
Select the correct order of stability of carbocation among the following carbocations.
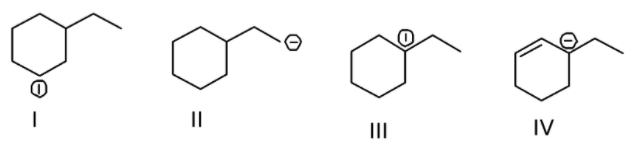
A. $\text{I > II > III > IV}$
B. $\text{IV > III > I > II}$
C. $\text{IV > I > II > III}$
D. $\text{IV > III > II > I}$

Answer
528.1k+ views
Hint: A carbocation carries a positive charge on the atom of a carbon. The name itself indicates that ‘carbo’ refers to the carbon atom while ‘cation’ refers to a positive ion.
Complete answer:
Different types of carbocations include primary, secondary and tertiary carbocations. In a primary carbocation, the carbon carrying the positive charge is attached to only one alkyl group. The structure II in the question contains a primary carbocation. In a secondary carbocation, the carbon carrying the positive charge is connected to two alkyl groups. The structure I in the question contains a secondary carbocation. In a tertiary carbocation, the carbon carrying the positive charge is linked with three alkyl groups. The structure III in the question contains a tertiary carbocation. The structure IV in the question refers to resonance stabilized and thus, is the most stable. Among primary, secondary and the tertiary carbocations, tertiary carbocation is the most stable whereas primary carbocation is considered to be the least stable owing to the decreasing –I (inductive) effect of the alkyl group. In other words, the electron pushing effect of the \[C{H_3}\] group is placing more negative charge on carbocation as you shift from primary to secondary or tertiary carbocation. At the same moment, the region around various \[C{H_3}\] groups is becoming positive. As a result, positive charge is spreading out over more atoms as you shift from primary to secondary or tertiary ions. The more is the charge around, more is the stability of carbocation. Hence the order of stability of the carbocation is \[IV > III > I > II\].
Hence, the correct answer is Option B.
Note:
Always remember that alkyl groups are considered to be weakly electron donating groups owing to the presence of hyperconjugation as well as inductive effects. And the existence of resonance effects can add further stability to the carbocations.
Complete answer:
Different types of carbocations include primary, secondary and tertiary carbocations. In a primary carbocation, the carbon carrying the positive charge is attached to only one alkyl group. The structure II in the question contains a primary carbocation. In a secondary carbocation, the carbon carrying the positive charge is connected to two alkyl groups. The structure I in the question contains a secondary carbocation. In a tertiary carbocation, the carbon carrying the positive charge is linked with three alkyl groups. The structure III in the question contains a tertiary carbocation. The structure IV in the question refers to resonance stabilized and thus, is the most stable. Among primary, secondary and the tertiary carbocations, tertiary carbocation is the most stable whereas primary carbocation is considered to be the least stable owing to the decreasing –I (inductive) effect of the alkyl group. In other words, the electron pushing effect of the \[C{H_3}\] group is placing more negative charge on carbocation as you shift from primary to secondary or tertiary carbocation. At the same moment, the region around various \[C{H_3}\] groups is becoming positive. As a result, positive charge is spreading out over more atoms as you shift from primary to secondary or tertiary ions. The more is the charge around, more is the stability of carbocation. Hence the order of stability of the carbocation is \[IV > III > I > II\].
Hence, the correct answer is Option B.
Note:
Always remember that alkyl groups are considered to be weakly electron donating groups owing to the presence of hyperconjugation as well as inductive effects. And the existence of resonance effects can add further stability to the carbocations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




