
PQR is a triangle right angled at P and M is a point on QR such that $\text{PM}\bot \text{QR}$. Show that $\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}=\text{QM}\cdot \text{MR}$.
Answer
583.2k+ views
Hint: We have a right angled triangle and a perpendicular to the hypotenuse of this triangle. We will use the Pythagoras theorem multiple times to prove that $\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}=\text{QM}\cdot \text{MR}$. The Pythagoras theorem states that in a right angled triangle, ${{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{side}_1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{side}_2 \right)}^{2}}$. We will also use the algebraic identity ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+2ab+{{b}^{2}}$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let us draw a rough diagram of the triangle $\text{PQR}$.
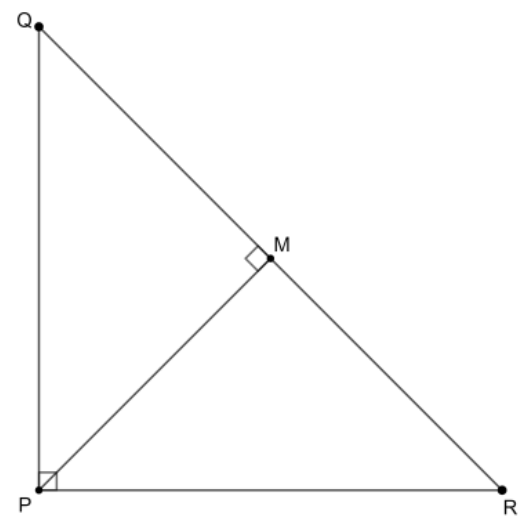
In $\Delta \text{PQR}$, $\angle \text{QPR}$ is the right angle. According to the Pythagoras theorem, in a right angled triangle, ${{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{side }_1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{side}_2 \right)}^{2}}$. Using the Pythagoras theorem on $\Delta \text{PQR}$, we get the following equation,
$\text{Q}{{\text{R}}^{2}}=\text{P}{{\text{Q}}^{2}}+\text{P}{{\text{R}}^{2}}....(i)$
Now, we know that $\text{PM}\bot \text{QR}$. Let us consider $\Delta \text{PMQ}$ with the right angle at vertex $\text{M}$. Using the Pythagoras theorem for this triangle, we get
$\text{P}{{\text{Q}}^{2}}=\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{Q}{{\text{M}}^{2}}$.
Next, we will consider $\Delta \text{PMR}$ with the right angle at vertex $\text{M}$. In this triangle, we will use the Pythagoras theorem again, as follows,
$\text{P}{{\text{R}}^{2}}=\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{M}{{\text{R}}^{2}}$.
Now, substituting the values of $\text{P}{{\text{Q}}^{2}}$ and $\text{P}{{\text{R}}^{2}}$ in equation $(i)$, we get
$\begin{align}
&\text{Q}{{\text{R}}^{2}}=\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{Q}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{M}{{\text{R}}^{2}} \\
& =2\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{Q}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{M}{{\text{R}}^{2}}
\end{align}$
Now, from the above diagram, we can see that $\text{QR = QM + MR}$. Substituting this value in the above equation, we get
${{\left(\text{QM+MR}\right)}^{2}}=2\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{Q}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{M}{{\text{R}}^{2}}$
We will expand the left hand side of the above equation using the algebraic identity ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+2ab+{{b}^{2}}$. So, we have the following equation,
$\text{Q}{{\text{M}}^{2}}\text{+M}{{\text{R}}^{2}}+2\text{QM}\cdot \text{MR}=2\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{Q}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{M}{{\text{R}}^{2}}$
Simplifying the above equation, we get
$\begin{align}
& 2\text{QM}\cdot \text{MR}=2\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}} \\
& \therefore \text{QM}\cdot \text{MR}=\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, proved.
Note: It is useful to draw a rough diagram for such types of questions. Looking at the diagram, it becomes clear which triangles should be used to get the required result. When we have a right-angled triangle, it is natural to consider the use of the Pythagoras theorem. It is better to write the names of all sides explicitly so that minor mistakes in calculations can be avoided.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let us draw a rough diagram of the triangle $\text{PQR}$.

In $\Delta \text{PQR}$, $\angle \text{QPR}$ is the right angle. According to the Pythagoras theorem, in a right angled triangle, ${{\left( \text{Hypotenuse} \right)}^{2}}={{\left( \text{side }_1 \right)}^{2}}+{{\left( \text{side}_2 \right)}^{2}}$. Using the Pythagoras theorem on $\Delta \text{PQR}$, we get the following equation,
$\text{Q}{{\text{R}}^{2}}=\text{P}{{\text{Q}}^{2}}+\text{P}{{\text{R}}^{2}}....(i)$
Now, we know that $\text{PM}\bot \text{QR}$. Let us consider $\Delta \text{PMQ}$ with the right angle at vertex $\text{M}$. Using the Pythagoras theorem for this triangle, we get
$\text{P}{{\text{Q}}^{2}}=\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{Q}{{\text{M}}^{2}}$.
Next, we will consider $\Delta \text{PMR}$ with the right angle at vertex $\text{M}$. In this triangle, we will use the Pythagoras theorem again, as follows,
$\text{P}{{\text{R}}^{2}}=\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{M}{{\text{R}}^{2}}$.
Now, substituting the values of $\text{P}{{\text{Q}}^{2}}$ and $\text{P}{{\text{R}}^{2}}$ in equation $(i)$, we get
$\begin{align}
&\text{Q}{{\text{R}}^{2}}=\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{Q}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{M}{{\text{R}}^{2}} \\
& =2\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{Q}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{M}{{\text{R}}^{2}}
\end{align}$
Now, from the above diagram, we can see that $\text{QR = QM + MR}$. Substituting this value in the above equation, we get
${{\left(\text{QM+MR}\right)}^{2}}=2\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{Q}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{M}{{\text{R}}^{2}}$
We will expand the left hand side of the above equation using the algebraic identity ${{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}={{a}^{2}}+2ab+{{b}^{2}}$. So, we have the following equation,
$\text{Q}{{\text{M}}^{2}}\text{+M}{{\text{R}}^{2}}+2\text{QM}\cdot \text{MR}=2\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{Q}{{\text{M}}^{2}}+\text{M}{{\text{R}}^{2}}$
Simplifying the above equation, we get
$\begin{align}
& 2\text{QM}\cdot \text{MR}=2\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}} \\
& \therefore \text{QM}\cdot \text{MR}=\text{P}{{\text{M}}^{2}} \\
\end{align}$
Hence, proved.
Note: It is useful to draw a rough diagram for such types of questions. Looking at the diagram, it becomes clear which triangles should be used to get the required result. When we have a right-angled triangle, it is natural to consider the use of the Pythagoras theorem. It is better to write the names of all sides explicitly so that minor mistakes in calculations can be avoided.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




