
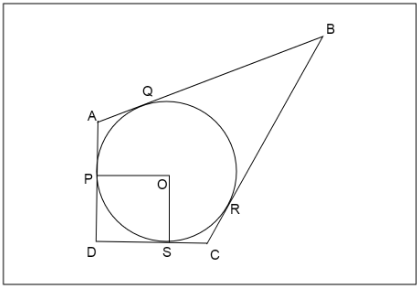
In figure, a circle is inscribed within a quadrilateral ABCD. Given that \[BC = 38\]cm,\[BQ = 27\]cm and \[DC = 25\]cm and that AD is perpendicular to DC. The radius of the circle is
A. 10cm
B. 14cm
C. 8cm
D. 12cm

Answer
573.3k+ views
Hint: We use the property of tangents that tangents from an external point to the circle are equal in length. Calculate the lengths from the given measurements and use the concept of radius making the right angle at the point of contact with the tangent to make OPDS a square.
* The radius of the circle is perpendicular to the tangent at the point of contact.
* Tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal in length.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We have a quadrilateral ABCD where AD is perpendicular to DC, so \[\angle D = {90^ \circ }\]
We are given the lengths \[BC = 38\]cm,\[BQ = 27\]cm and \[DC = 25\]cm
Since BQ and BR are tangents from point B to the circle
\[ \Rightarrow BQ = BR\]
\[ \Rightarrow BR = 27\]cm
Also, \[RC = BC - BR\]
\[ \Rightarrow RC = 38 - 27\]cm
\[ \Rightarrow RC = 11\]cm
Since, RC and SC are tangents from point C to the circle
\[ \Rightarrow SC = RC\]
\[ \Rightarrow SC = 11\]cm (as \[RC = 11\]cm)
Now we know \[DC = 25\]cm
Then \[DS = DC - SC\]
\[ \Rightarrow DS = 25 - 11\]cm
\[ \Rightarrow DS = 14\]cm
We know the radius of the circle is perpendicular to the tangent at the point of contact.
So, \[OP \bot AD,OS \bot DC\]
Since all angles of quadrilateral OPDS are right angles, then it can be a rectangle or a square.
But since a rectangle has opposite sides equal in length, OPDS cannot be a rectangle as adjacent sides OP is equal to OS and PD is equal to DS.
So, OPDS must be a square.
Now we know a square has all sides of equal length, then \[OP = PD\]
\[ \Rightarrow OP = 14\]cm
So, the radius of the circle is 14cm
\[\therefore \]Option B is the correct answer.
Note: Students many times get confused between the pair of tangents that are equal and end up doing wrong calculations. Keep in mind we take the vertices of the triangle as the external points and the tangents are from that point to the circle, always write first the point associated with the equal tangents and then proceed with the solution. Also, the point of contact means the point where the tangent touches the circle.
* The radius of the circle is perpendicular to the tangent at the point of contact.
* Tangents drawn from an external point to a circle are equal in length.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We have a quadrilateral ABCD where AD is perpendicular to DC, so \[\angle D = {90^ \circ }\]
We are given the lengths \[BC = 38\]cm,\[BQ = 27\]cm and \[DC = 25\]cm
Since BQ and BR are tangents from point B to the circle
\[ \Rightarrow BQ = BR\]
\[ \Rightarrow BR = 27\]cm
Also, \[RC = BC - BR\]
\[ \Rightarrow RC = 38 - 27\]cm
\[ \Rightarrow RC = 11\]cm
Since, RC and SC are tangents from point C to the circle
\[ \Rightarrow SC = RC\]
\[ \Rightarrow SC = 11\]cm (as \[RC = 11\]cm)
Now we know \[DC = 25\]cm
Then \[DS = DC - SC\]
\[ \Rightarrow DS = 25 - 11\]cm
\[ \Rightarrow DS = 14\]cm
We know the radius of the circle is perpendicular to the tangent at the point of contact.
So, \[OP \bot AD,OS \bot DC\]
Since all angles of quadrilateral OPDS are right angles, then it can be a rectangle or a square.
But since a rectangle has opposite sides equal in length, OPDS cannot be a rectangle as adjacent sides OP is equal to OS and PD is equal to DS.
So, OPDS must be a square.
Now we know a square has all sides of equal length, then \[OP = PD\]
\[ \Rightarrow OP = 14\]cm
So, the radius of the circle is 14cm
\[\therefore \]Option B is the correct answer.
Note: Students many times get confused between the pair of tangents that are equal and end up doing wrong calculations. Keep in mind we take the vertices of the triangle as the external points and the tangents are from that point to the circle, always write first the point associated with the equal tangents and then proceed with the solution. Also, the point of contact means the point where the tangent touches the circle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




