
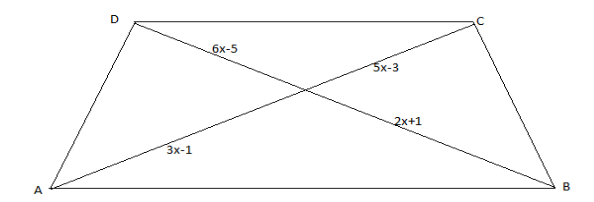
In fig., if \[AB\parallel CD\] , find the value of \[x\].

Answer
591k+ views
Hint: At first, we will try to find whether the triangles \[AOB\] and \[COD\] are congruent or not.
By the condition of similarity, we will try to prove that.
If two triangles are similar, the ratio of their sides is also the same.
Using the above condition, we will find the required value.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that; \[AB\parallel CD\].
We have to find the value of \[x\].
Let us consider the diagonals \[AC\] and \[BD\]meets at \[O\].
At first, we will try to find whether the triangles \[AOB\] and \[COD\]are congruent or not.
We know that, if three angles of any triangle are equal to the respective angles of another triangle, then by AAA condition the triangles are similar to each other.
Again, we know that the alternate angles of two parallel lines are equal.
Here, \[AB\parallel CD\] and \[AC\] and \[BD\] are transversal.
So, \[\angle CDB = \angle DBA\] and \[\angle DCA = \angle CAB\], as they are alternate angles.
Here, we will take the triangles of \[AOB\] and \[COD\].
In \[\Delta AOB\] and \[\Delta COD\]
\[\angle CDB = \angle DBA\] as they are alternate angles.
\[\angle DCA = \angle CAB\] as they are alternate angles.
\[\angle AOB = \angle COD\] as they are vertically opposite angles.
Then by AAA condition \[\Delta AOB \sim \Delta COD\]
Therefore, we have \[\dfrac{{AO}}{{CO}} = \dfrac{{BO}}{{DO}}\]
Substitute the values we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{6x - 5}}{{2x + 1}} = \dfrac{{5x - 3}}{{3x - 1}}\]
By cross multiplication we get,
\[ \Rightarrow (6x - 5)(3x - 1) = (5x - 3)(2x + 1)\]
Simplifying again we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 18{x^2} - 21x + 5 = 10{x^2} - x - 3\]
Simplifying again we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 8{x^2} - 20x + 8 = 0\]
Simplifying again we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 2{x^2} - 5x + 2 = 0\]
Now, we will apply middle term theorem,
\[ \Rightarrow 2{x^2} - 4x - x + 2 = 0\]
Simplifying again we get,
\[ \Rightarrow (2x - 1)(x - 2) = 0\]
If the product of two terms is zero, then each of the terms is individually zero.
\[ \Rightarrow 2x - 1 = 0 \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x - 2 = 0 \Rightarrow x = 2\]
Hence,
$\therefore $ The value of \[x\] is \[\dfrac{1}{2}\] and \[2\].
Note: If any two angles of a triangle are equal to any two angles of another triangle, then the two triangles are similar to each other.
If two triangles are similar, the ratio of their sides is also the same.
We know that the alternate angles of two parallel lines are equal.
By the condition of similarity, we will try to prove that.
If two triangles are similar, the ratio of their sides is also the same.
Using the above condition, we will find the required value.
Complete step-by-step answer:
It is given that; \[AB\parallel CD\].
We have to find the value of \[x\].
Let us consider the diagonals \[AC\] and \[BD\]meets at \[O\].
At first, we will try to find whether the triangles \[AOB\] and \[COD\]are congruent or not.
We know that, if three angles of any triangle are equal to the respective angles of another triangle, then by AAA condition the triangles are similar to each other.
Again, we know that the alternate angles of two parallel lines are equal.
Here, \[AB\parallel CD\] and \[AC\] and \[BD\] are transversal.
So, \[\angle CDB = \angle DBA\] and \[\angle DCA = \angle CAB\], as they are alternate angles.
Here, we will take the triangles of \[AOB\] and \[COD\].
In \[\Delta AOB\] and \[\Delta COD\]
\[\angle CDB = \angle DBA\] as they are alternate angles.
\[\angle DCA = \angle CAB\] as they are alternate angles.
\[\angle AOB = \angle COD\] as they are vertically opposite angles.
Then by AAA condition \[\Delta AOB \sim \Delta COD\]
Therefore, we have \[\dfrac{{AO}}{{CO}} = \dfrac{{BO}}{{DO}}\]
Substitute the values we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{6x - 5}}{{2x + 1}} = \dfrac{{5x - 3}}{{3x - 1}}\]
By cross multiplication we get,
\[ \Rightarrow (6x - 5)(3x - 1) = (5x - 3)(2x + 1)\]
Simplifying again we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 18{x^2} - 21x + 5 = 10{x^2} - x - 3\]
Simplifying again we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 8{x^2} - 20x + 8 = 0\]
Simplifying again we get,
\[ \Rightarrow 2{x^2} - 5x + 2 = 0\]
Now, we will apply middle term theorem,
\[ \Rightarrow 2{x^2} - 4x - x + 2 = 0\]
Simplifying again we get,
\[ \Rightarrow (2x - 1)(x - 2) = 0\]
If the product of two terms is zero, then each of the terms is individually zero.
\[ \Rightarrow 2x - 1 = 0 \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow x - 2 = 0 \Rightarrow x = 2\]
Hence,
$\therefore $ The value of \[x\] is \[\dfrac{1}{2}\] and \[2\].
Note: If any two angles of a triangle are equal to any two angles of another triangle, then the two triangles are similar to each other.
If two triangles are similar, the ratio of their sides is also the same.
We know that the alternate angles of two parallel lines are equal.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

What is the color of ferrous sulphate crystals? How does this color change after heating? Name the products formed on strongly heating ferrous sulphate crystals. What type of chemical reaction occurs in this type of change.

Find the greatest fivedigit number which is a perfect class 9 maths CBSE

Find the mode and median of the data 13 16 12 14 1-class-9-maths-CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it




