
Prove that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the square of two sides.
Answer
582.9k+ views
Hint: Start by drawing the triangle and label the sides, do the required construction. Take two triangles and try to look for the similarity between the two and then apply the property of similar triangles that their corresponding sides are proportional to each other. Use the relation formed for another similar triangle and prove the required.
Complete step-by-step answer:
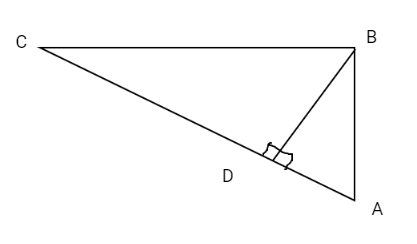
A right-angled triangle ABC which is right-angled at B
To prove: $A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
Construction: Draw a perpendicular BD from B to AC
Proof:-
In triangle ABC and ABD
$\angle ADB = \angle ABC = {90^ \circ }({\text{Given)}}$
$\angle DAB = \angle BAC = \left( {common{\text{ }}angle} \right)$
$\therefore \Delta ABC\sim\Delta ABD\left( {using{\text{ }}AA{\text{ }}similarity{\text{ }}criteria} \right)$
AA similarity criterion :- It states that if two triangles have two pairs of congruent angles, then the triangles are similar.
Now, Applying properties of similar triangle, we have corresponding sides proportional to each other
$\dfrac{{AD}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}$
$\Rightarrow A{B^2} = AD \times AC \to eqn.1$
Similarly, $\therefore \Delta ABC\sim\Delta BDC\left( {using{\text{ }}AA{\text{ }}similarity{\text{ }}criteria} \right)$
Again, Applying properties of similar triangle, we have corresponding sides proportional to each other
$\dfrac{{BC}}{{CD}} = \dfrac{{AC}}{{BC}}$
$\Rightarrow B{C^2} = CD \times AC \to eqn.2$
Adding equation (1) and (2), we get
$A{B^2} + B{C^2} = AD \times AC + CD \times AC$
Taking AC common, we get
$A{B^2} + B{C^2} = AC\left( {AD + CD} \right) \to eqn.3$
And from the figure we know that AD + CD = AC
After changing the obtained value of AC above in equation (3), we get
$A{B^2} + B{C^2} = AC \times AC = A{C^2}$
Hence proved
$A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{C^2}$
Note: Similar questions can be solved by using the same procedure as above. Students must know all the properties of similar triangles and conditions for similarity. Diagrams are very important as they help in understanding the solution and question both very easily.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A right-angled triangle ABC which is right-angled at B
To prove: $A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$
Construction: Draw a perpendicular BD from B to AC

Proof:-
In triangle ABC and ABD
$\angle ADB = \angle ABC = {90^ \circ }({\text{Given)}}$
$\angle DAB = \angle BAC = \left( {common{\text{ }}angle} \right)$
$\therefore \Delta ABC\sim\Delta ABD\left( {using{\text{ }}AA{\text{ }}similarity{\text{ }}criteria} \right)$
AA similarity criterion :- It states that if two triangles have two pairs of congruent angles, then the triangles are similar.
Now, Applying properties of similar triangle, we have corresponding sides proportional to each other
$\dfrac{{AD}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{AC}}$
$\Rightarrow A{B^2} = AD \times AC \to eqn.1$
Similarly, $\therefore \Delta ABC\sim\Delta BDC\left( {using{\text{ }}AA{\text{ }}similarity{\text{ }}criteria} \right)$
Again, Applying properties of similar triangle, we have corresponding sides proportional to each other
$\dfrac{{BC}}{{CD}} = \dfrac{{AC}}{{BC}}$
$\Rightarrow B{C^2} = CD \times AC \to eqn.2$
Adding equation (1) and (2), we get
$A{B^2} + B{C^2} = AD \times AC + CD \times AC$
Taking AC common, we get
$A{B^2} + B{C^2} = AC\left( {AD + CD} \right) \to eqn.3$
And from the figure we know that AD + CD = AC
After changing the obtained value of AC above in equation (3), we get
$A{B^2} + B{C^2} = AC \times AC = A{C^2}$
Hence proved
$A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{C^2}$
Note: Similar questions can be solved by using the same procedure as above. Students must know all the properties of similar triangles and conditions for similarity. Diagrams are very important as they help in understanding the solution and question both very easily.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




