
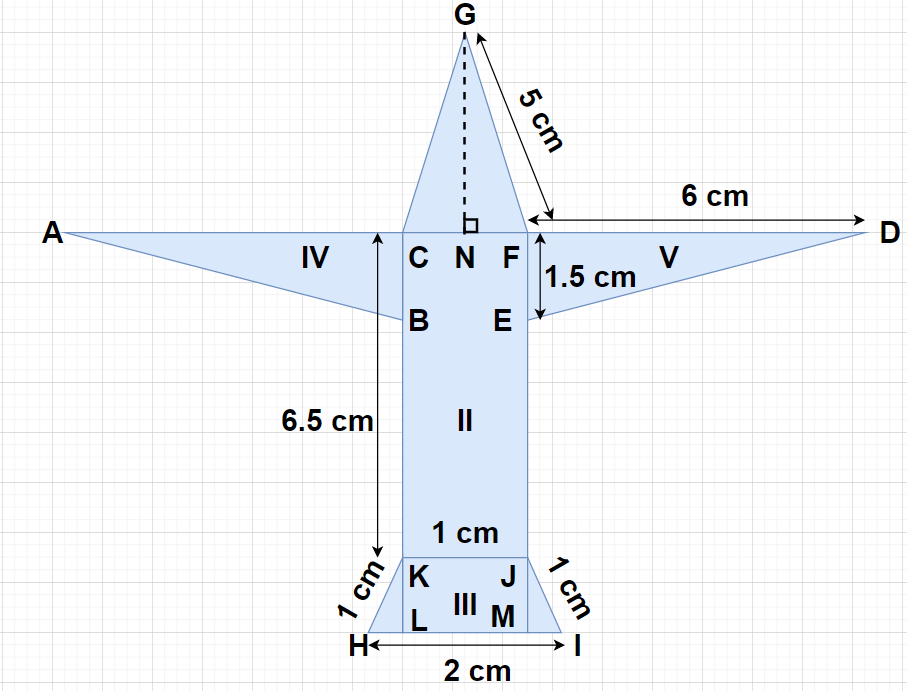
Radha made a picture of an aeroplane with coloured paper as shown in the figure. Find the total area of the paper used.

Answer
620.7k+ views
Hint- Here, we will be dividing the figure of the aeroplane into simpler figures like rectangle, triangle and trapezium whose formulas for areas we already know and then using those formulas we will find the area of the whole figure.
“Complete step-by-step answer:”
From the figure, we can see that the picture of the aeroplane can be divided into five regions as shown.
As we know that area of the triangle$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)\left( {{\text{Height}}} \right)$.
Also, area of the rectangle\[ = \left( {{\text{Length}}} \right)\left( {{\text{Breadth}}} \right)\]
Also, area of the trapezium$ = \dfrac{{\left( {{\text{Height of trapezium}}} \right)}}{2} \times \left( {{\text{Sum of parallel sides}}} \right)$
In $\vartriangle {\text{GFN}}$, ${\text{NF}} = \dfrac{{{\text{CF}}}}{2} = \dfrac{{{\text{KJ}}}}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}$ cm and $GF = 5$ cm
According to Pythagoras Theorem, ${\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)^2}$
$
\Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{GF}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{GN}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{NF}}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {\text{5}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{GN}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{2}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{GN}}} \right)^2} = 25 - \dfrac{{\text{1}}}{4} = \dfrac{{99}}{4} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{GN}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{99}}{4}} = \dfrac{{3\sqrt {11} }}{2}{\text{ cm}} \\
$
So, height of the $\vartriangle {\text{GCF}}$ is \[{\text{GN}} = \dfrac{{3\sqrt {11} }}{2}{\text{ cm}}\]
Area of region I = Area of $\vartriangle {\text{GCF}}$ $ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{\text{CF}}} \right)\left( {{\text{GN}}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\text{1}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{3\sqrt {11} }}{2}} \right) = \dfrac{{3\sqrt {11} }}{4}{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
Area of region II = Area of rectangle KJFC\[ = \left( {{\text{KJ}}} \right)\left( {{\text{CK}}} \right) = \left( {\text{1}} \right)\left( {{\text{6}}{\text{.5}}} \right) = 6.5{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
Since, the height of the trapezium KHIJ = KL = JM
In $\vartriangle {\text{JMI}}$, IJ = 1 cm and MI = HL = $\dfrac{{{\text{HI}} - {\text{KJ}}}}{2} = \dfrac{{{\text{2}} - {\text{1}}}}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}$ cm
According to Pythagoras Theorem, ${\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)^2}$
$
\Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{IJ}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{JM}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{MI}}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {\text{1}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{JM}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{2}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{JM}}} \right)^2} = 1 - \dfrac{{\text{1}}}{4} = \dfrac{3}{4} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{JM}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{3}{4}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}{\text{ cm}} \\
$
So, the height of trapezium KHIJ is ${\text{JM}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}{\text{ cm}}$
Area of region III = Area of trapezium KHIJ$ = \dfrac{{\left( {{\text{JM}}} \right)}}{2} \times \left( {{\text{KJ}} + {\text{HI}}} \right) = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)}}{2} \times \left( {1 + 2} \right) = \dfrac{{3\sqrt 3 }}{4}{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
Area of region IV = Area of region V [because both the triangles ABC and DEF have equal areas due to their same dimensions]
Area of region IV = Area of region V = Area of $\vartriangle {\text{DEF}}$$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{\text{EF}}} \right)\left( {{\text{DF}}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{\text{1}}{\text{.5}}} \right)\left( {\text{6}} \right) = \dfrac{9}{2}{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
Therefore, the total area of the paper used = Area of region I + Area of region II + Area of region III + Area of region IV + Area of region V \[ = \dfrac{{3\sqrt {11} }}{4} + 6.5 + \dfrac{{3\sqrt 3 }}{4} + \dfrac{9}{2} + \dfrac{9}{2} = \dfrac{{3\sqrt {11} + 26 + 3\sqrt 3 + 18 + 18}}{4} = 19.2865{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
So, the total area of the coloured paper used is 19.2865 \[{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
Note- In this particular problem, from symmetry point of view we can say that the perpendicular GN drawn from point G to the line CF divides the line into two equal parts which are CN and NF i.e., ${\text{NF}} = {\text{CN}} = \dfrac{{{\text{CF}}}}{2} = \dfrac{{{\text{KJ}}}}{2}$ and the triangles KLH and JMI are symmetrically same that’s why MI = HL = $\dfrac{{{\text{HI}} - {\text{KJ}}}}{2}$.
“Complete step-by-step answer:”
From the figure, we can see that the picture of the aeroplane can be divided into five regions as shown.
As we know that area of the triangle$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)\left( {{\text{Height}}} \right)$.
Also, area of the rectangle\[ = \left( {{\text{Length}}} \right)\left( {{\text{Breadth}}} \right)\]
Also, area of the trapezium$ = \dfrac{{\left( {{\text{Height of trapezium}}} \right)}}{2} \times \left( {{\text{Sum of parallel sides}}} \right)$
In $\vartriangle {\text{GFN}}$, ${\text{NF}} = \dfrac{{{\text{CF}}}}{2} = \dfrac{{{\text{KJ}}}}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}$ cm and $GF = 5$ cm
According to Pythagoras Theorem, ${\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)^2}$
$
\Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{GF}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{GN}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{NF}}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {\text{5}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{GN}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{2}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{GN}}} \right)^2} = 25 - \dfrac{{\text{1}}}{4} = \dfrac{{99}}{4} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{GN}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{{99}}{4}} = \dfrac{{3\sqrt {11} }}{2}{\text{ cm}} \\
$
So, height of the $\vartriangle {\text{GCF}}$ is \[{\text{GN}} = \dfrac{{3\sqrt {11} }}{2}{\text{ cm}}\]
Area of region I = Area of $\vartriangle {\text{GCF}}$ $ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{\text{CF}}} \right)\left( {{\text{GN}}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {\text{1}} \right)\left( {\dfrac{{3\sqrt {11} }}{2}} \right) = \dfrac{{3\sqrt {11} }}{4}{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
Area of region II = Area of rectangle KJFC\[ = \left( {{\text{KJ}}} \right)\left( {{\text{CK}}} \right) = \left( {\text{1}} \right)\left( {{\text{6}}{\text{.5}}} \right) = 6.5{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
Since, the height of the trapezium KHIJ = KL = JM
In $\vartriangle {\text{JMI}}$, IJ = 1 cm and MI = HL = $\dfrac{{{\text{HI}} - {\text{KJ}}}}{2} = \dfrac{{{\text{2}} - {\text{1}}}}{2} = \dfrac{1}{2}$ cm
According to Pythagoras Theorem, ${\left( {{\text{Hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{Perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{Base}}} \right)^2}$
$
\Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{IJ}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{JM}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{MI}}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {\text{1}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{JM}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {\dfrac{{\text{1}}}{2}} \right)^2} \\
\Rightarrow {\left( {{\text{JM}}} \right)^2} = 1 - \dfrac{{\text{1}}}{4} = \dfrac{3}{4} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{JM}} = \sqrt {\dfrac{3}{4}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}{\text{ cm}} \\
$
So, the height of trapezium KHIJ is ${\text{JM}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}{\text{ cm}}$
Area of region III = Area of trapezium KHIJ$ = \dfrac{{\left( {{\text{JM}}} \right)}}{2} \times \left( {{\text{KJ}} + {\text{HI}}} \right) = \dfrac{{\left( {\dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right)}}{2} \times \left( {1 + 2} \right) = \dfrac{{3\sqrt 3 }}{4}{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
Area of region IV = Area of region V [because both the triangles ABC and DEF have equal areas due to their same dimensions]
Area of region IV = Area of region V = Area of $\vartriangle {\text{DEF}}$$ = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{\text{EF}}} \right)\left( {{\text{DF}}} \right) = \dfrac{1}{2}\left( {{\text{1}}{\text{.5}}} \right)\left( {\text{6}} \right) = \dfrac{9}{2}{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}$
Therefore, the total area of the paper used = Area of region I + Area of region II + Area of region III + Area of region IV + Area of region V \[ = \dfrac{{3\sqrt {11} }}{4} + 6.5 + \dfrac{{3\sqrt 3 }}{4} + \dfrac{9}{2} + \dfrac{9}{2} = \dfrac{{3\sqrt {11} + 26 + 3\sqrt 3 + 18 + 18}}{4} = 19.2865{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
So, the total area of the coloured paper used is 19.2865 \[{\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
Note- In this particular problem, from symmetry point of view we can say that the perpendicular GN drawn from point G to the line CF divides the line into two equal parts which are CN and NF i.e., ${\text{NF}} = {\text{CN}} = \dfrac{{{\text{CF}}}}{2} = \dfrac{{{\text{KJ}}}}{2}$ and the triangles KLH and JMI are symmetrically same that’s why MI = HL = $\dfrac{{{\text{HI}} - {\text{KJ}}}}{2}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




