Hint: In this question, first we need to draw a quadrilateral ABCD divided in two triangles by making diagonal. After that we will apply the area of triangle formula in both the triangles and in the end, we will find the sum of both the areas. Let the vertices of the quadrilateral be A(1,2),B (6,2), C(5,3) and D(3,4) join BD to form two triangles $\vartriangle BCD$ and $\vartriangle BCD$.
As we know that,
Area of triangle with coordinates $(x,y),({x_2},{y_2}),({x_3},{y_3})$is given: $\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}({y_2} - {y_1}) + {x_2}({y_3} - {y_1}) + {x_3}({y_1} - {y_2})} \right]$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us divide the quadrilateral ABCD into two triangles ABD and BCD.
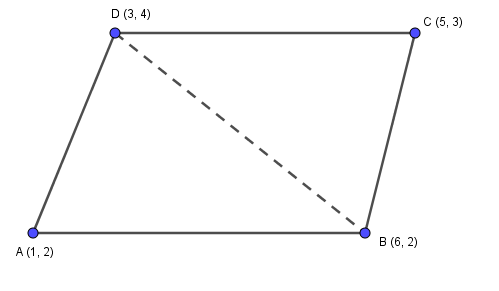
Now, by using the formula.
Area of triangle with coordinates or vertices $(x,y),({x_2},{y_2}),({x_3},{y_3})$ is given by the formula $\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}({y_2} - {y_1}) + {x_2}({y_3} - {y_1}) + {x_3}({y_1} - {y_2})} \right]$.
Area of triangle ABD with coordinates A (1,2), B (6,2) and D (3,4).
$\Rightarrow$ Area of triangle ABD = $\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {1(2 - 1) + 6(4 - 2) + 3(2 - 2)} \right]$
$
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {1 \times - 2 + 6 \times 2 + 3 \times 0} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 2 + 12 + 0} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10 \\
= 5\,sq.units \\
$
Again, Area of triangle BCD with coordinates B (6,2), C (5,3) and D (3,4).
$\Rightarrow$ Area of triangle BCD $ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {6(3 - 4) + 5(4 - 2) + 3(2 - 3)} \right]$
$
= \dfrac{1}{2}(6 \times - 1 + 5 \times 2 + 3 \times - 1) \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}(10 - 9) \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} = \,0.5\,sq.units \\
$$$
Now, Area of quadrilateral ABCD = Area of triangle ABD + Area of triangle BCD
= 5 sq. units + 0.5 sq. units
= 5.5 sq. units.
Note: In this question we need to calculate the area of two triangles. So that’s why we used triangle formulas. Also, we have used the concept of quadrilateral so we can also define it: A quadrilateral is a plane figure that has four sides or edges, and also has four corners or vertices. Quadrilateral with four sides like rectangle, rhombus, square, trapezoid, parallelogram, trapezium and kite. In a quadrilateral total interior angle is 360 $^\circ $. Every quadrilateral has four vertices, four angles, and four sides.
As we know that,
Area of triangle with coordinates $(x,y),({x_2},{y_2}),({x_3},{y_3})$is given: $\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}({y_2} - {y_1}) + {x_2}({y_3} - {y_1}) + {x_3}({y_1} - {y_2})} \right]$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us divide the quadrilateral ABCD into two triangles ABD and BCD.

Now, by using the formula.
Area of triangle with coordinates or vertices $(x,y),({x_2},{y_2}),({x_3},{y_3})$ is given by the formula $\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {{x_1}({y_2} - {y_1}) + {x_2}({y_3} - {y_1}) + {x_3}({y_1} - {y_2})} \right]$.
Area of triangle ABD with coordinates A (1,2), B (6,2) and D (3,4).
$\Rightarrow$ Area of triangle ABD = $\dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {1(2 - 1) + 6(4 - 2) + 3(2 - 2)} \right]$
$
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {1 \times - 2 + 6 \times 2 + 3 \times 0} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ { - 2 + 12 + 0} \right] \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} \times 10 \\
= 5\,sq.units \\
$
Again, Area of triangle BCD with coordinates B (6,2), C (5,3) and D (3,4).
$\Rightarrow$ Area of triangle BCD $ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {6(3 - 4) + 5(4 - 2) + 3(2 - 3)} \right]$
$
= \dfrac{1}{2}(6 \times - 1 + 5 \times 2 + 3 \times - 1) \\
= \dfrac{1}{2}(10 - 9) \\
= \dfrac{1}{2} = \,0.5\,sq.units \\
$$$
Now, Area of quadrilateral ABCD = Area of triangle ABD + Area of triangle BCD
= 5 sq. units + 0.5 sq. units
= 5.5 sq. units.
Note: In this question we need to calculate the area of two triangles. So that’s why we used triangle formulas. Also, we have used the concept of quadrilateral so we can also define it: A quadrilateral is a plane figure that has four sides or edges, and also has four corners or vertices. Quadrilateral with four sides like rectangle, rhombus, square, trapezoid, parallelogram, trapezium and kite. In a quadrilateral total interior angle is 360 $^\circ $. Every quadrilateral has four vertices, four angles, and four sides.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




