
Solve the following system of linear equations graphically:
3x+y-11=0, x-y-1=0.
Shade the region bounded by these lines and y-axis. Also, find the area of the region bounded by these lines and y-axis.
Answer
610.5k+ views
Hint: Draw the graph of the two given equations. To draw the graph of a straight line, we need at least two points. So, choose one of the equations and substitute x = 0, determine y, then substitute y = 0, determine x. Now, apply the same process for the second equation. Plot the graph of the two equations using the points obtained. To determine the vertices of the triangle, solve the given equations algebraically. Finally use the formula: $\text{Area}=\dfrac{1}{2}\times \text{base}\times \text{height}$, to determine the area of the triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume the two equations as:
$\begin{align}
& 3x+y-11=0...............(i) \\
& x-y-1=0..................(ii) \\
\end{align}$
Considering equation (i),
$3x+y-11=0$
Substituting x = 0, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& y-11=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=11 \\
\end{align}\]
Substituting y = 0, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& 3x-11=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 3x=11 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{11}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the two points are: \[A\left( 0,11 \right)\text{ and }B\left( \dfrac{11}{3},0 \right)\].
Considering equation (ii),
$x-y-1=0$
Substituting x = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& -y-1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-1 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting y = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& x-1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=1 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the two points are: $C\left( 0,-1 \right)\text{ and }D\left( 1,0 \right)$.
Therefore, the graph of the two functions can be plotted as:
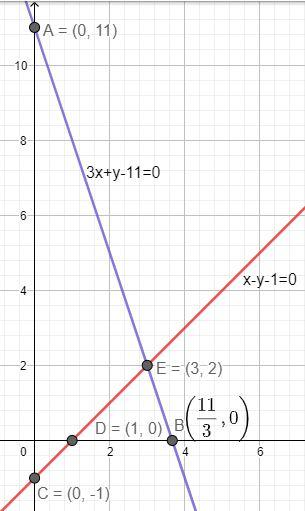
Clearly, we can see that the two lines are intersecting each other at a particular point E. To determine this point of intersection, we have to solve the equations algebraically. Let us solve the two equations.
Adding equation (i) and (ii) we get,
$\begin{align}
& 3x+y-11+x-y-1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 4x-12=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 4x=12 \\
& \Rightarrow x=3 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting x=3 in equation (ii), we get,
$\begin{align}
& 3-y-1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=2 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the intersection point is given by: E(3, 2).
So, the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and x-axis are: E(3, 2); C(0, -1) and A(0, 11). From the graph,
Length of the base of the triangle = length of AC = 12 units
Height of the triangle = distance of the point E from y-axis = 2 units
Therefore, area of the triangle
$\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{1}{2}\times \text{base}\times \text{height} \\
& =\dfrac{1}{2}\times 12\times 2 \\
& =12\text{ square units} \\
\end{align}$
Note: One may note that it is necessary to substitute the value of x and y equal to 0 because we have to determine the vertices of the base of the triangle which lies on the y-axis. Also, it is important to solve these equations algebraically to determine the third vertex of the triangle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let us assume the two equations as:
$\begin{align}
& 3x+y-11=0...............(i) \\
& x-y-1=0..................(ii) \\
\end{align}$
Considering equation (i),
$3x+y-11=0$
Substituting x = 0, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& y-11=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=11 \\
\end{align}\]
Substituting y = 0, we get,
\[\begin{align}
& 3x-11=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 3x=11 \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{11}{3} \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the two points are: \[A\left( 0,11 \right)\text{ and }B\left( \dfrac{11}{3},0 \right)\].
Considering equation (ii),
$x-y-1=0$
Substituting x = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& -y-1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-1 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting y = 0, we get,
$\begin{align}
& x-1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow x=1 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the two points are: $C\left( 0,-1 \right)\text{ and }D\left( 1,0 \right)$.
Therefore, the graph of the two functions can be plotted as:

Clearly, we can see that the two lines are intersecting each other at a particular point E. To determine this point of intersection, we have to solve the equations algebraically. Let us solve the two equations.
Adding equation (i) and (ii) we get,
$\begin{align}
& 3x+y-11+x-y-1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 4x-12=0 \\
& \Rightarrow 4x=12 \\
& \Rightarrow x=3 \\
\end{align}$
Substituting x=3 in equation (ii), we get,
$\begin{align}
& 3-y-1=0 \\
& \Rightarrow y=2 \\
\end{align}$
Therefore, the intersection point is given by: E(3, 2).
So, the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and x-axis are: E(3, 2); C(0, -1) and A(0, 11). From the graph,
Length of the base of the triangle = length of AC = 12 units
Height of the triangle = distance of the point E from y-axis = 2 units
Therefore, area of the triangle
$\begin{align}
& =\dfrac{1}{2}\times \text{base}\times \text{height} \\
& =\dfrac{1}{2}\times 12\times 2 \\
& =12\text{ square units} \\
\end{align}$
Note: One may note that it is necessary to substitute the value of x and y equal to 0 because we have to determine the vertices of the base of the triangle which lies on the y-axis. Also, it is important to solve these equations algebraically to determine the third vertex of the triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




