
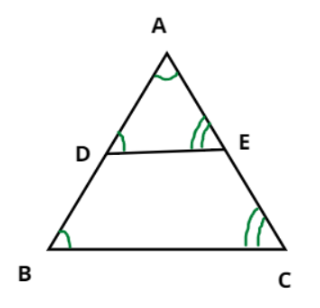
In the given figure, DE is parallel to BC
\[{\text{(i)}}\] If \[{\text{DE = 4 cm, BC = 6 cm}}\] and \[{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE) = 16 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\], find the area of \[\vartriangle {\text{ABC}}\].
\[{\text{(ii)}}\] If \[{\text{DE = 4 cm, BC = 8 cm}}\] and \[{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE) = 25 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\], find the area of \[\vartriangle {\text{ABC}}\].
\[{\text{(iii)}}\] If \[{\text{DE:BC = 3:5}}\]. Calculate the ratio of the areas of \[\vartriangle {\text{ADE}}\] and the area of BCED.

Answer
524k+ views
Hint- Here, we will be using the properties of congruent triangles.
Given, DE is parallel to BC.
From the figure, in \[\vartriangle {\text{ADE}}\] and \[\vartriangle {\text{ABC}}\]
\[\angle {\text{A = }}\angle {\text{A}}\] (Common angle)
Since, DE is parallel to BC therefore the below angles will be equal because they are corresponding angles.
\[ \Rightarrow \angle {\text{D = }}\angle {\text{B}}\] (Corresponding angles) and (Corresponding angles)
Therefore, by AAA congruence criteria, the triangles ADE and ABC are congruent
i.e., \[\vartriangle {\text{ADE}} \cong \vartriangle {\text{ABC}}\]
\[{\text{(i)}}\] Given, \[{\text{DE = 4 cm, BC = 6 cm}}\] and \[{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE) = 16 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\]
Since, for two congruent triangles, the ratio of their areas will be equal to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
As, \[\vartriangle {\text{ADE}} \cong \vartriangle {\text{ABC}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ABC)}}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{DE}}}}{{{\text{BC}}}}} \right)^2} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{16}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ABC)}}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{\text{4}}}{{\text{6}}}} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{16}}{{36}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ABC)}} = \dfrac{{36 \times 16}}{{16}} = 36{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\]
Therefore, the area of triangle ABC is \[36{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
\[{\text{(ii)}}\] Given, \[{\text{DE = 4 cm, BC = 8 cm}}\] and \[{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE) = 25 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\]
Since, for two congruent triangles, the ratio of their areas will be equal to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
As, \[\vartriangle {\text{ADE}} \cong \vartriangle {\text{ABC}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ABC)}}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{DE}}}}{{{\text{BC}}}}} \right)^2} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{25}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ABC)}}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{\text{4}}}{8}} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{16}}{{64}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ABC)}} = \dfrac{{25 \times 64}}{{16}} = 100{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\]
Therefore, the area of triangle ABC is \[{\text{100 c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
\[(iii)\] Given, \[{\text{DE:BC = 3:5}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{DE}}}}{{{\text{BC}}}} = \dfrac{3}{5}\]
Since, for two congruent triangles, the ratio of their areas will be equal to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
As, \[\vartriangle {\text{ADE}} \cong \vartriangle {\text{ABC}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ABC)}}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{DE}}}}{{{\text{BC}}}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{3}{5}} \right)^2} = \dfrac{9}{{25}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE) + Area(BCED)}}}} = \dfrac{9}{{25}}\]
Reciprocating the above equation, we get
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE) + Area(BCED)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}} = \dfrac{{25}}{9} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}} + \dfrac{{{\text{Area(BCED)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}} = \dfrac{{25}}{9} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{1}} + \dfrac{{{\text{Area(BCED)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}} = \dfrac{{25}}{9} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(BCED)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}} = \dfrac{{25}}{9} - 1 = \dfrac{{16}}{9} \\
\]
Now again reciprocating the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}}{{{\text{Area(BCED)}}}} = \dfrac{9}{{16}}\]
Therefore, the ratio of triangle ADE to the quadrilateral BCED is \[{\text{9:16}}\].
Note- These type of problems are mostly solved with the help of geometry. Hence, congruency rule is used to obtain the relation between known and unknown data. By these relations, the required value of the unknown can be computed easily.
Given, DE is parallel to BC.
From the figure, in \[\vartriangle {\text{ADE}}\] and \[\vartriangle {\text{ABC}}\]
\[\angle {\text{A = }}\angle {\text{A}}\] (Common angle)
Since, DE is parallel to BC therefore the below angles will be equal because they are corresponding angles.
\[ \Rightarrow \angle {\text{D = }}\angle {\text{B}}\] (Corresponding angles) and (Corresponding angles)
Therefore, by AAA congruence criteria, the triangles ADE and ABC are congruent
i.e., \[\vartriangle {\text{ADE}} \cong \vartriangle {\text{ABC}}\]
\[{\text{(i)}}\] Given, \[{\text{DE = 4 cm, BC = 6 cm}}\] and \[{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE) = 16 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\]
Since, for two congruent triangles, the ratio of their areas will be equal to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
As, \[\vartriangle {\text{ADE}} \cong \vartriangle {\text{ABC}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ABC)}}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{DE}}}}{{{\text{BC}}}}} \right)^2} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{16}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ABC)}}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{\text{4}}}{{\text{6}}}} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{16}}{{36}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ABC)}} = \dfrac{{36 \times 16}}{{16}} = 36{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\]
Therefore, the area of triangle ABC is \[36{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
\[{\text{(ii)}}\] Given, \[{\text{DE = 4 cm, BC = 8 cm}}\] and \[{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE) = 25 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{2}}}\]
Since, for two congruent triangles, the ratio of their areas will be equal to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
As, \[\vartriangle {\text{ADE}} \cong \vartriangle {\text{ABC}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ABC)}}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{DE}}}}{{{\text{BC}}}}} \right)^2} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{25}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ABC)}}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{\text{4}}}{8}} \right)^2} = \dfrac{{16}}{{64}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow {\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ABC)}} = \dfrac{{25 \times 64}}{{16}} = 100{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\]
Therefore, the area of triangle ABC is \[{\text{100 c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\].
\[(iii)\] Given, \[{\text{DE:BC = 3:5}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{DE}}}}{{{\text{BC}}}} = \dfrac{3}{5}\]
Since, for two congruent triangles, the ratio of their areas will be equal to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides.
As, \[\vartriangle {\text{ADE}} \cong \vartriangle {\text{ABC}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ABC)}}}} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{DE}}}}{{{\text{BC}}}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {\dfrac{3}{5}} \right)^2} = \dfrac{9}{{25}} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE) + Area(BCED)}}}} = \dfrac{9}{{25}}\]
Reciprocating the above equation, we get
\[
\Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE) + Area(BCED)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}} = \dfrac{{25}}{9} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}} + \dfrac{{{\text{Area(BCED)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}} = \dfrac{{25}}{9} \\
\Rightarrow {\text{1}} + \dfrac{{{\text{Area(BCED)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}} = \dfrac{{25}}{9} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(BCED)}}}}{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}} = \dfrac{{25}}{9} - 1 = \dfrac{{16}}{9} \\
\]
Now again reciprocating the above equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Area(}}\vartriangle {\text{ADE)}}}}{{{\text{Area(BCED)}}}} = \dfrac{9}{{16}}\]
Therefore, the ratio of triangle ADE to the quadrilateral BCED is \[{\text{9:16}}\].
Note- These type of problems are mostly solved with the help of geometry. Hence, congruency rule is used to obtain the relation between known and unknown data. By these relations, the required value of the unknown can be computed easily.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




