
If $ax+by+cz=p$, then minimum value of ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}$ is.
A. ${{\left( \dfrac{p}{a+b+c} \right)}^{2}}$
B. $\left( \dfrac{{{p}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}} \right)$
C. $\left( \dfrac{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}{{{p}^{2}}} \right)$
D. ${{\left( \dfrac{a+b+c}{p} \right)}^{2}}$
Answer
615.6k+ views
Hint: We will use the concept of 3D coordinate geometry to solve this question. We know that the minimum distance between any two points is its perpendicular distance. Thus, we will try to find the perpendicular distance between the given plane and point.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have to find the minimum value of ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}$, when the given condition is $ax+by+cz=p$. We will use the concept of 3D coordinate geometry to solve this question. The given equation is the equation of the plane. So, we will find the distance of the point $(x,y,z)$ which is lying somewhere on the plane $ax+by+cz=p$ and the origin.
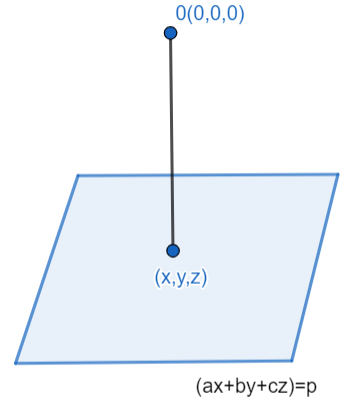
We have assumed that the point $(x,y,z)$ is perpendicular to origin, this is because the minimum distance between any two points is given by the perpendicular distance and also we have to find the minimum value of ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}$. We know that the distance between two points is as,
$d=\sqrt{{{({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})}^{2}}+{{({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})}^{2}}+{{({{z}_{2}}-{{z}_{1}})}^{2}}}$
So, the distance between point $(x,y,z)$ to the origin
is.$d=\sqrt{{{(x-0)}^{2}}+{{(y-0)}^{2}}+{{(z-0)}^{2}}}$.
$\Rightarrow d=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}$
Squaring on both sides, we get
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}$
Also, we know that distance between any plane and a point is given as.
${{d}_{\min }}=\left| \dfrac{-p}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}} \right|$, we will use the direct formula of distance between plane and point by squaring, we get
$d_{\min }^{2}=\dfrac{-p}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}}$
Thus, we get $d_{\min }^{2}=\dfrac{{{p}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}$
$=({{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}})$
Therefore, the minimum value of $({{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}})$ is
$\dfrac{{{p}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}$ and option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: There are many alternate possible methods for solving this particular question but the other methods are slightly complex to solve and the probability of error while solving is higher. But if we follow the this method we will get the minimum value of ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}$ directly. Some of the alternate methods are:
1. We can solve this question using the Lagrange multipliers method. In this method, we will find the value of $x,y,z$ individually to get minimum value.
2. We can also use the vector concept or we can name it as the Cauchy Schwarz inequality method. In this method we will assume two vectors $\overrightarrow{A}=(a,b,c)$ and $\overrightarrow{B}=(x,y,z)$, then solve the question to get the minimum value.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We have to find the minimum value of ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}$, when the given condition is $ax+by+cz=p$. We will use the concept of 3D coordinate geometry to solve this question. The given equation is the equation of the plane. So, we will find the distance of the point $(x,y,z)$ which is lying somewhere on the plane $ax+by+cz=p$ and the origin.

We have assumed that the point $(x,y,z)$ is perpendicular to origin, this is because the minimum distance between any two points is given by the perpendicular distance and also we have to find the minimum value of ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}$. We know that the distance between two points is as,
$d=\sqrt{{{({{x}_{2}}-{{x}_{1}})}^{2}}+{{({{y}_{2}}-{{y}_{1}})}^{2}}+{{({{z}_{2}}-{{z}_{1}})}^{2}}}$
So, the distance between point $(x,y,z)$ to the origin
is.$d=\sqrt{{{(x-0)}^{2}}+{{(y-0)}^{2}}+{{(z-0)}^{2}}}$.
$\Rightarrow d=\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}}$
Squaring on both sides, we get
$\Rightarrow {{d}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}$
Also, we know that distance between any plane and a point is given as.
${{d}_{\min }}=\left| \dfrac{-p}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}} \right|$, we will use the direct formula of distance between plane and point by squaring, we get
$d_{\min }^{2}=\dfrac{-p}{\sqrt{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}}$
Thus, we get $d_{\min }^{2}=\dfrac{{{p}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}$
$=({{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}})$
Therefore, the minimum value of $({{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}})$ is
$\dfrac{{{p}^{2}}}{{{a}^{2}}+{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}}$ and option (B) is the correct answer.
Note: There are many alternate possible methods for solving this particular question but the other methods are slightly complex to solve and the probability of error while solving is higher. But if we follow the this method we will get the minimum value of ${{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}+{{z}^{2}}$ directly. Some of the alternate methods are:
1. We can solve this question using the Lagrange multipliers method. In this method, we will find the value of $x,y,z$ individually to get minimum value.
2. We can also use the vector concept or we can name it as the Cauchy Schwarz inequality method. In this method we will assume two vectors $\overrightarrow{A}=(a,b,c)$ and $\overrightarrow{B}=(x,y,z)$, then solve the question to get the minimum value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What is Contraception List its four different methods class 10 biology CBSE




