
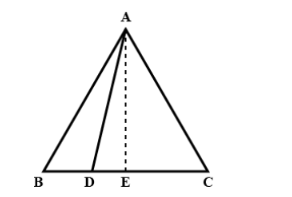
In the given figure ABC is a triangle in which AB=AC and D is any point in BC. Prove that $$A{B^2} - A{D^2} = BD.CD$$

Answer
621.9k+ views
Hint: We need to draw a perpendicular from A to BC which divides the triangle into two equal parts.
Draw $AE \bot BC$
In $\Delta AEB$ and $\Delta AEC$, we have
From the given information $AB = AC$
$AE = AE$ [Common to both triangles AEB and AEC] and
$\angle b = \angle c$ [Because AB=AC]
$\therefore \Delta AEB \cong \Delta AEC$
$ \Rightarrow BE = CE$
Since $\Delta AED$ and $\Delta ABE$ are right angles triangles at E.
Therefore, Using Pythagoras theorem we can write
$A{D^2} = A{E^2} + D{E^2}$-- (1)
$A{B^2} = A{E^2} + B{E^2}$--- (2)
Subtracting the (2) – (1)
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} - A{D^2} = B{E^2} - D{E^2}$
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} - A{D^2} = \left( {BE + DE} \right)\left( {BE - DE} \right)$ $\left[ {\because {a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} - A{D^2} = \left( {CE + DE} \right)\left( {BE - DE} \right)$ $\left[ {\because BE = CE} \right]$
By observing the figure we can easily understand that CE + DE = CD and BE – DE = BD
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} - A{D^2} = CD \cdot BD$
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} - A{D^2} = BD \cdot CD$
Hence proved
Note: We have drawn a perpendicular from A to BC to make the resulting triangles congruent. When two triangles are congruent they will have exactly the same three sides and exactly the same three angles.
Draw $AE \bot BC$
In $\Delta AEB$ and $\Delta AEC$, we have
From the given information $AB = AC$
$AE = AE$ [Common to both triangles AEB and AEC] and
$\angle b = \angle c$ [Because AB=AC]
$\therefore \Delta AEB \cong \Delta AEC$
$ \Rightarrow BE = CE$
Since $\Delta AED$ and $\Delta ABE$ are right angles triangles at E.
Therefore, Using Pythagoras theorem we can write
$A{D^2} = A{E^2} + D{E^2}$-- (1)
$A{B^2} = A{E^2} + B{E^2}$--- (2)
Subtracting the (2) – (1)
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} - A{D^2} = B{E^2} - D{E^2}$
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} - A{D^2} = \left( {BE + DE} \right)\left( {BE - DE} \right)$ $\left[ {\because {a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)} \right]$
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} - A{D^2} = \left( {CE + DE} \right)\left( {BE - DE} \right)$ $\left[ {\because BE = CE} \right]$
By observing the figure we can easily understand that CE + DE = CD and BE – DE = BD
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} - A{D^2} = CD \cdot BD$
$ \Rightarrow A{B^2} - A{D^2} = BD \cdot CD$
Hence proved
Note: We have drawn a perpendicular from A to BC to make the resulting triangles congruent. When two triangles are congruent they will have exactly the same three sides and exactly the same three angles.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

State and prove converse of BPT Basic Proportionality class 10 maths CBSE




