
Molecules whose mirror image is non-superimposable over them are known as chiral. Which of the following molecules is chiral in nature?
A. 2-bromobutane
B. 1-bromobutane
C. 2-bromopropane
D. 2-bromopropan-2-ol
Answer
594.9k+ views
Hint: Chirality is based mainly on the number of groups attached to a carbon. It also depends on the nature of groups whether it is similar or different. It is also influenced by the ability to superimpose.
Complete step by step solution:
Stereoisomers are a type of isomers where the spatial arrangements of atoms differ. They have identical molecular formulas but not structural formulas. When the mirror images of organic molecules cannot be matched, they are non-superimposable and chiral. Our hands are the best example. They are non-superimposable mirror images.
Molecules are said to be chiral if they have one or more chiral carbons. Chiral carbon is the one that is bonded to four different groups.
A. The structure of 2-bromobutane is given below:

Here the carbon with bromine is the chiral carbon. It does not have any plane of symmetry.
B.

This molecule does not have a chiral carbon. It has a plane of symmetry.
C.

Here there is no chiral carbon. The second carbon is attached to two methyl groups and one bromine group which do not satisfy the chirality. Thus not a chiral molecule.
D.
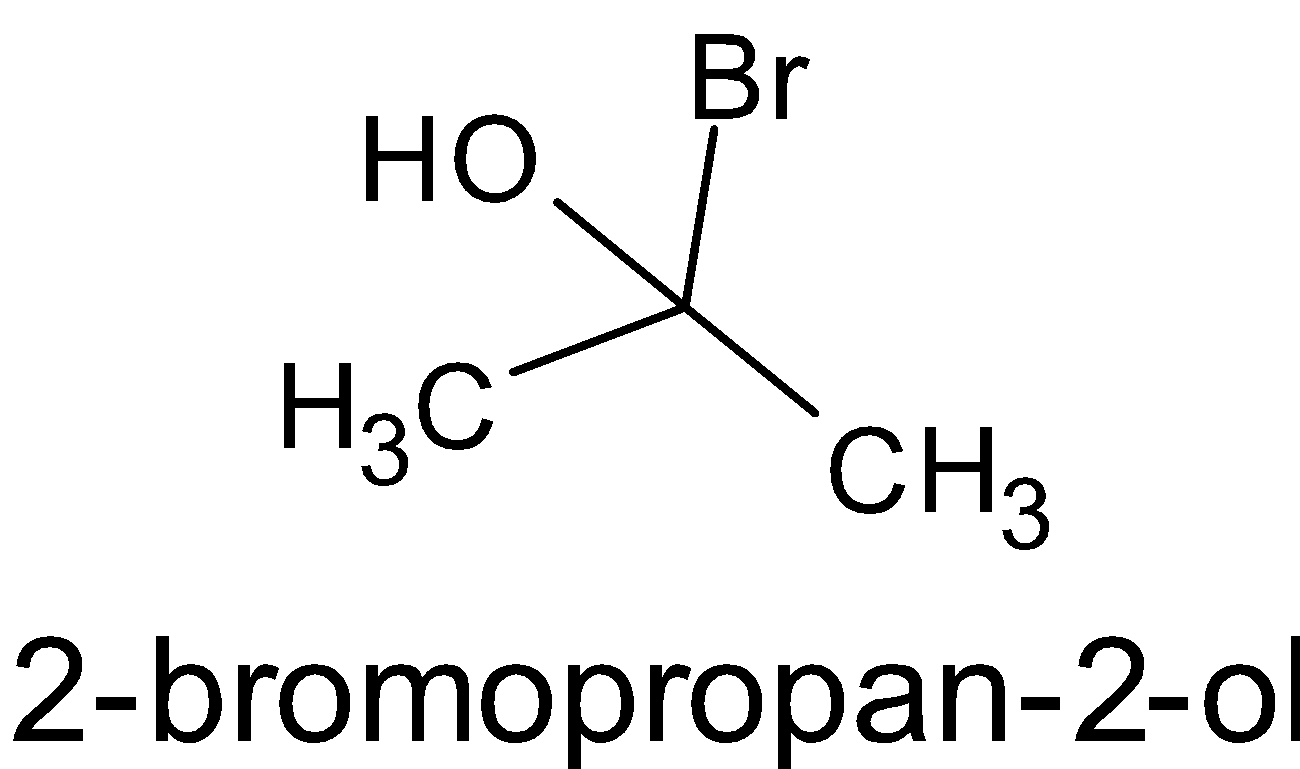
Here, there is no chiral carbon since the second carbon is attached to two methyl groups. So it is not chiral.
Thus only 2-bromobutane is chiral.
Hence, option A is correct.
Additional information:
When the mirror images of molecules are identical and superimposable, the molecules are achiral. Achiral molecules should have a plane of symmetry. When the mirror image of achiral structure is rotated, and the structures can be aligned with each other, their mirror images are called achiral carbon atoms.
Note: Chirality often leads to optical activity in a compound. But, it is not a necessary condition for optical activity. Optical activity is the ability of a molecule to rotate plane-polarized light.
Complete step by step solution:
Stereoisomers are a type of isomers where the spatial arrangements of atoms differ. They have identical molecular formulas but not structural formulas. When the mirror images of organic molecules cannot be matched, they are non-superimposable and chiral. Our hands are the best example. They are non-superimposable mirror images.
Molecules are said to be chiral if they have one or more chiral carbons. Chiral carbon is the one that is bonded to four different groups.
A. The structure of 2-bromobutane is given below:

Here the carbon with bromine is the chiral carbon. It does not have any plane of symmetry.
B.

This molecule does not have a chiral carbon. It has a plane of symmetry.
C.

Here there is no chiral carbon. The second carbon is attached to two methyl groups and one bromine group which do not satisfy the chirality. Thus not a chiral molecule.
D.

Here, there is no chiral carbon since the second carbon is attached to two methyl groups. So it is not chiral.
Thus only 2-bromobutane is chiral.
Hence, option A is correct.
Additional information:
When the mirror images of molecules are identical and superimposable, the molecules are achiral. Achiral molecules should have a plane of symmetry. When the mirror image of achiral structure is rotated, and the structures can be aligned with each other, their mirror images are called achiral carbon atoms.
Note: Chirality often leads to optical activity in a compound. But, it is not a necessary condition for optical activity. Optical activity is the ability of a molecule to rotate plane-polarized light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




