
If \[\dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = f\left( x \right) + \dfrac{A}{{x - 2}} + \dfrac{B}{{x - 3}}\], then \[f\left( x \right) = \]
(a) \[x - 1\]
(b) \[x + 1\]
(c) \[x\]
(d) \[x + 2\]
Answer
573.6k+ views
Hint: Here, we need to find the value of \[f\left( x \right)\]. We will simplify the left hand side using a long division method. Then, we will use the division algorithm and rewrite the expression. Finally, we will compare the equation obtained with the given equation to find the value of \[f\left( x \right)\].
Formula Used:
The division algorithm states that if \[p\left( x \right)\] and \[g\left( x \right)\] are two polynomials where \[g\left( x \right) \ne 0\], then there are two polynomials \[q\left( x \right)\] and \[r\left( x \right)\] such that \[p\left( x \right) = q\left( x \right) \times g\left( x \right) + r\left( x \right)\]. Here, \[p\left( x \right)\] is the dividend, \[g\left( x \right)\] is the divisor, \[q\left( x \right)\] is the quotient, and \[r\left( x \right)\] is the remainder.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will use a long division method to divide \[{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2\] by \[{x^2} - 5x + 6\].
Therefore, we get
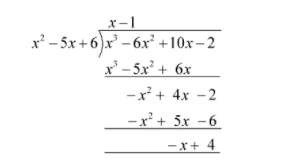
We can observe that when \[{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2\] is divided by \[{x^2} - 5x + 6\] using long division method, the quotient is \[x - 1\], and the remainder is \[ - x + 4\].
Now, we will use the division algorithm.
The division algorithm states that if \[p\left( x \right)\] and \[g\left( x \right)\] are two polynomials where \[g\left( x \right) \ne 0\], then there are two polynomials \[q\left( x \right)\] and \[r\left( x \right)\] such that \[p\left( x \right) = q\left( x \right) \times g\left( x \right) + r\left( x \right)\]. Here, \[p\left( x \right)\] is the dividend, \[g\left( x \right)\] is the divisor, \[q\left( x \right)\] is the quotient, and \[r\left( x \right)\] is the remainder.
Thus, we get
\[p\left( x \right) = {x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2\]
\[q\left( x \right) = x - 1\]
\[r\left( x \right) = - x + 4\]
\[g\left( x \right) = {x^2} - 5x + 6\]
Substituting \[p\left( x \right) = {x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2\], \[q\left( x \right) = x - 1\], \[r\left( x \right) = - x + 4\], and \[g\left( x \right) = {x^2} - 5x + 6\] in the division algorithm, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2 = \left( {x - 1} \right)\left( {{x^2} - 5x + 6} \right) + \left( { - x + 4} \right)\]
Dividing both sides by \[{x^2} - 5x + 6\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 + \left( {\dfrac{{ - x + 4}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}}} \right)\]
Rewriting the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \left( {\dfrac{{x - 4}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}}} \right)\]
Factoring the denominator, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \left( {\dfrac{{x - 4}}{{{x^2} - 3x - 2x + 6}}} \right)\\ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \left[ {\dfrac{{x - 4}}{{x\left( {x - 3} \right) - 2\left( {x - 3} \right)}}} \right]\\ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \left[ {\dfrac{{x - 4}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\end{array}\]
Multiplying and dividing the fraction by 2, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{2}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{x - 4}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\\ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{2\left( {x - 4} \right)}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\end{array}\]
Multiplying the above terms using the distributive property, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{2x - 8}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\]
Rewriting the numerator, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{x + x - 3 - 3 - 2}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\\ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{x - 3 + x - 2 - 3}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\end{array}\]
Separating the fractions with the same denominator, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{x - 3}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}} + \dfrac{{x - 2}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}} - \dfrac{3}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\]
Simplifying the expressions, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{x - 2}} + \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}} - \dfrac{3}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\]
Multiplying the above terms using the distributive property, we get\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{1}{{2\left( {x - 2} \right)}} - \dfrac{1}{{2\left( {x - 3} \right)}} + \dfrac{3}{{2\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}\]
Rearranging the terms of the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 + \dfrac{3}{{2\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}} + \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{1}{2}}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)}} + \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{1}{2}}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}}\]
It is given that \[\dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = f\left( x \right) + \dfrac{A}{{x - 2}} + \dfrac{B}{{x - 3}}\].
Here, \[A\] and \[B\] are constants.
Therefore, from the equations \[\dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 + \dfrac{3}{{2\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}} + \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{1}{2}}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)}} + \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{1}{2}}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}}\] and \[\dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = f\left( x \right) + \dfrac{A}{{x - 2}} + \dfrac{B}{{x - 3}}\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow x - 1 + \dfrac{3}{{2\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}} + \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{1}{2}}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)}} + \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{1}{2}}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}} = f\left( x \right) + \dfrac{A}{{x - 2}} + \dfrac{B}{{x - 3}}\]
Comparing the terms of the expressions, we get
\[x - 1 + \dfrac{3}{{2\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}} = f\left( x \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow - \dfrac{1}{2} = A\]
\[\Rightarrow - \dfrac{1}{2} = B\]
Therefore, we get the value of \[f\left( x \right)\] as \[x - 1 + \dfrac{3}{{2\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}\].
Thus, none of the given options are correct.
Note: We have used the distributive law of multiplication to multiply some expressions in the solution. The distributive law of multiplication states that \[a\left( {b + c} \right) = a \cdot b + a \cdot c\]. Here for finding the value of \[f\left( x \right)\] it is important for us to find the value of A and B.
Formula Used:
The division algorithm states that if \[p\left( x \right)\] and \[g\left( x \right)\] are two polynomials where \[g\left( x \right) \ne 0\], then there are two polynomials \[q\left( x \right)\] and \[r\left( x \right)\] such that \[p\left( x \right) = q\left( x \right) \times g\left( x \right) + r\left( x \right)\]. Here, \[p\left( x \right)\] is the dividend, \[g\left( x \right)\] is the divisor, \[q\left( x \right)\] is the quotient, and \[r\left( x \right)\] is the remainder.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First, we will use a long division method to divide \[{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2\] by \[{x^2} - 5x + 6\].
Therefore, we get
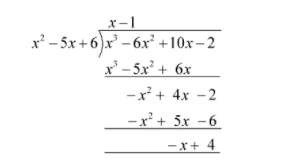
We can observe that when \[{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2\] is divided by \[{x^2} - 5x + 6\] using long division method, the quotient is \[x - 1\], and the remainder is \[ - x + 4\].
Now, we will use the division algorithm.
The division algorithm states that if \[p\left( x \right)\] and \[g\left( x \right)\] are two polynomials where \[g\left( x \right) \ne 0\], then there are two polynomials \[q\left( x \right)\] and \[r\left( x \right)\] such that \[p\left( x \right) = q\left( x \right) \times g\left( x \right) + r\left( x \right)\]. Here, \[p\left( x \right)\] is the dividend, \[g\left( x \right)\] is the divisor, \[q\left( x \right)\] is the quotient, and \[r\left( x \right)\] is the remainder.
Thus, we get
\[p\left( x \right) = {x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2\]
\[q\left( x \right) = x - 1\]
\[r\left( x \right) = - x + 4\]
\[g\left( x \right) = {x^2} - 5x + 6\]
Substituting \[p\left( x \right) = {x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2\], \[q\left( x \right) = x - 1\], \[r\left( x \right) = - x + 4\], and \[g\left( x \right) = {x^2} - 5x + 6\] in the division algorithm, we get
\[ \Rightarrow {x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2 = \left( {x - 1} \right)\left( {{x^2} - 5x + 6} \right) + \left( { - x + 4} \right)\]
Dividing both sides by \[{x^2} - 5x + 6\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 + \left( {\dfrac{{ - x + 4}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}}} \right)\]
Rewriting the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \left( {\dfrac{{x - 4}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}}} \right)\]
Factoring the denominator, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \left( {\dfrac{{x - 4}}{{{x^2} - 3x - 2x + 6}}} \right)\\ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \left[ {\dfrac{{x - 4}}{{x\left( {x - 3} \right) - 2\left( {x - 3} \right)}}} \right]\\ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \left[ {\dfrac{{x - 4}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\end{array}\]
Multiplying and dividing the fraction by 2, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{2}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{x - 4}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\\ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{2\left( {x - 4} \right)}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\end{array}\]
Multiplying the above terms using the distributive property, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{2x - 8}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\]
Rewriting the numerator, we get
\[\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{x + x - 3 - 3 - 2}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\\ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{x - 3 + x - 2 - 3}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\end{array}\]
Separating the fractions with the same denominator, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{{x - 3}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}} + \dfrac{{x - 2}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}} - \dfrac{3}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\]
Simplifying the expressions, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{1}{2}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{x - 2}} + \dfrac{1}{{x - 3}} - \dfrac{3}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}} \right]\]
Multiplying the above terms using the distributive property, we get\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 - \dfrac{1}{{2\left( {x - 2} \right)}} - \dfrac{1}{{2\left( {x - 3} \right)}} + \dfrac{3}{{2\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}\]
Rearranging the terms of the expression, we get
\[ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 + \dfrac{3}{{2\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}} + \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{1}{2}}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)}} + \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{1}{2}}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}}\]
It is given that \[\dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = f\left( x \right) + \dfrac{A}{{x - 2}} + \dfrac{B}{{x - 3}}\].
Here, \[A\] and \[B\] are constants.
Therefore, from the equations \[\dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = x - 1 + \dfrac{3}{{2\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}} + \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{1}{2}}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)}} + \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{1}{2}}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}}\] and \[\dfrac{{{x^3} - 6{x^2} + 10x - 2}}{{{x^2} - 5x + 6}} = f\left( x \right) + \dfrac{A}{{x - 2}} + \dfrac{B}{{x - 3}}\], we get
\[ \Rightarrow x - 1 + \dfrac{3}{{2\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}} + \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{1}{2}}}{{\left( {x - 2} \right)}} + \dfrac{{ - \dfrac{1}{2}}}{{\left( {x - 3} \right)}} = f\left( x \right) + \dfrac{A}{{x - 2}} + \dfrac{B}{{x - 3}}\]
Comparing the terms of the expressions, we get
\[x - 1 + \dfrac{3}{{2\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}} = f\left( x \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow - \dfrac{1}{2} = A\]
\[\Rightarrow - \dfrac{1}{2} = B\]
Therefore, we get the value of \[f\left( x \right)\] as \[x - 1 + \dfrac{3}{{2\left( {x - 3} \right)\left( {x - 2} \right)}}\].
Thus, none of the given options are correct.
Note: We have used the distributive law of multiplication to multiply some expressions in the solution. The distributive law of multiplication states that \[a\left( {b + c} \right) = a \cdot b + a \cdot c\]. Here for finding the value of \[f\left( x \right)\] it is important for us to find the value of A and B.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




