
If PAB is a secant to a circle of Centre O intersecting the circle of A and B and PT is tangent segment, then prove that-
${\text{PA}} \times {\text{PB = P}}{{\text{T}}^2}$
Answer
620.7k+ views
Hint – In this question first make a circle then draw a tangent and a secant from an external point of the circle and also, draw a perpendicular line from the Centre of the circle to the secant, then apply Pythagoras theorem .
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given Data, PAB is a secant, Centre of circle O, PT is a tangent
We make a construction that is OM ⊥ AB, OA, OP, OT, Ob are joined.
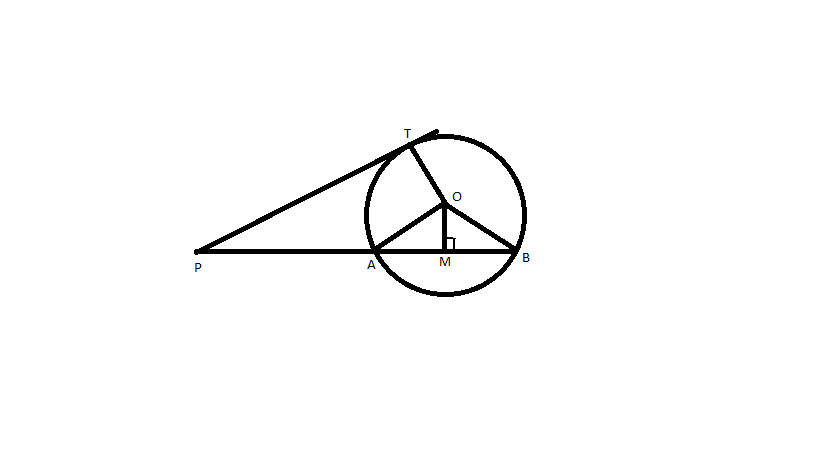
Here PAB is secant intersecting the circle with Centre O at A and B and a tangent PT at T.
Now PA = PM – AM
PB = PM + MB
As we know AM = BM (perpendicular drawn from the Centre of the circle to a chord is also a bisector of chord)
PA.PB = (PM – AM) × (PM + AM) = ${\text{P}}{{\text{M}}^2} - {\text{A}}{{\text{M}}^2}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ Equation 1}}$
Also from the diagram OM ⊥ AB
We can apply Pythagoras theorem in ∆OMP
${\text{P}}{{\text{M}}^2} = {\text{O}}{{\text{P}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{M}}^2}$
We can apply Pythagoras theorem in ∆OMA
${\text{A}}{{\text{M}}^2} = {\text{O}}{{\text{A}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{M}}^2}$
Put these values in Equation 1, we get
PA.PB = ${\text{P}}{{\text{M}}^2} - {\text{A}}{{\text{M}}^2}$
PA.PB = (${\text{O}}{{\text{P}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{M}}^2}$) – (${\text{O}}{{\text{A}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{M}}^2}$)
PA.PB = ${\text{O}}{{\text{P}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{A}}^2}$
As OA = OT (radii)
PA.PB = ${\text{O}}{{\text{P}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{T}}^2}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ Equation 2}}$
As radius is perpendicular to the tangent so this will form a right angled triangle, we can apply Pythagoras theorem in ∆OPT
We get ${\text{P}}{{\text{T}}^2}{\text{ = O}}{{\text{P}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{T}}^2}$
By putting this in the Equation 2, we get
PA.PB = ${\text{P}}{{\text{T}}^2}$
Hence Proved.
Note – In order to solve this type of questions, draw an appropriate figure and construct any other additional elements using known geometrical properties. Pythagoras theorem can be used if we construct a right angled triangle. Properties of straight lines are very important in order to approach the answer or proof.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given Data, PAB is a secant, Centre of circle O, PT is a tangent
We make a construction that is OM ⊥ AB, OA, OP, OT, Ob are joined.

Here PAB is secant intersecting the circle with Centre O at A and B and a tangent PT at T.
Now PA = PM – AM
PB = PM + MB
As we know AM = BM (perpendicular drawn from the Centre of the circle to a chord is also a bisector of chord)
PA.PB = (PM – AM) × (PM + AM) = ${\text{P}}{{\text{M}}^2} - {\text{A}}{{\text{M}}^2}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ Equation 1}}$
Also from the diagram OM ⊥ AB
We can apply Pythagoras theorem in ∆OMP
${\text{P}}{{\text{M}}^2} = {\text{O}}{{\text{P}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{M}}^2}$
We can apply Pythagoras theorem in ∆OMA
${\text{A}}{{\text{M}}^2} = {\text{O}}{{\text{A}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{M}}^2}$
Put these values in Equation 1, we get
PA.PB = ${\text{P}}{{\text{M}}^2} - {\text{A}}{{\text{M}}^2}$
PA.PB = (${\text{O}}{{\text{P}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{M}}^2}$) – (${\text{O}}{{\text{A}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{M}}^2}$)
PA.PB = ${\text{O}}{{\text{P}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{A}}^2}$
As OA = OT (radii)
PA.PB = ${\text{O}}{{\text{P}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{T}}^2}{\text{ }} \to {\text{ Equation 2}}$
As radius is perpendicular to the tangent so this will form a right angled triangle, we can apply Pythagoras theorem in ∆OPT
We get ${\text{P}}{{\text{T}}^2}{\text{ = O}}{{\text{P}}^2} - {\text{O}}{{\text{T}}^2}$
By putting this in the Equation 2, we get
PA.PB = ${\text{P}}{{\text{T}}^2}$
Hence Proved.
Note – In order to solve this type of questions, draw an appropriate figure and construct any other additional elements using known geometrical properties. Pythagoras theorem can be used if we construct a right angled triangle. Properties of straight lines are very important in order to approach the answer or proof.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




